RDA method and kit for rapidly detecting influenza A virus
An influenza A virus and kit technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of lack of influenza A detection kits, difficulty in obtaining, hindering rapid qualitative detection of influenza, etc., and achieve low detection cost, low mass production cost, The effect of high-precision rapid molecular detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] Example 1 Establishment of a detection method for influenza A virus (FluA) RDA fluorescence detection kit
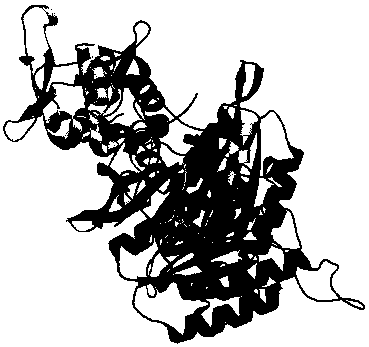
[0082] (1) Acquisition of recombinant enzyme KX and KY proteins
[0083] The reported recombinant enzyme UvsX has poor stability and is difficult to mass produce and store for a long time. In order to solve this problem, the research and development team used bioinformatics methods to analyze and simulate large quantities of protein structures, and finally found a new recombinant enzyme Enzyme KX and its accessory protein KY.
[0084] In this example, the R&D team extracted the key functional site information in the recombinase structure, such as DNA binding site, ATP hydrolysis site, etc., and mapped it to the three-dimensional structure of the protein to obtain secondary structure information and tertiary structure information , by integrating the functional residues of the primary structure sequence, secondary structure features and tertiary structure spatial ...
Embodiment 2
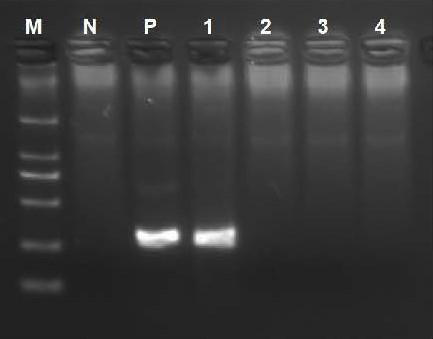
[0135] Example 2 RDA fluorescence method detection reagent sensitivity test
[0136] The positive control is the pUC57-M1 plasmid containing the M1 gene of influenza A virus (FluA), and the negative control is the empty vector pUC57 plasmid.
[0137] The specific operation is as follows:
[0138] Step 1: Dilute the positive control plasmid to 10^4c, and then dilute to 10^3c, 10^2c, and 10^1c by 10-fold serial dilution.
[0139] Step two, sample processing. Take 5 μL of each concentration of the plasmid in step 1 in an EP tube, and take 5 μL of the negative control in another EP tube, add 20 μL of Buffer A respectively, shake and mix, and let stand at room temperature for 10-15 minutes;
[0140] Step 3, system preparation and testing. Add 25 μL Buffer B to each tube, shake and mix, add 50 μL of the mixed solution to the RDA fluorescence method reaction module, cover the tube cap, shake and centrifuge, and detect immediately; the reaction program is: 39°C for 1 minute, 30 cyc...
Embodiment 3
[0152] Example 3 RDA fluorescence method detection reagent specificity test
[0153] 3 cases of influenza A virus (Influenza A virus, FluA), 1 case of influenza B virus (Influenza B virus, FluB), and 1 case of respiratory syncytial virus (Respiratory Sycytial Virus, RSV) were collected clinically, a total of 5 cases It was verified by fluorescent quantitative PCR that the corresponding virus-positive samples were tested to test the specificity of the kit.
[0154] The specific operation is as follows:
[0155] Step 1. Sample processing. Take 5 μL of each of the above 5 positive samples in EP tubes, and at the same time take 5 μL of the positive control and negative control of the kit in a new EP tube, add 20 μL Buffer A respectively, shake and mix, and let stand at room temperature for 10-15 minutes;
[0156] Step 3, system preparation and testing. Add 25 μL Buffer B to each tube, shake and mix, add 50 μL of the mixed solution to the RDA fluorescence method reaction module,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com