Local plating resistance protective method of SOP packaged to-be-plated circuit module
A circuit module and plating resist technology, applied in the field of local resist plating protection of the circuit module to be plated, can solve the problems of increased adhesion, corrosion of outer leads, influence of solderability, etc., to prevent insufficient strength, short curing time, Combine good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
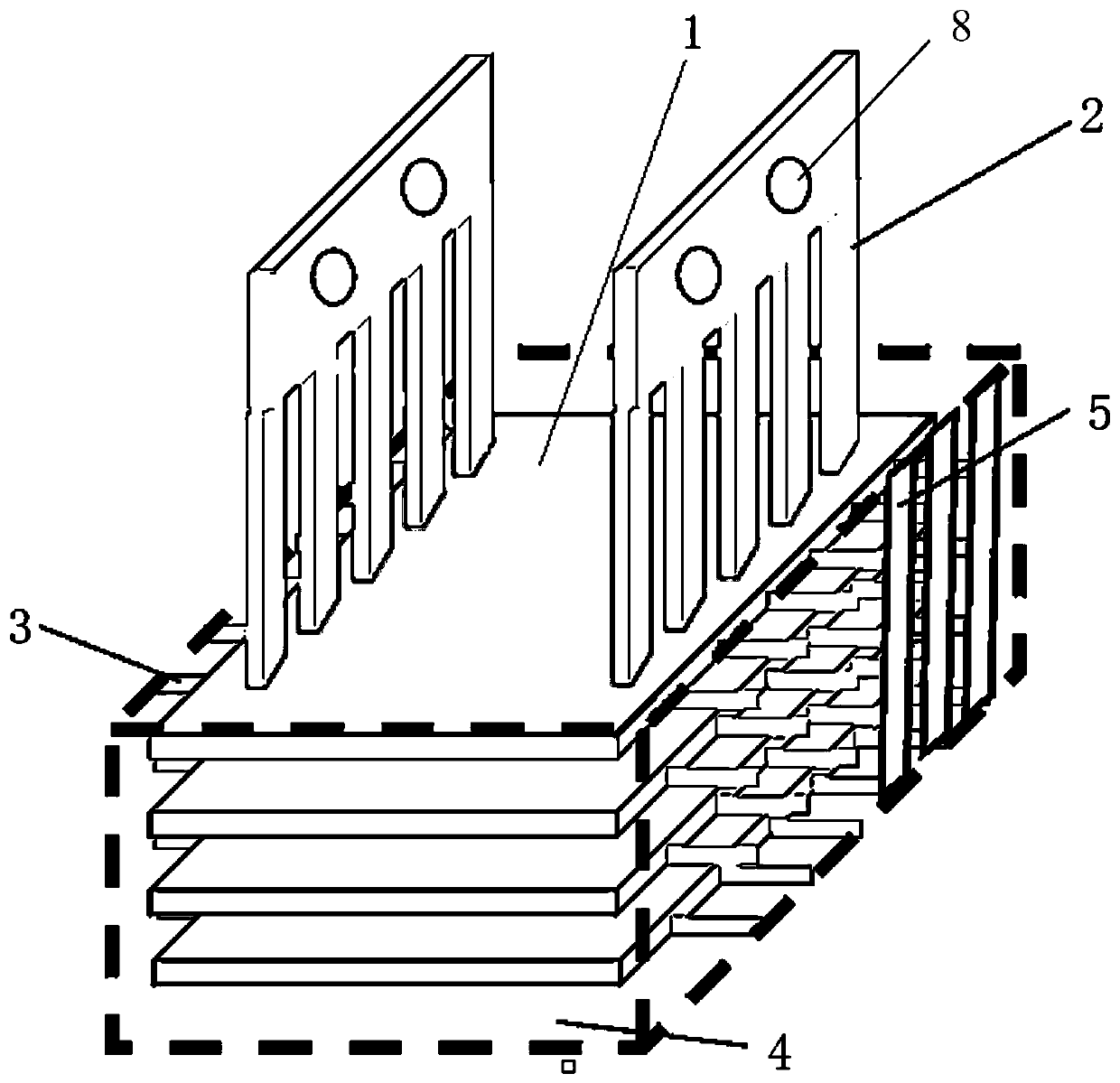
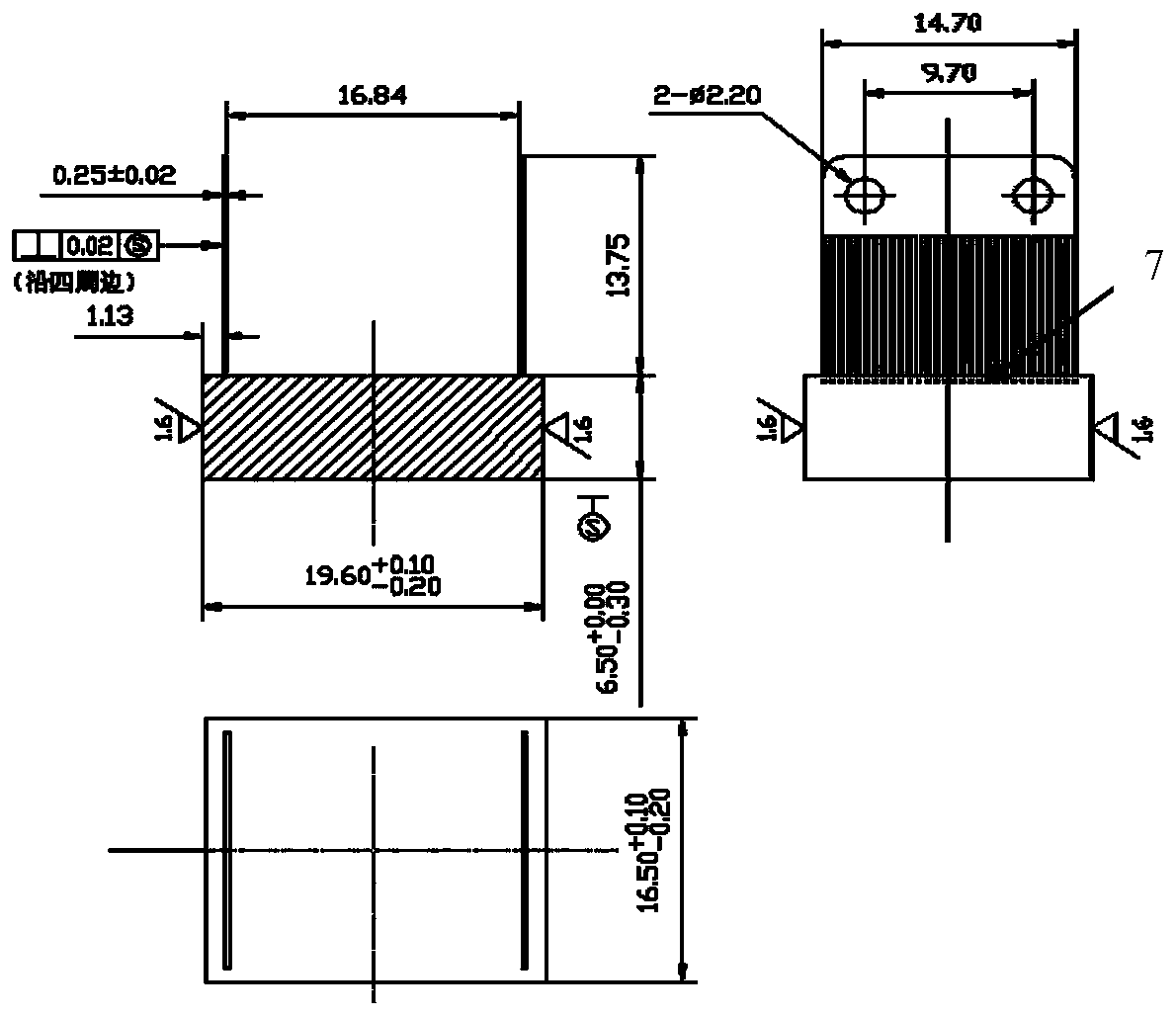
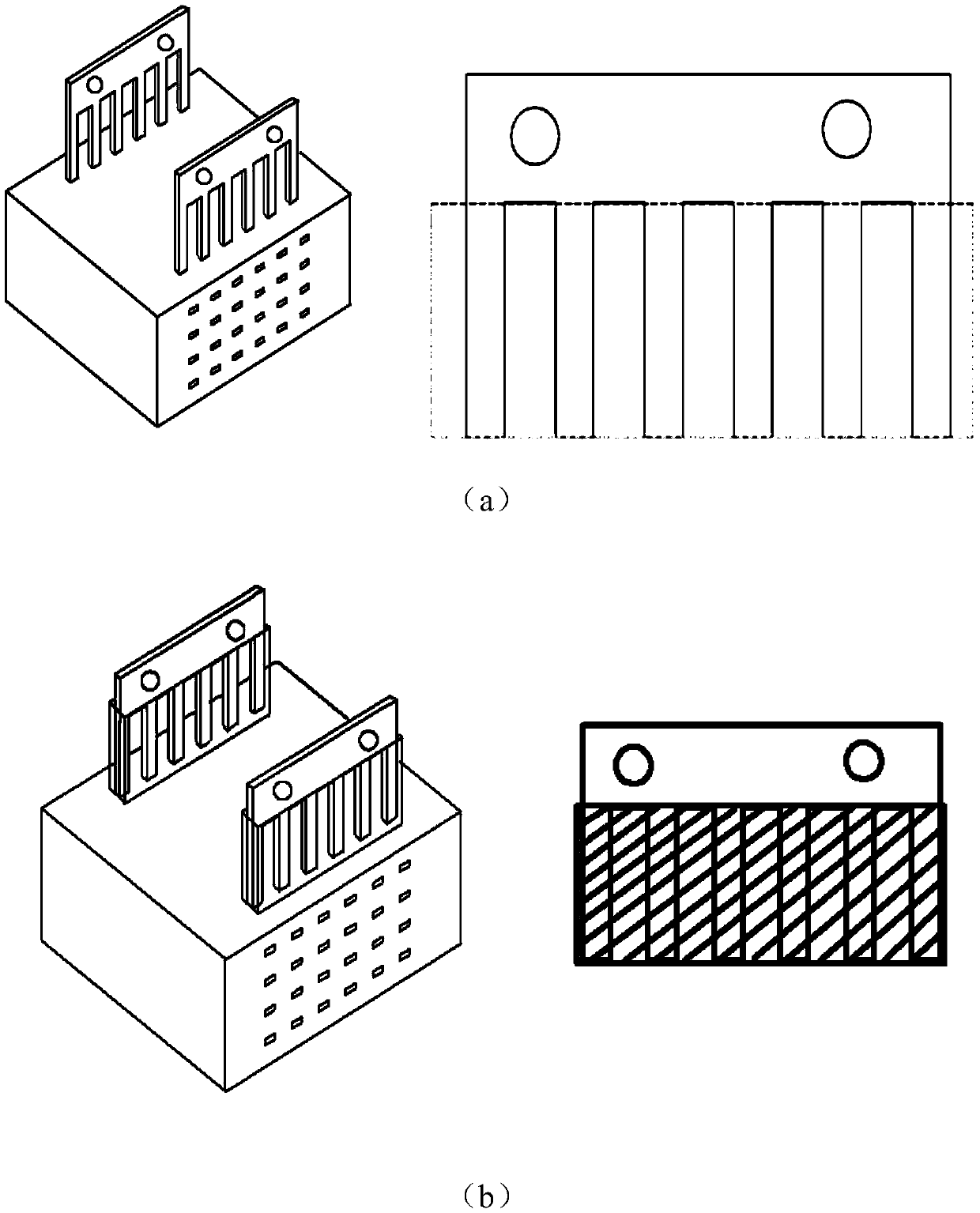
[0047] Step 1. Apply anti-corrosion glue on the outer lead: dip a small amount of anti-corrosion glue with a fine hook line pen and apply it along the direction of the outer lead 2 from bottom to top to ensure that the leakage part of the outer lead 2 is protected.
[0048] Step 2. Baking and curing in oven: temperature is 80℃, time is 60min.
[0049] Step 3. Protect the outer lead with plating resist tape: Wrap a layer of plating resist tape with the same width as the height of the comb-shaped area of outer lead 2 along the side of outer lead 2. Put it in an oven to heat: temperature 80℃, time 10min, flattened with bamboo Use tweezers to compact and adhere the plating resist tape along the outer lead 2 direction.
[0050] Step 4, bonding and fixing the clamp block: fix the clamp block 6 on the bottom plate 1 between the two outer leads 2 with non-transferring tape, ensure that the width of the clamp block 6 matches the span of the outer lead 2, and the length of the clamp block 6 ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The difference from Example 1 is: the baking temperature of step 2 is 75° C. and the time is 55 min; the oven heating temperature of step 3 is 75° C. and the time is 55 min; step 6 is naturally dried for 13 h; and step 9 is soaked in solvent for 2 min.
Embodiment 3
[0060] The difference from Example 1 is that the baking temperature in step 2 is 85° C. and the time is 65 min; the oven heating temperature in step 3 is 85° C. and the time is 65 min; step 6 is naturally dried for 14 hours; and step 9 is soaked in solvent for 3 min.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com