Production process of rapidly biodegradable micro-porous polyester fibers
A biodegradable, polyester fiber technology, applied in the direction of fiber processing, fiber chemical characteristics, single-component polyester rayon, etc., can solve the problems of slow degradation, dense fiber structure, and longer biodegradation time. The effect of accelerating the speed of biodegradation, easy biodegradation, and shortening the degradation cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
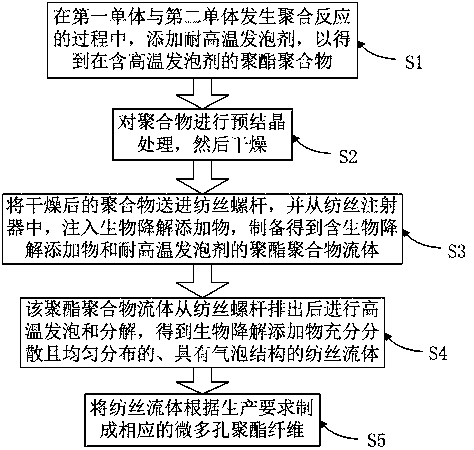
[0055] (1) Preparation of polymer
[0056] Wherein, the first monomer is terephthalic acid: the second monomer is ethylene glycol: 2 / 1. During the polymerization reaction of the first monomer and the second monomer, a high temperature resistant commercial blowing agent F240B is added. The decomposition temperature of the high-temperature-resistant foaming agent is ≥300°C, and it is released after high-temperature thermal decomposition and nitrogen. Wherein the proportion of foaming agent accounts for 1 / 97 of the whole.
[0057] (2) Perform pre-crystallization treatment on the polymer, and then dry it.
[0058] (3) Send the dried polymer into the spinning screw, and inject the biodegradable additive from the spinning syringe, the biodegradable additive is a kind of biodegradant, biodegradable fiber and The biodegradation agent disclosed in the preparation method is added in an amount of 2% of the total weight of the rapidly biodegradable microporous polyester fiber, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0064] (1) Preparation of polymer
[0065] Wherein, the first monomer is terephthalic acid: the second monomer is ethylene glycol: 3 / 1. During the polymerization reaction of the first monomer and the second monomer, a high-temperature-resistant KGF-1 high-temperature foaming agent is added. The decomposition temperature of the high-temperature-resistant foaming agent is ≥300°C, and it is released after high-temperature thermal decomposition and nitrogen. Wherein the proportion of foaming agent accounts for 1 / 95 of the whole.
[0066] (2) Pre-crystallize the polymer and then dry it.
[0067] (3) Feed the dried polymer into the spinning screw, and inject the biodegradable additive from the spinning syringe. The biodegradable additive is a biodegradable agent, biodegradable fiber and The biodegradation agent disclosed in the preparation method is added in an amount of 5% of the total weight of the rapidly biodegradable microporous polyester fiber. The polyester polymer flui...
Embodiment 3
[0073] (1) Preparation of polymer
[0074] Wherein, the first monomer is terephthalic acid: the second monomer is ethylene glycol: 4 / 1. During the polymerization reaction of the first monomer and the second monomer, a high temperature resistant PMP-1 foaming agent is added. The decomposition temperature of the high-temperature-resistant foaming agent is ≥300°C, and it is released after high-temperature thermal decomposition and nitrogen. Wherein the proportion of foaming agent accounts for 1 / 98 of the whole.
[0075] (2) Pre-crystallize the polymer and then dry it.
[0076] (3) Feed the dried polymer into the spinning screw, and inject biodegradable additives from the spinning syringe, the biodegradable additives include artificially synthesized polycaprolactone, polyvinyl alcohol, aliphatic-aromatic A mixture of family lipids, modified polylactic acid, monosaccharides, and aldohexose, the addition amount is 3% of the total weight of the microporous polyester fiber that i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com