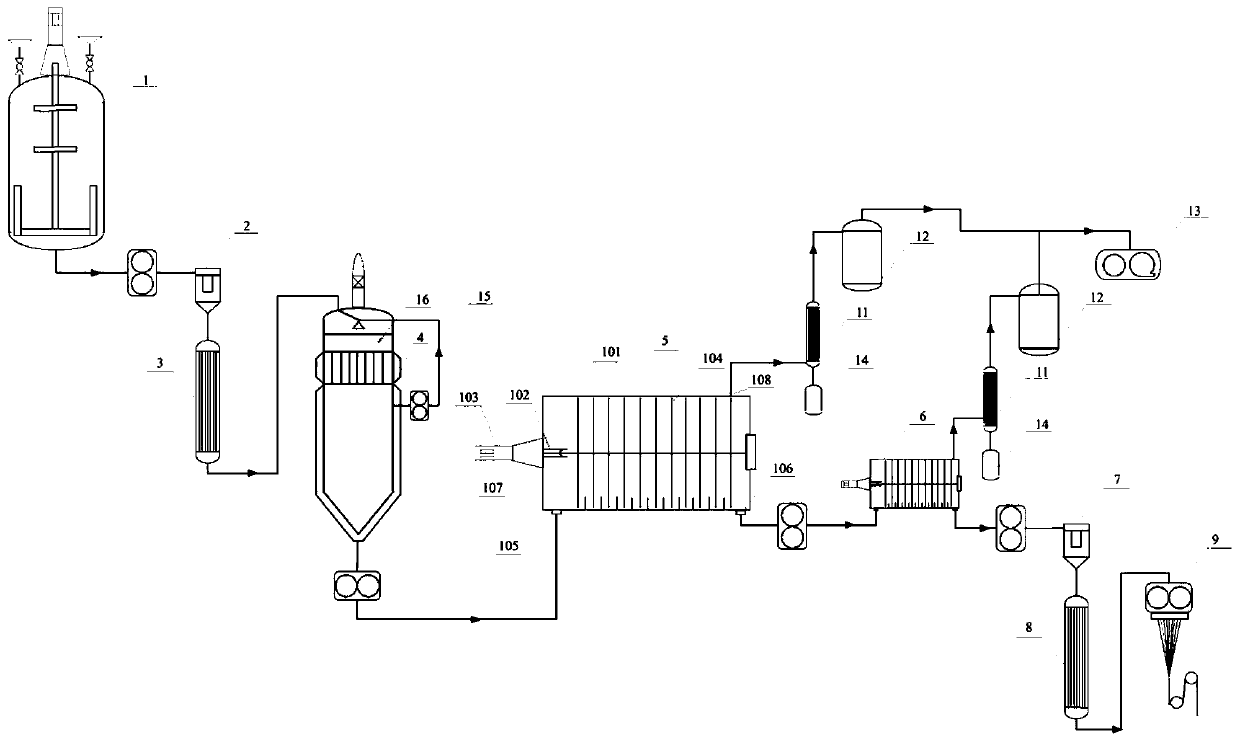
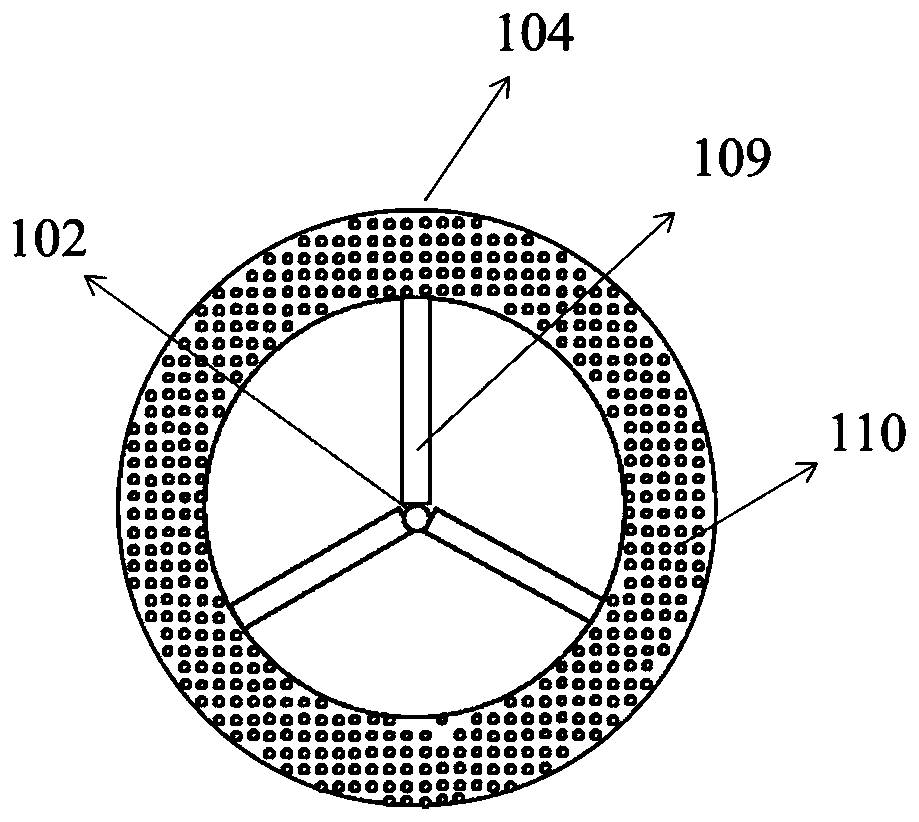
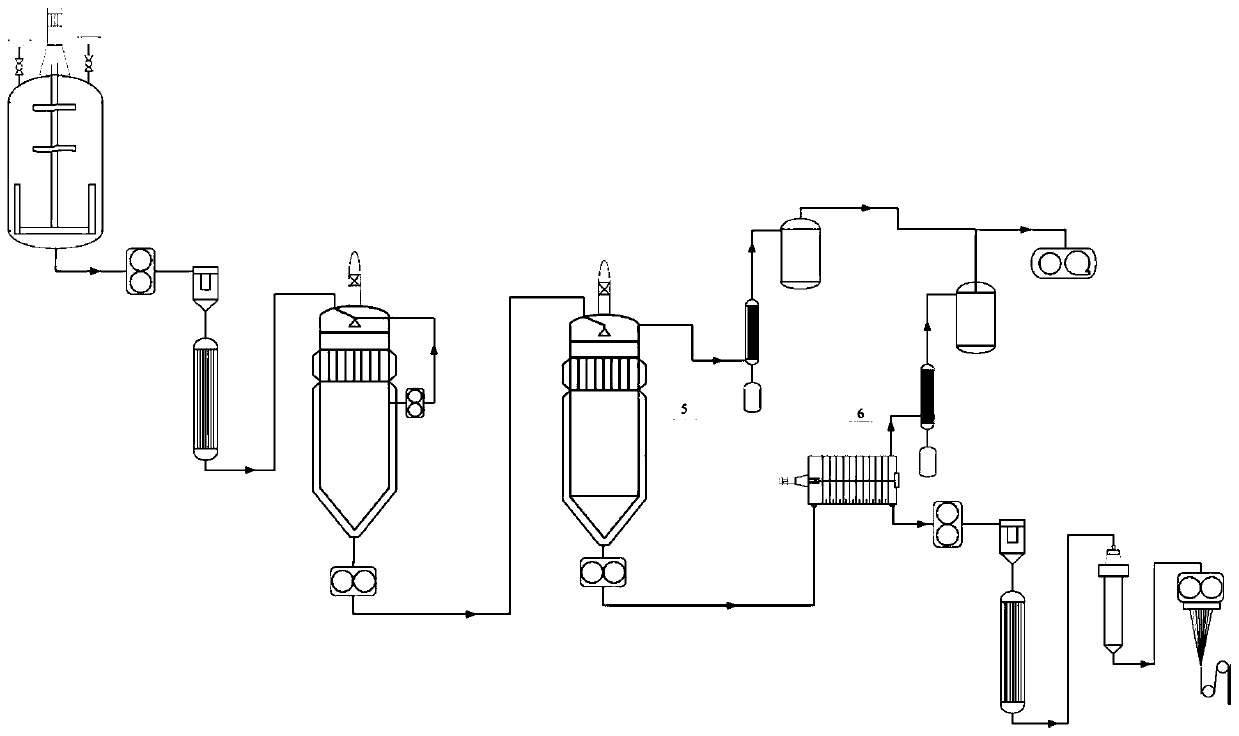
Melting direct-spinning method of copolymerized modified low-melting-point nylon fibers
A technology of copolymerization modification and nylon fiber, which is applied in the field of nylon materials, can solve the problems of low polymer number-average molecular weight, oligomer control, and slow reaction speed, and achieve the goals of lowering the melting point of nylon, ensuring quality, and increasing the devolatilization area Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] The first step: at a temperature of 130°C, caprolactam, caprolactone, deionized water, HOOC (CH 2 ) 4 COOH, NH 2 (CH 2 ) 6 COOH was mixed in proportion; wherein relative to caprolactam, deionized water was added in an amount of 3wt%, HOOC(CH 2 ) 2 The amount of COOH added is 0.3wt%, NH 2 (CH 2 ) 4 The amount of COOH added is 0.03wt%, and the amount of caprolactone added is 30wt%;
[0076] The second step: After the mixture obtained in the first step is heated by the melt pump and the pre-heater, it is transported to the ring-opening kettle for ring-opening reaction. The polymerization temperature is controlled at 205 ° C, and the polymerization pressure is controlled at 1.3 MPa; the reaction time is The 0.6h prepolymer is transported to the top of the tower by a melt pump, mixed with fresh caprolactam, and the reflux rate is 1.5wt% of the caprolactam flow rate. When the following conditions are met, the reaction is terminated: the number average molecular weigh...
Embodiment 2
[0083] The first step: at a temperature of 90°C, caprolactam, -CO(CH 2 ) 2 CONH(CH 2 ) 4 NH-, deionized water, HOOC(CH 2 ) 3 COOH and nylon 66 salt were mixed in proportion; wherein relative to caprolactam, the amount of deionized water added was 1.2wt%, HOOC(CH 2 ) 3 The amount of COOH added is 0.15wt%, the amount of nylon 66 salt added is 0.07wt%, -COCONHCH 2 NH-added amount is 40wt%;
[0084] The second step: After the mixture obtained in the first step is heated by the melt pump and the pre-heater, it is transported to the ring-opening kettle for ring-opening reaction. The polymerization temperature is controlled at 240 ° C, and the polymerization pressure is controlled at 1.5 MPa; the reaction time is The 1.3h prepolymer is transported to the top of the tower by a melt pump, mixed with fresh caprolactam, and the reflux flow is 0.7wt% of the caprolactam flow. When the following conditions are met, the reaction is terminated: the number average molecular weight of t...
Embodiment 3
[0091] The first step: at a temperature of 130°C, caprolactam, NH 2 (CH 2 ) 10 COOH, deionized water, phthalic acid, NH 2 (CH 2 )5 COOH is mixed in proportion; among them, relative to caprolactam, the amount of deionized water added is 1.2wt%, the amount of phthalic acid added is 0.3wt%, and the amount of NH 2 (CH 2 ) 5 The amount of COOH added is 0.04wt%, NH 2 (CH 2 ) 10 The amount of COOH added is 50wt%;
[0092] The second step: After the mixture obtained in the first step is heated by the melt pump and the pre-heater, it is transported to the ring-opening kettle for ring-opening reaction. The polymerization temperature is controlled at 248 ° C, and the polymerization pressure is controlled at 0.6 MPa; the reaction time is The 1.2h prepolymer is transported to the top of the tower by a melt pump, mixed with fresh caprolactam, and the reflux flow is 0.8wt% of the caprolactam flow. When the following conditions are met, the reaction is terminated: the number average...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com