Larimichthys crocea hemoglobin antibacterial peptide and application thereof
A technology of hemoglobin and antimicrobial peptides, applied in the field of large yellow croaker hemoglobin antimicrobial peptides, can solve the problems of discovering antimicrobial peptides and achieve low toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: Screening of large yellow croaker hemoglobin-derived antimicrobial peptides
[0038] Since fish hemoglobin is rich in α-helical structure, which is the most common characteristic structure of antimicrobial peptides, we used AntiBP server to predict potential antimicrobial peptides with α-helical structure from large yellow croaker hemoglobin, and used CAMP software to check the reliability of the predicted peptides. commented. Six potential antimicrobial peptides with α-helix were predicted, as shown in Table 1.
[0039] Table 1 Prediction of potential antimicrobial peptides in large yellow croaker hemoglobin
[0040]
[0041] It can be seen from Table 1 that the peptide LCH4 has the highest score, and at the same time, the peptide LCH4 also has the characteristics of typical antimicrobial peptides, namely the number of amino acids (30% ). The first four peptides (LCH1-LCH4) with the highest scores were synthesized, and antibacterial experiments were ca...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Determination
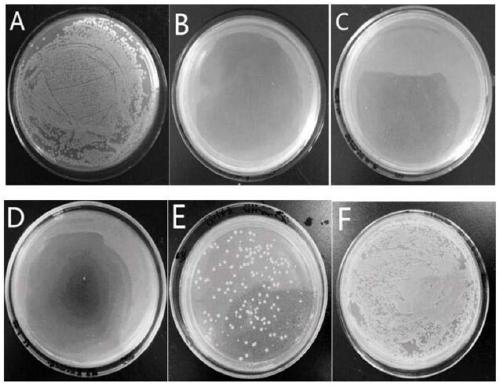
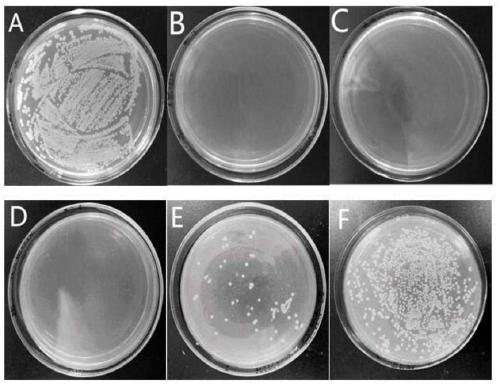
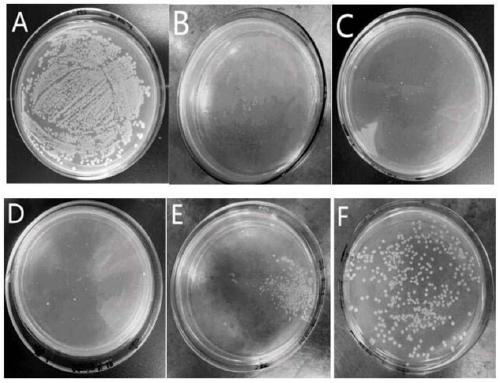
[0043] Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Streptococcus iniae were cultured at 37°C for 12 hours to logarithmic growth phase, and diluted to 10 in 0.01M pH 7.2 phosphate buffer6-7 CFU / mL. Dissolve the peptide in phosphate buffer, and mix it with bacteria in an equal volume at 37°C for 2 hours. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial peptide at which no bacterial growth is visible from the microtiter plate after overnight incubation at 37°C. Such as figure 1 , figure 2 with image 3 As shown, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of LCH4 to Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli was 15.6 μg / mL, and the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) to Streptococcus iniae was 62.5 μg / mL.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: transmission electron microscope analysis
[0045] to 10 6-7 CFU / mL bacteria were treated with 2×MIC LCH4 at 37°C for 2h, then centrifuged at 2700g for 10min, and washed twice with phosphate buffer (pH 7.2). After fixing with 1% osmic acid, dehydrate with 95% ethanol, and then treat with acetone for 20 min. The samples were baked at 70°C for 24 h, and thin slices of 70–90 nm were prepared on copper grids, which were then stained with lead citrate and uranyl acetate. The ultrastructure was observed and captured with a H-7650 transmission electron microscope.
[0046] Such as Figure 4 , Figure 5 with Image 6 As shown, for untreated bacteria, the intracellular organization and structural integrity of the bacterial cells were good. However, after treatment with the peptide LCH4, it could be seen that the structure of the bacterial cell membrane began to blur as the cells vacuolated, the shape of the cells became irregular, the cell membrane completely...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com