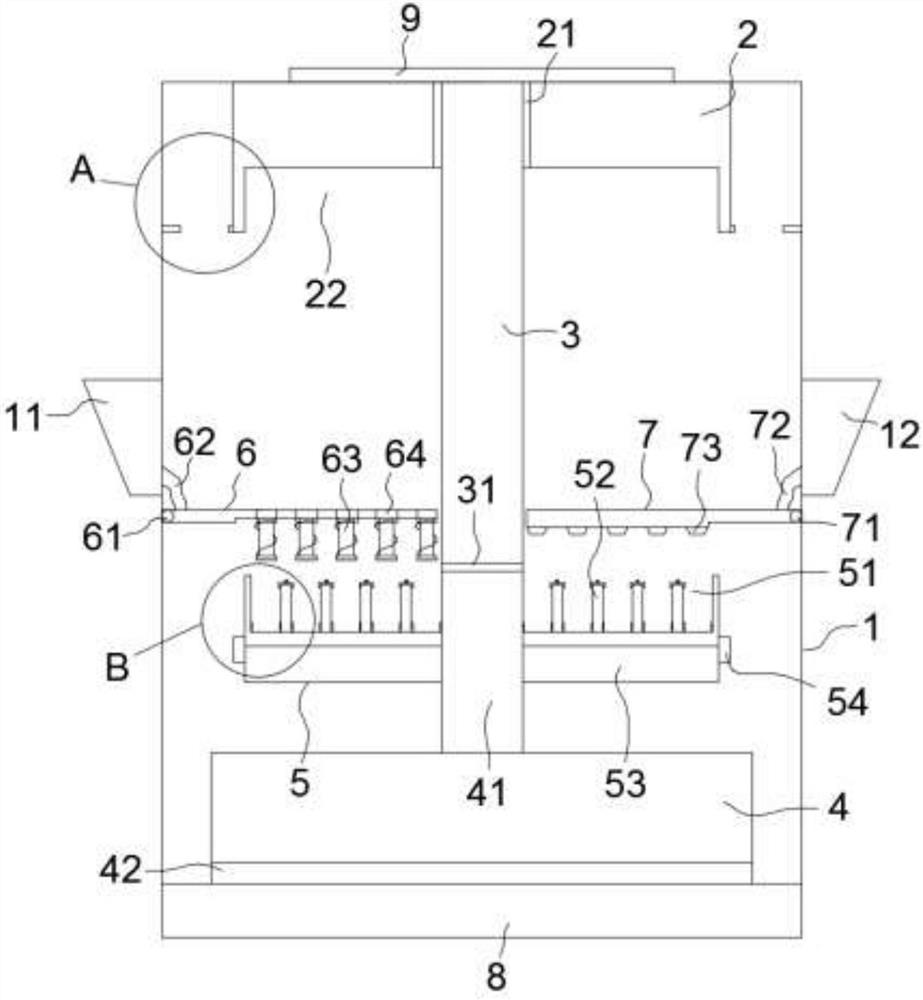
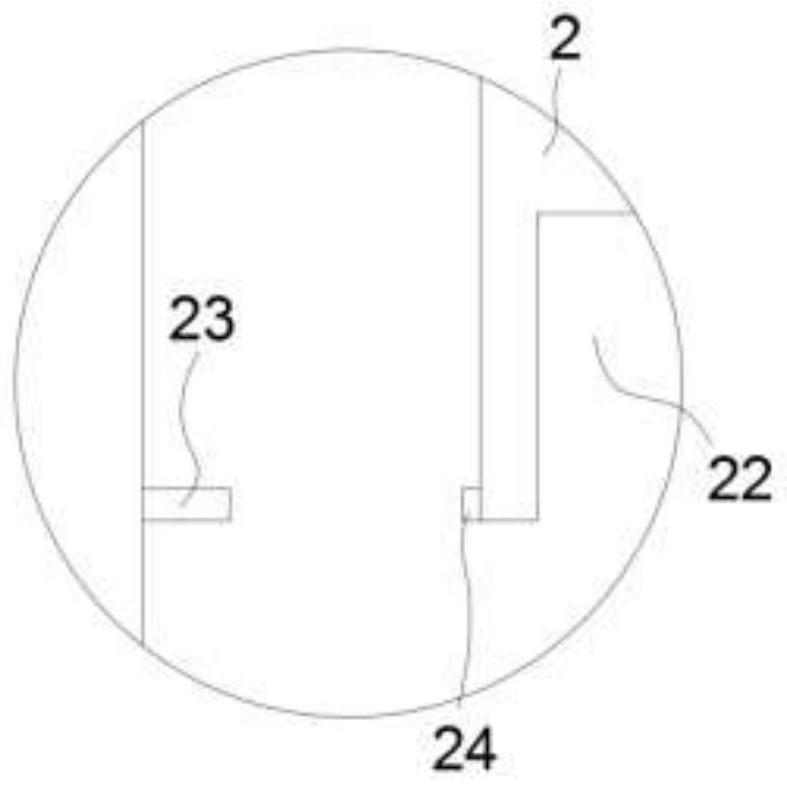
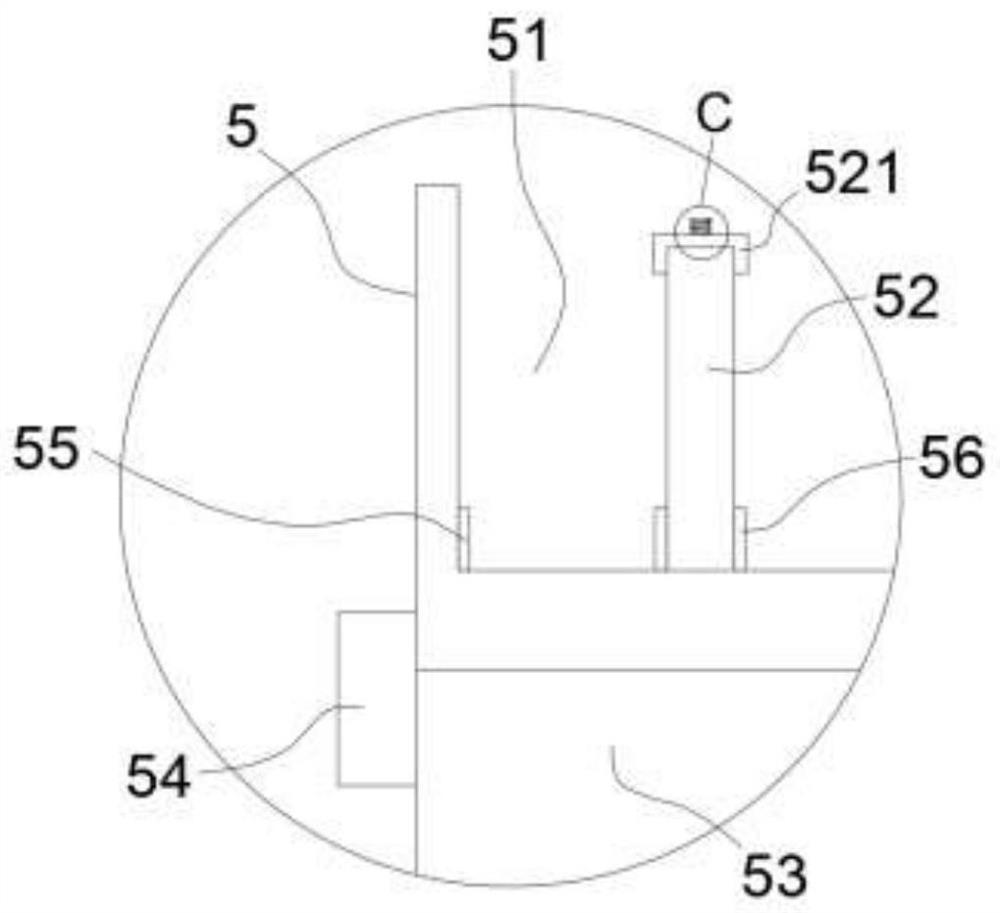
A process for degrading lignocellulose to produce hydrogen and produce ethanol
A technology for lignocellulose and ethanol production, which is applied in the direction of biomass post-treatment, biomass pretreatment, gas production bioreactor, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, limited development and application, low cellulose conversion rate, etc., and achieve Improve efficiency and effect, easy and fast operation, long service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] A process for degrading lignocellulose to produce hydrogen and produce ethanol, the process includes the following steps:
[0041] S1: Use toluene:ethanol=2:1 (v / v) as the extractant to dewax the cleaned and dried straw for 6 hours at 150°C, and finally wash the dewaxed straw with ethanol for 3 times, and dry it in cold air to obtain dewaxed straw. Waxed rice straw, use 12.5% peracetic acid to treat dewaxed rice straw at 80°C for 2 hours to obtain solid a, and alkalinize the obtained solid a with sodium hydroxide, the concentration of sodium hydroxide aqueous solution is 15%, and the liquid-solid ratio is 20 : 1, the reaction temperature is 30°C, the reaction time is 1.5h, and solid b is obtained, and the solid b is cleaned with 40°C deionized water until the pH of the cleaning solution is neutral, and crushed to 16 mesh by a crusher. The solid after pretreatment is obtained; the exposed fiber bundles obtained by PAA-NaOH treatment are more than those obtained by othe...
Embodiment 2
[0046] This example is basically the same as Example 1, except that steps S3 and S3: the hydrolyzate is heated to 58°C at a rate of 2°C, and activated Clostridium thermocellum and nutrient solution are added to carry out anaerobic fermentation reaction. When the pressure in the fermenter exceeds 0.25MPa, the gas produced in the fermenter is collected to make the pressure in the fermenter reach 0.02MPa, and the hydrogen and ethanol produced by the anaerobic fermentation reaction are respectively subjected to the enrichment and separation of the produced gas and the separation of the produced liquid. Separate and obtain hydrogen and ethanol; the anaerobic fermentation reaction is specifically: 1) adjust the pH of the liquid in the tank to 7.2 after 3 days of fermentation reaction, discharge and collect 1 / 2 of the supernatant in the fermentation tank after 4 days of fermentation reaction, and press Proportionally add activated Clostridium thermocellum, nutrient solution and hydrol...
Embodiment 3
[0048] This example is basically the same as Example 1, except that steps S3 and S3: the hydrolyzate is heated to 58°C at a rate of 2°C, and activated Clostridium thermocellum and nutrient solution are added to carry out anaerobic fermentation reaction. When the pressure in the fermenter exceeds 0.35MPa, the gas produced in the fermenter is collected to make the pressure in the fermenter reach 0.02MPa, and the hydrogen and ethanol produced by the anaerobic fermentation reaction are respectively subjected to the enrichment and separation of the produced gas and the separation of the produced liquid. Separate and obtain hydrogen and ethanol; the anaerobic fermentation reaction is specifically: 1) adjust the pH of the liquid in the tank to 7.2 after 3 days of fermentation reaction, discharge and collect 2 / 3 of the supernatant in the fermentation tank after 6 days of fermentation reaction, and press Proportionally add activated Clostridium thermocellum, nutrient solution and hydrol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com