Method for identifying corn bacterial stripe disease caused by Pantoea ananatis
A technology of Pantoea pineapple and identification method, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbe measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of sweet corn hazards, etc., achieve good repeatability, shorten the identification time, and shorten the time from inoculation to onset Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0041] The preparation method of LB liquid medium is: 10g Tryptone (Tryptone), 5g Yeastextract (Yeasextract), 5g NaCl, NaOH to adjust the pH to 7.4, and dilute to 1L with deionized water. Steam sterilization under high pressure for 20min.
[0042]The preparation method of LB solid medium is: 10g Tryptone (Tryptone), 5g Yeastextract (Yeasextract), 5g NaCl, 15g agar, adjust pH to 7.4 with NaOH, and dilute to 1L with deionized water. Steam sterilize under high pressure for 20min, pour into 10cm Petri dish.
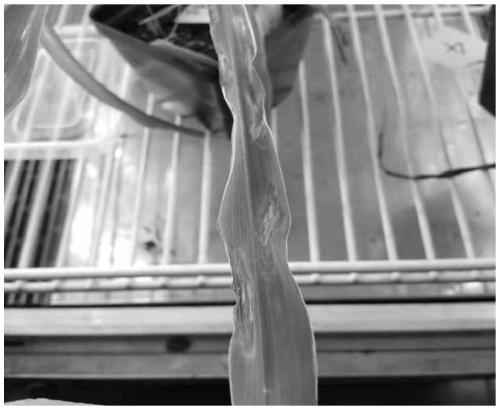
[0043] Field-affected strains of bacterial streak disease, such as figure 1 shown.
[0044] The following biological materials are involved in the examples:
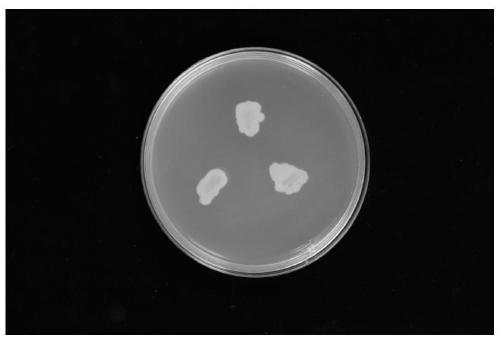
[0045] Pantoea ananatis was purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center, CGMCC: 1.15633. The result graph of Pantoea pineapple cultured on LB solid medium, such as figure 2 shown.
[0046] Yuetian No. 28, approval number: Yueshenyu 20170004, can also be obtained from the Cr...
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1: Identification of resistance to bacterial stripe disease of sweet corn variety Yuetian 28
[0050] 1. Cultivation of inoculated seedlings of sweet corn
[0051] (1) Take 40 seeds of Yuetian No. 28 in ddH 2 Soak in O at 28°C for 16h. The seeds after imbibition were soaked with 75% alcohol for 5 minutes to carry out surface disinfection, and then the seeds were sterilized with ddH 2 O was washed three times; after cleaning, the seeds were soaked in 10% NaClO for 30 min, disinfected again, and then sterilized with ddH 2 O washed three times.
[0052] (2) Seeds are sown in nutrient soil, using small flowerpots with a diameter of 10 cm, and 4 seeds are sown in each flowerpot. Place the sown pots in the light incubator. The environment of the incubator was set at 28° C., humidity 60%, light time 16 hours, light intensity 30000 Lx, dark time 8 hours, light intensity 0 Lx. The corn seedlings were cultivated to the stage of three leaves and one heart.
[0053] ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2: Identification of resistance to bacterial stripe disease of sweet corn inbred line group 1-1
[0068] 1. Cultivation of inoculated seedlings of sweet corn
[0069] (1) Take 40 seeds of group 1-1 in ddH 2 Soak in O at 28°C for 16h. The seeds after imbibition were soaked with 75% alcohol for 5 minutes to carry out surface disinfection, and then the seeds were sterilized with ddH 2 O was washed three times; after cleaning, the seeds were soaked in 10% NaClO for 30 min, disinfected again, and then sterilized with ddH 2 O washed three times.
[0070] (2) Seeds are sown in nutrient soil, using small flowerpots with a diameter of 10 cm, and 4 seeds are sown in each flowerpot. Place the sown pots in the light incubator. The environment of the incubator was set at 28° C., humidity 60%, light time 16 hours, light intensity 30000 Lx, dark time 8 hours, light intensity 0 Lx. The corn seedlings were cultivated to the stage of three leaves and one heart.
[0071] 2....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com