Lubricating drug-carrying nanospheres, drug and preparation method thereof
A drug-loaded nano-drug technology, applied in the field of lubrication, can solve the problems of loss of lubrication function, thinning, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
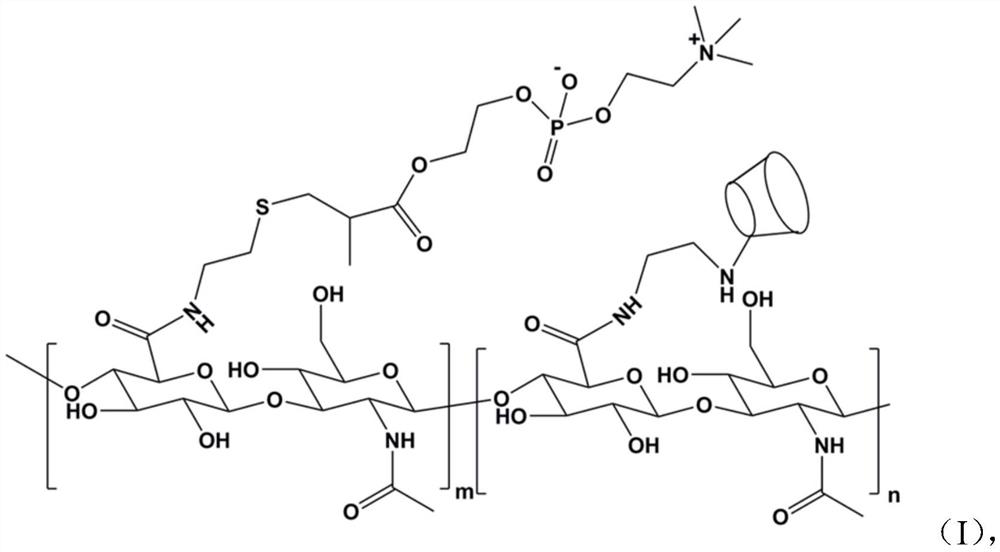
[0054] The present application also provides a method for preparing lubricated drug-loaded nanospheres, comprising the following steps:
[0055] a, reacting hyaluronic acid, initiator, catalyst, cystamine dihydrochloride, and aminated β-cyclodextrin in water to obtain thiolated and grafted hyaluronic acid with β-cyclodextrin;
[0056] b, reducing the product of step a and precipitating under acidic conditions to obtain a solid component;
[0057] c. Mix the solid component obtained in step b with tetrabutylammonium hydroxide in water, and dialyze to obtain the solid component;
[0058] d. Dissolving the solid component obtained in step c with 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine in an organic solvent for reaction, and dialyzing to obtain the solid component.
[0059] The preparation method of this embodiment has simple steps and mild conditions. Compared with other methods, the obtained material has good biocompatibility and lubricity. The preparation is realized by amid...
Embodiment
[0079] (1) Add hyaluronic acid, initiator EDC, catalyst HOBT, cystamine dihydrochloride, and aminated β-cyclodextrin into deionized water, stir at room temperature for 16 hours, and add dithiothreitol to the obtained solution after dialysis , after stirring overnight, adjust the pH to 3.5 by ethanol precipitation and freeze-drying.
[0080] (2) The product of step (1) was dissolved in deionized water, added dropwise into tetrabutylammonium hydroxide solution, stirred at room temperature, dialyzed and freeze-dried.
[0081](3) The product of step (2) was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide, added MPC, and reacted for 6 hours under nitrogen protection. The solution was precipitated in acetone, dissolved in deionized water, dialyzed, and then lyophilized and stored.
[0082] (4) The product of step (3) and the drug honokiol were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide, added dropwise to deionized water to promote thiol cross-linking, stirred for 24 hours, lyophilized and stored after dialysi...
experiment example 2
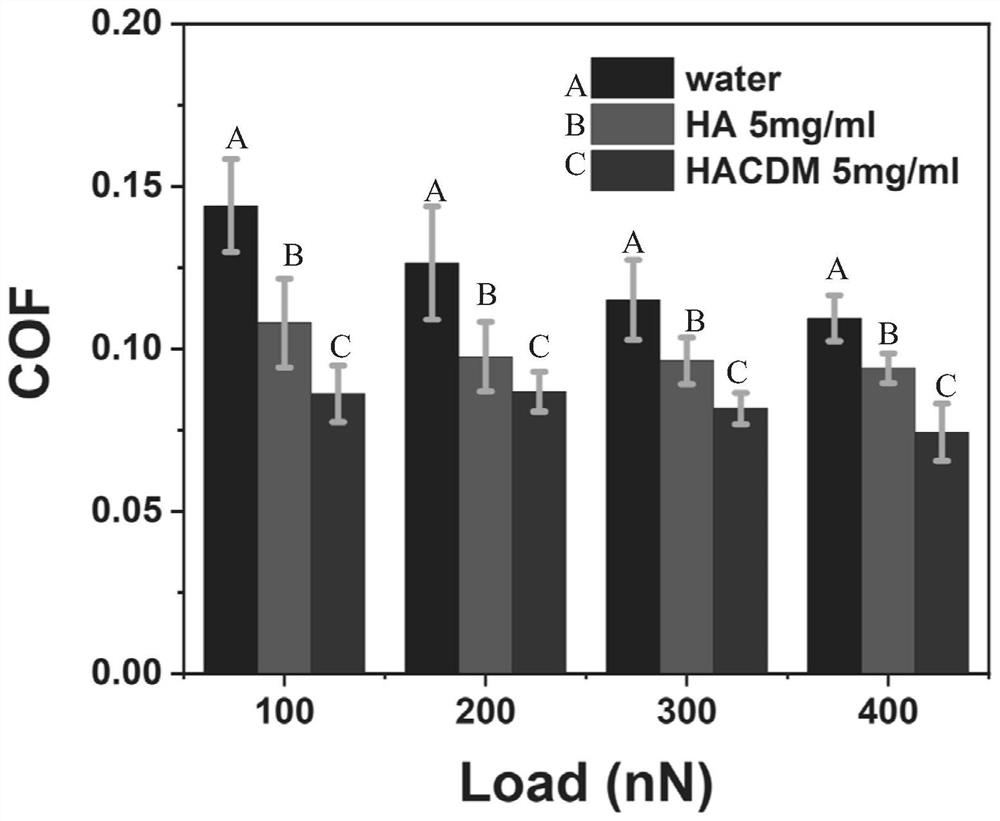
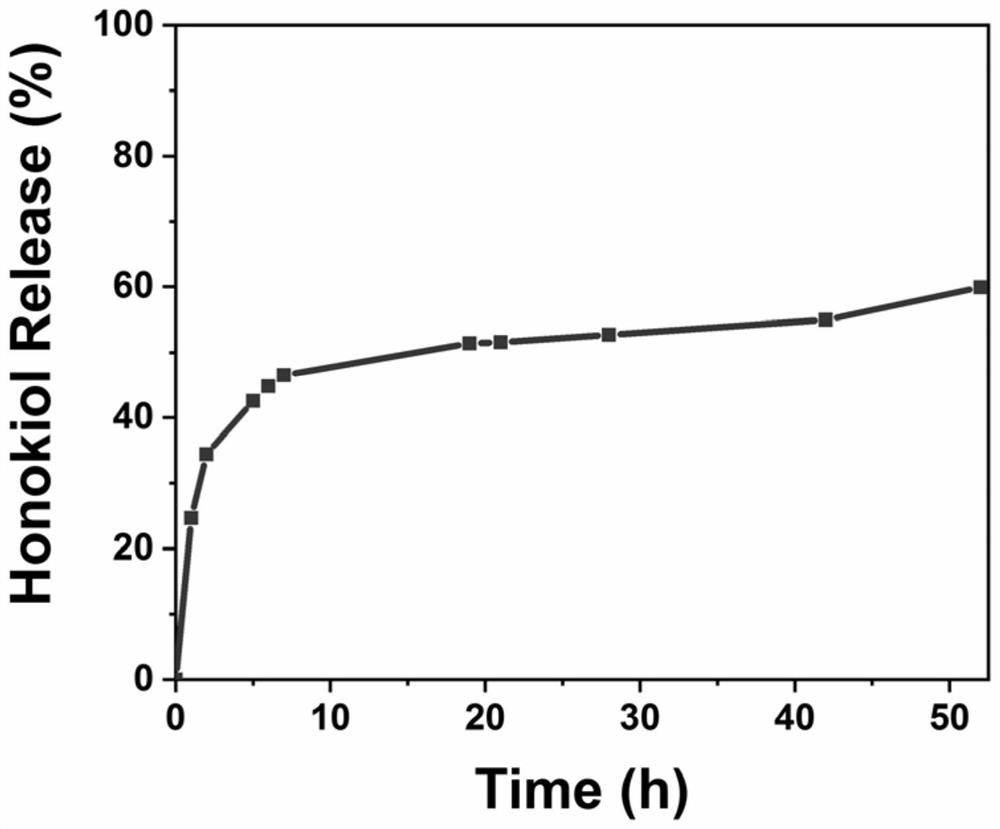
[0089] Experimental example 2 drug release
[0090] Carry out drug release test according to conventional method to the lubricated drug particle prepared by embodiment, the result is as follows: figure 2 shown. The results show that the lubricated drug-loaded nanospheres of the present application have the drug-loading ability to honokiol.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com