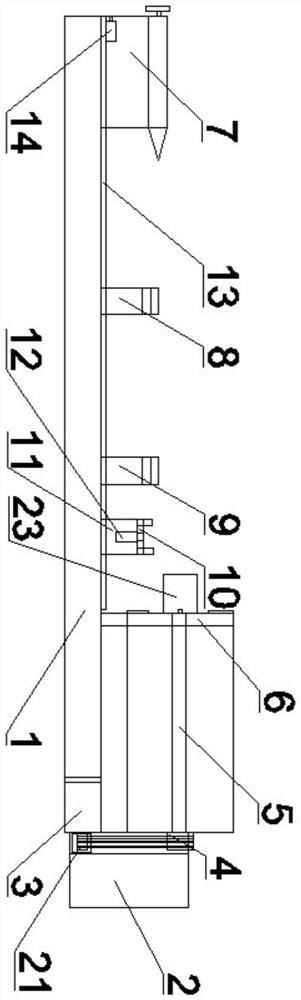
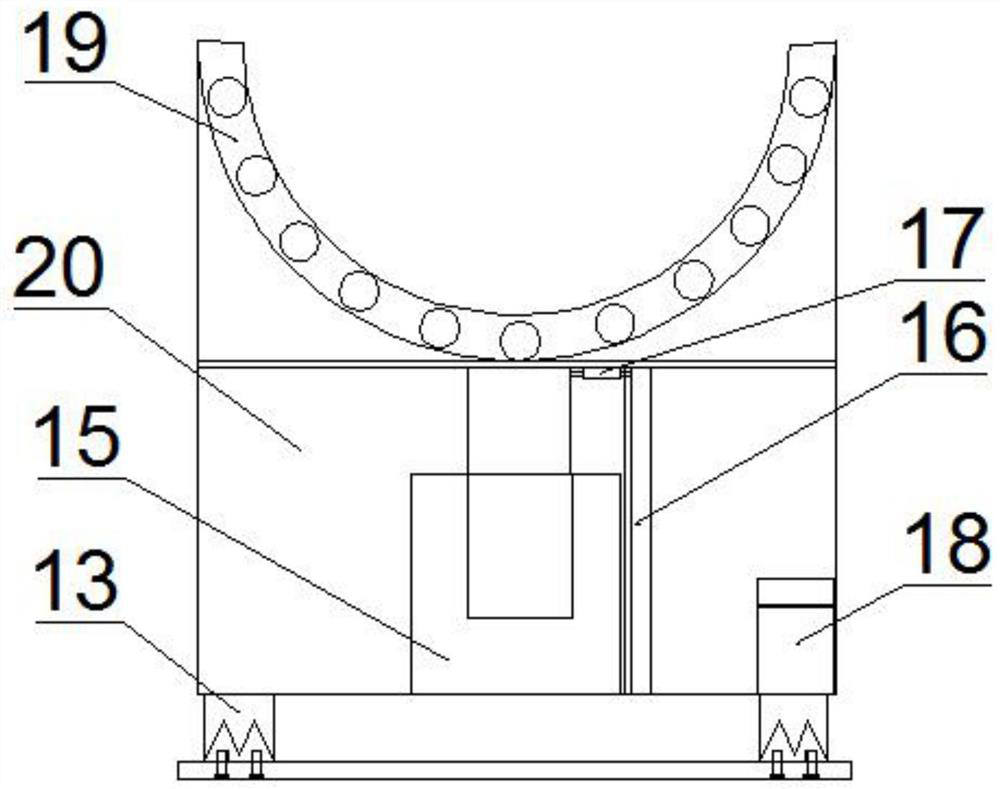
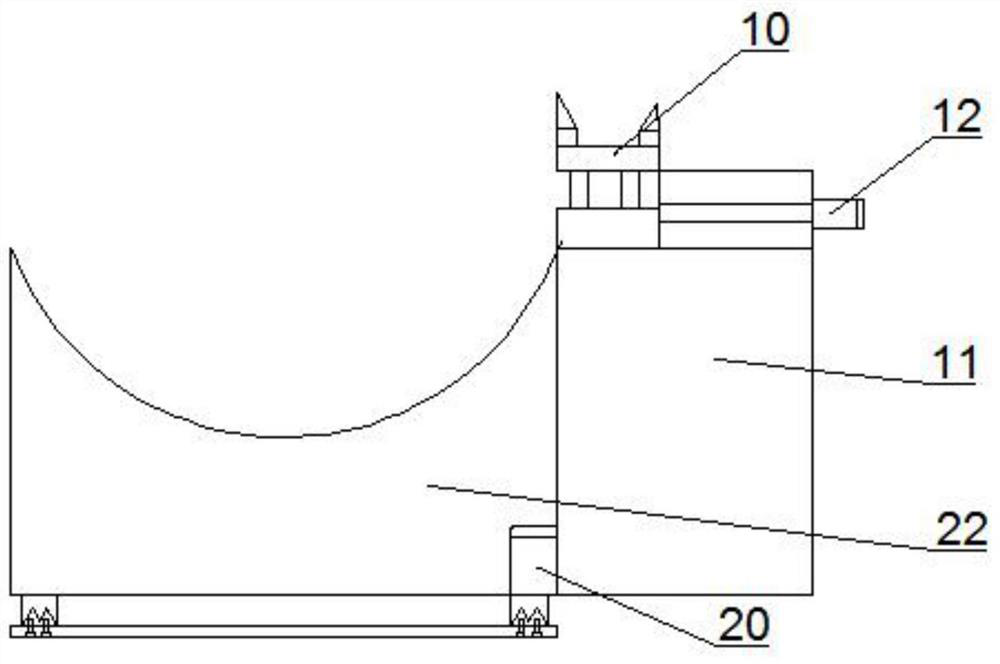
Machine tool capable of machining large-sized workpieces and use method of machine tool
A technology for large workpieces and lathes, applied in the field of lathes, can solve the problems of guide rail deformation machining accuracy, difficulty in machining special equipment parts, rough machining, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing economic benefits, reducing the difficulty of processing super-large, and reducing economic costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] The preparation method of aforementioned cemented carbide, comprises the steps:
[0037] S1: Take all raw materials according to the specified mass parts, mix them evenly, add ball milling medium and place them in a ball mill for ball milling, the liquid-solid ratio is 600-650mL / kg, the ball-to-material ratio is 7.5-9:1, and the speed of the ball mill is controlled at 200 -260r / min, ball milling time is 40-60h, wet mixture A is obtained;
[0038] S2: Put the wet mixture A obtained in step S1 into a desiccator and dry it for 30-60 minutes, recover the ball milling medium, then circulate and cool with frozen water, sieve to obtain the mixture B, and then put the above mixture B in a sealed state Carry out wax mixing, granulation, and prepare mixture C under the following conditions;
[0039] S3: isostatically press the mixture C obtained in step S2, and control the pressure at 180-300MPa to make a compact;
[0040] S4: The compact obtained in step S3 is sintered by a lo...
Embodiment 1
[0051] A cemented carbide used to make the lathe of the invention mainly consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 85 parts of tungsten carbide, 0.8 part of cobalt, 0.05 part of ruthenium powder, 0.7 part of samarium powder, 0.2 part of carbonyl nickel powder, vanadium carbide 0.4 parts, tantalum carbide 6 parts, niobium carbide 1.1 parts and titanium carbide 1.5 parts. The particle size of the tungsten carbide is 0.25 μm, the particle size of the cobalt is 0.6 μm, the particle size of the ruthenium powder is 0.6 μm, the particle size of the samarium powder is 0.5 μm, and the particle size of the nickel carbonyl powder is The particle size of the vanadium carbide is 0.5 μm, the particle size of the tantalum carbide is 1.2 μm, the particle size of the niobium carbide is 1.2 μm, and the particle size of the titanium carbide is 1.8 μm.
[0052] A kind of preparation method of cemented carbide for lathe, comprises the steps:
[0053] S1: Take all the raw materia...
Embodiment 2
[0065] A hard alloy for a lathe, mainly composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 80 parts of tungsten carbide, 0.1 part of cobalt, 0.01 part of ruthenium powder, 0.5 part of samarium powder, 0.1 part of nickel carbonyl powder, 0.1 part of vanadium carbide, tantalum carbide 5 parts, niobium carbide 0.8 part and titanium carbide 1 part. The particle size of the tungsten carbide is 0.2 μm, the particle size of the cobalt is 0.4 μm, the particle size of the ruthenium powder is 0.5 μm, the particle size of the samarium powder is 0.2 μm, and the particle size of the nickel carbonyl powder is The particle size of the vanadium carbide is 0.2 μm, the particle size of the tantalum carbide is 1 μm, the particle size of the niobium carbide is 1 μm, and the particle size of the titanium carbide is 1 μm.
[0066] A kind of preparation method of cemented carbide for lathe, comprises the steps:
[0067] S1: Take all the raw materials according to the specified mass parts, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com