Nano-material immobilized microorganism remediation agent and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for immobilizing microorganisms and nanomaterials, which is applied in the field of nanomaterial immobilized microbial repair agents and its preparation, and can solve the problems of low repair efficiency by adding free microorganisms and low mechanical strength of immobilized microbial agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
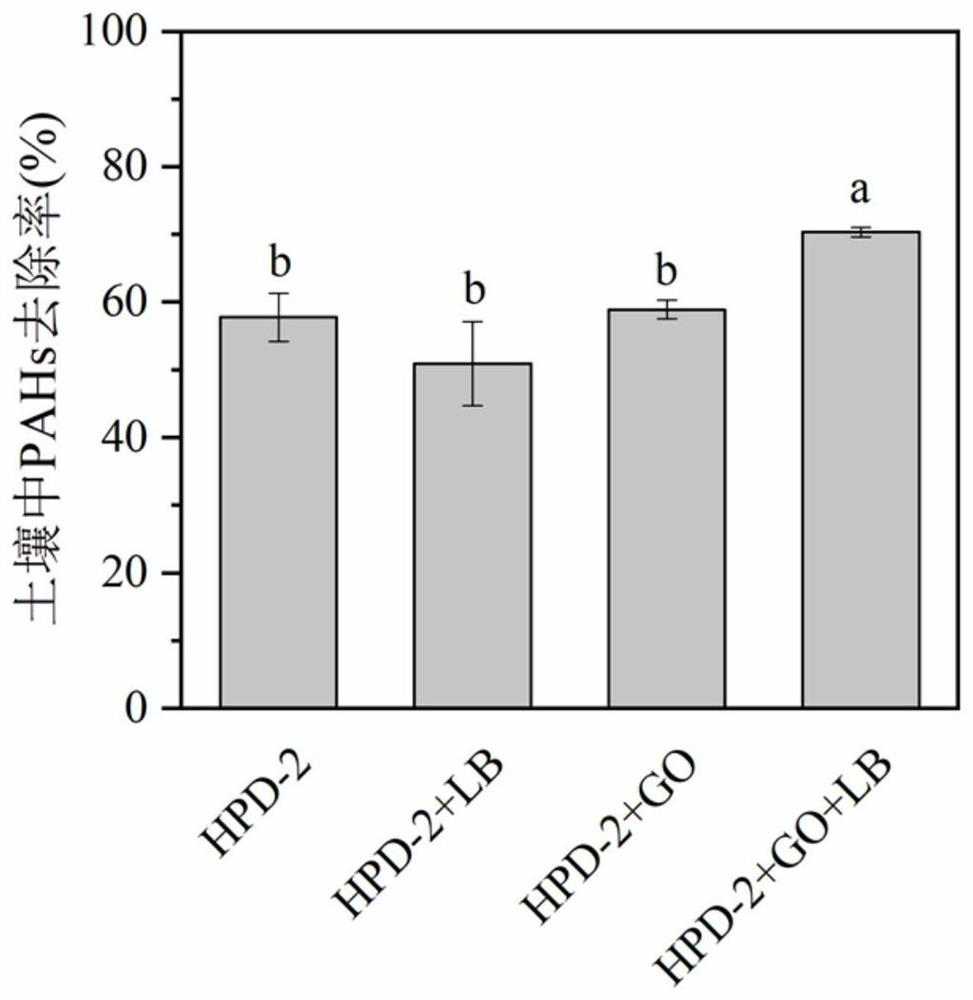
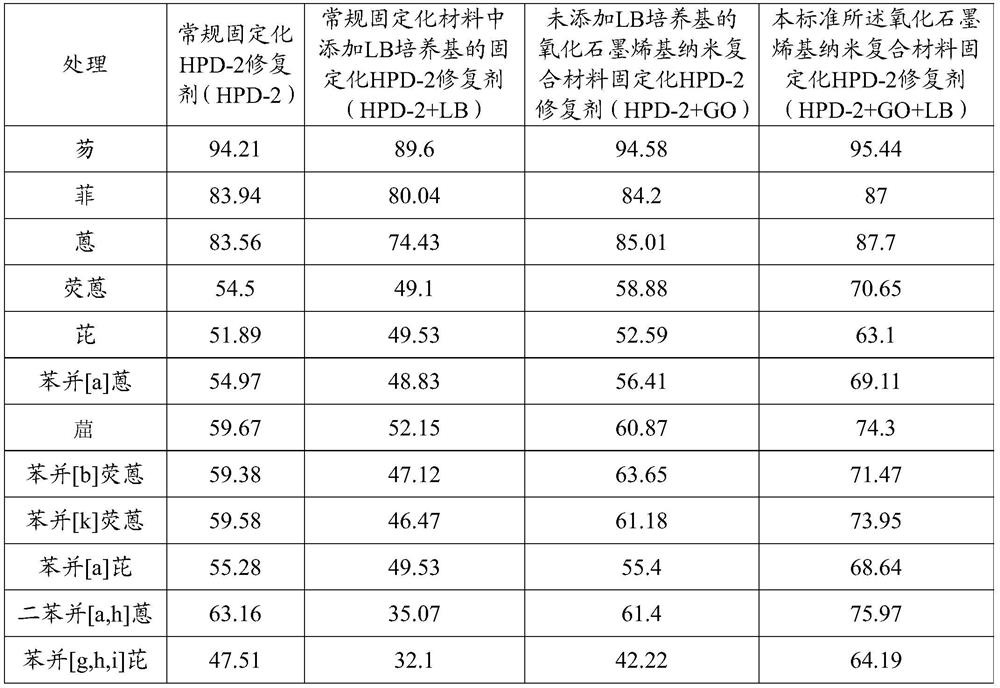
[0017] Example 1: Graphene oxide-based nanocomposite immobilized HPD-2 repair agent on the removal effect of PAHs in soil
[0018] Prepare LB medium, the ingredients and dosage: yeast extract 5.0g / L, peptone 10.0g / L, NaCl 10.0g / L, the rest is deionized water, adjust the pH to 7.0, sterilize at 0.12MPa, 121℃ Bacteria 20min standby. Take out the strain of Paracoccus ammophilus stored at -80°C, draw 100 μL of bacterial liquid and inoculate it into 10 mL of liquid LB medium for rejuvenation culture, cultivate it at 30°C and 150 r / min for 8 hours, and then inoculate it at a volume ratio of 10%. The culture was continued for 16 h in liquid LB medium. After centrifuging at a speed of 6000r / min for 5min, the logarithmic growth phase cells of the above bacteria were obtained; washed twice with phosphate buffer and resuspended to adjust the OD of the bacterial suspension 600 value to 1.0, centrifuge and concentrate 100mL of the bacterial suspension to obtain Paracoccus ammonophilus ba...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: Graphene oxide-based nanocomposite immobilized HPD-2 repair agent on the removal effect of PAHs in soil
[0023] Compared with Example 1, LB medium was added to the sodium alginate solution in a volume ratio of 5% in this example, and other steps and parameters were the same as in Example 1, and the graphene-based nanocomposite immobilized HPD was prepared. -2 Repair Potion. The soil collected from a contaminated site of a coking plant in Nanjing was used as the test soil. The content of PAHs in the soil was 344.48 mg / kg. The graphene-based nanocomposite immobilized HPD-2 restoration agent prepared above was added at a dosage of 3wt.%. Add to the soil. After 35 days of remediation, the removal rate of PAHs in the soil immobilized with HPD-2 remediation agent using graphene oxide-based nanocomposites was 68.24%, which was not significantly different from that of the immobilized remediation agent added with 10% LB medium. Immobilized HPD-2 remediation agent t...
Embodiment 3
[0024]Example 3: Graphene oxide-based nanocomposite immobilized HPD-2 repair agent on the removal effect of PAHs in soil
[0025] Compared with Examples 1 and 2, LB medium was added to the sodium alginate solution in a volume ratio of 8% in this example, and other steps and parameters were the same as in Examples 1 and 2, and the graphene-based nanocomposite was prepared. Material-immobilized HPD-2 restoration agent. The soil collected from a contaminated site of a coking plant in Nanjing was used as the test soil. The content of PAHs in the soil was 344.48 mg / kg. The graphene-based nanocomposite immobilized HPD-2 restoration agent prepared above was added at a dosage of 3wt.%. Add to the soil. After 35 days of remediation, the removal rate of PAHs in the soil immobilized with graphene oxide-based nanocomposite HPD-2 remediation agent was 71.35%, which was not significantly different from that of the immobilized remediation agent added with 10% LB medium, and compared with th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com