Application of stem cell-derived microvesicles in preparation of preparation for repairing scars
A technology of microvesicles and stem cells, applied in the application field of preparations, can solve the problems of slow skin pigmentation changes, stem cell ethics, safety and difficulty in storage and transportation, and slow wound healing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Obtaining microvesicles derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hucMSCs)
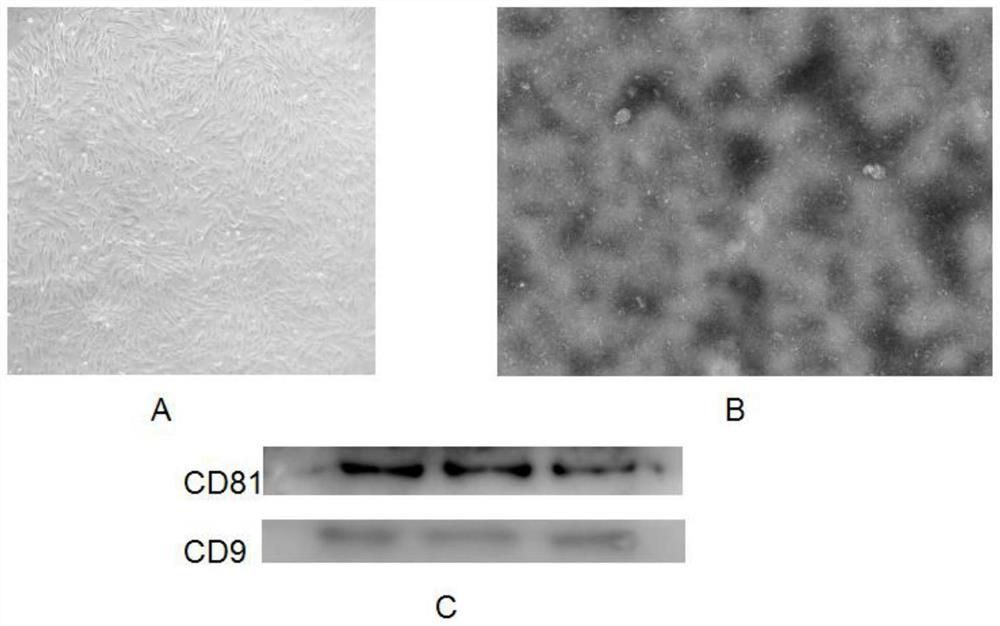
[0036](1) Isolation and culture of umbilical cord MSC: according to the established HucMSC isolation and identification method, in vitro culture and expansion of MSC (Qiao Chun et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the umbilical cord. Cell Biol Int. 2008 Jan; 32 (1): 8-15), select healthy human MSCs with strong proliferative ability and good condition ( figure 1 In A), the growth area covered 80%, cultured in serum-free medium for 48 hours to collect the culture supernatant, centrifuged at 2000g for 10 minutes to remove cell debris, then it was MSC-CM, and refrigerated at -70°C for later use.
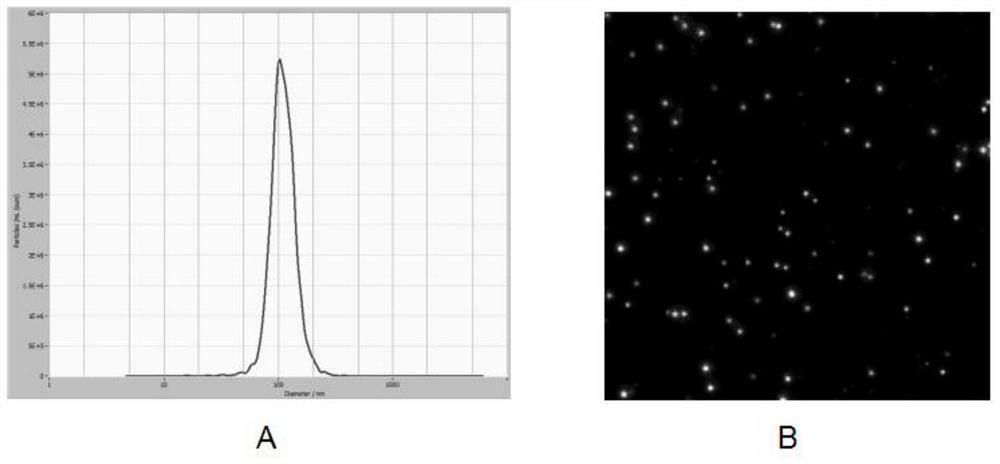
[0037] (2) Separation and purification of microvesicles in the supernatant secreted by umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: the collected MSC-CMs were subjected to differential centrifugation to discard cell debris and organelles, and then transferred to a 15ml 100 000Da MWCO ultr...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Construction of scar rat model and repair effect of hucMSC-microvesicles on scar rats
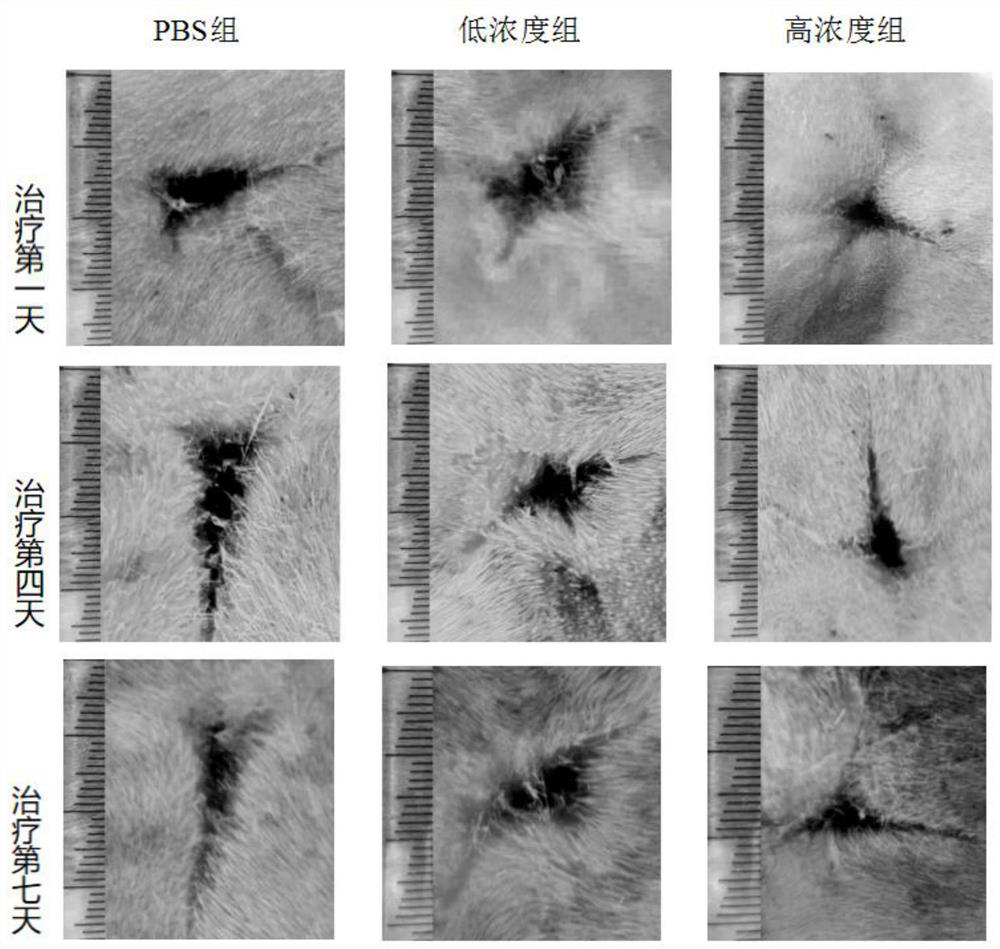
[0043] (1) Construction of SD rat skin scar model: 8-week-old female SD rats weighing 200 g were anesthetized with 10% chloral hydrate, and 8% Na 2 S was treated with hair removal, and a circular full-thickness skin defect wound with a diameter of 2 cm was prepared with sterile surgical instruments. Scabs formed on the 2nd to 3rd day, and a skin scar model was formed around the 7th day;
[0044] (2) Intervention treatment of HucMSC-microvesicles: set up three experimental groups, PBS control group, high concentration group, low concentration group (high concentration: 4.5×10 11 / experimental animal; low concentration: 4.5×10 8 / experimental animal); three rats in each group, each rat was injected with 200 μl of phosphate buffered saline (PBS) in the subcutaneous tissue around the scar to dissolve high-concentration and low-concentration microvesicles for treatment, and PBS was use...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Repair effect of human scar microvesicles
[0055] (1) Basic information and repair plan: 31-year-old female, underwent the first cesarean section in November 2017, and the second cesarean section in February 2020, resulting in scar tissue after surgery;
[0056] Restoration plan: divided into 6 treatments, each time 4.5×10 11 Particles / volume 200 μl. The nano-microvesicles are stored in the freezer layer of the refrigerator, take out one before use, and let it dissolve naturally at room temperature. After cleaning the scars, take pictures of the scars, and then lie down and apply the completely melted nano-microvesicles evenly on the scars, gently pat and massage until completely absorbed, and treat once every 3 days, initially 6 times.
[0057] (2) Observation of repair effect (such as Figure 8 shown):
[0058] 1) Gross evaluation of scar
[0059] ① Including the degree of scar protrusion: the protruding part of the scar gradually becomes flat;
[0060] ②Scar c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com