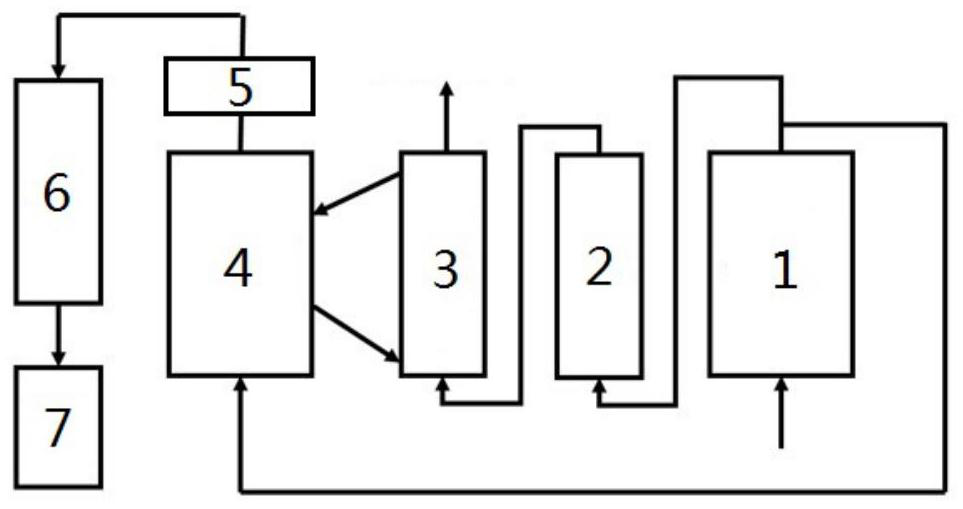
Method for reducing NO concentration in incomplete regeneration flue gas
A completely regeneration and flue gas technology, applied in separation methods, combustion methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of easy deactivation of NO oxidation catalysts, and achieve the effect of saving equipment investment and cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
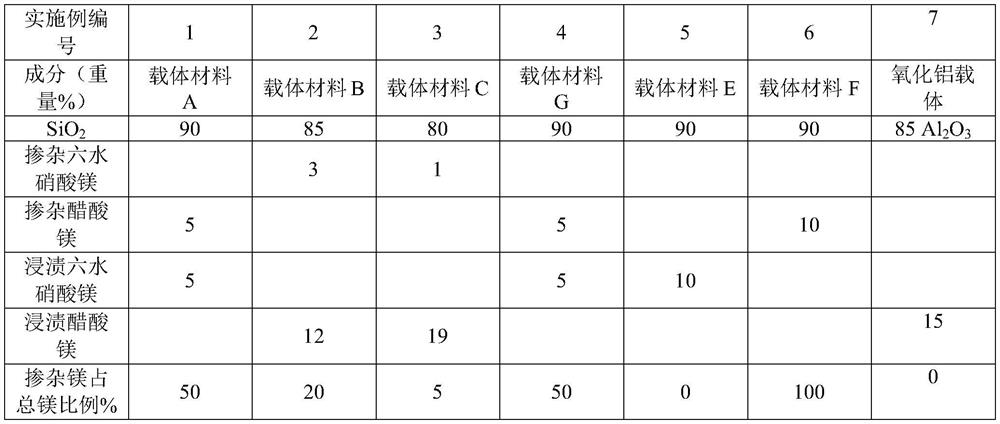
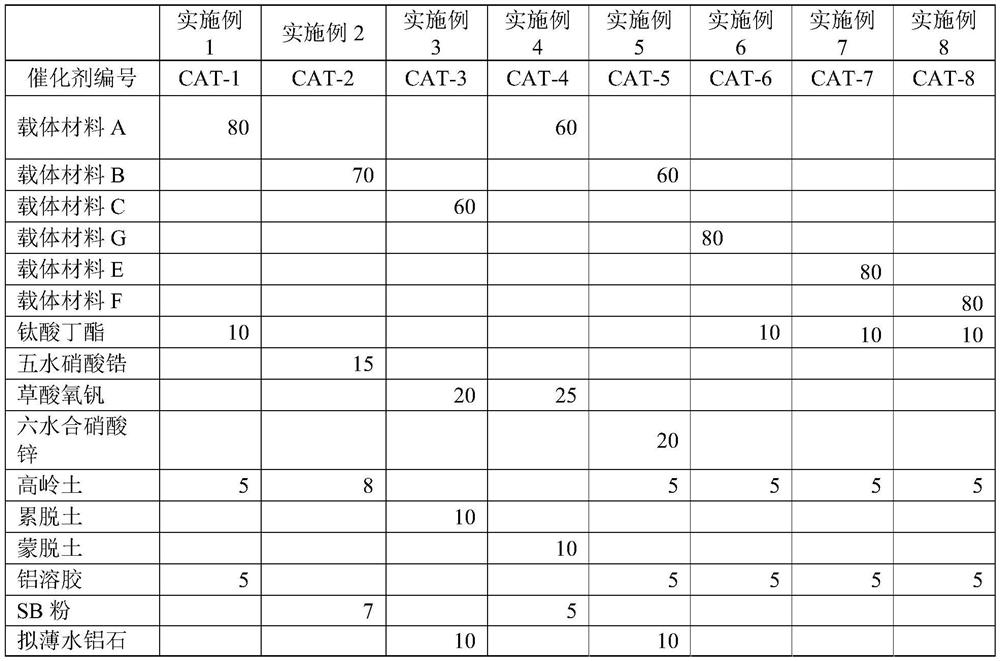
[0028] The method for reducing the concentration of NO in incompletely regenerated flue gas provided by the present invention, wherein the NO oxidation catalyst can be prepared according to existing methods, such as forming a mixture containing oxidation active components and magnesium oxide components and matrix, molding, roasting Or shape the matrix containing magnesium oxide components, impregnate and introduce oxidation active components, and bake. In one embodiment, the NO oxidation catalyst includes a magnesium component, an oxidation active component and a matrix, which can be obtained by forming a mixture of the magnesium component, an oxidation active component and a matrix, molding, and roasting, or by forming a part comprising Or the mixture of all matrix and magnesium oxide components, impregnated to introduce oxidation active components and then mixed with the rest of the matrix, shaped and roasted. The step of drying may also be included before firing. Based on ...
Embodiment 1
[0063] Under the condition of vigorous stirring, 216g of triethanolamine (TEA), 25.56g of magnesium acetate and 54g of deionized water were added dropwise to 300g of TEOS, and reacted for 40min to obtain the first mixture, and then 300g of TEAOH was added dropwise to the above The second mixture is obtained from the first mixture. The second mixture was aged at 30° C. for 24 h, and then heated at 98° C. for 24 h in an air atmosphere to obtain a gel. The gel was placed in a reaction kettle and reacted at 180° C. for 16 h. Finally, the product was heated up to 600° C. for 10 h in an air atmosphere at a rate of 1° C. per minute and calcined to obtain a calcined product. Dissolve 30.56g of magnesium nitrate hexahydrate in 86.5g of deionized water, impregnate an equal volume on the roasted product, place it at room temperature for aging for 24h, then dry it in the air at 100°C for 12h, and roast at 500°C for 4h to obtain the carrier material of this example. It is the carrier mat...
Embodiment 2
[0067] 284.16g of TEOS, 18.39g of magnesium nitrate hexahydrate and 136.87g of deionized water were mixed to obtain a first mixture. Under the condition of vigorous stirring, 52.11 g of TEA was added dropwise into the first mixture at a rate of 4-6 g per minute to obtain the second mixture. The second mixture was matured at 25° C. for 16 h, and then heated at 99° C. for 24 h in an air atmosphere to obtain a gel. The gel was placed in a reaction kettle and reacted at 190°C for 48h. Finally, the product was heated to 550° C. for 10 h in air at a rate of 1° C. per minute and calcined to obtain a calcined product. Dissolve 61.53g of magnesium acetate in 81.9g of deionized water, impregnate an equal volume on the roasted product, place it at room temperature for aging for 18 hours, then dry it in the air at 120°C for 18 hours, and roast it at 450°C for 5 hours to obtain the carrier material of this example, which is referred to as carrier Material B.
[0068] The specific surfac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com