Methods and devices for reducing vacular smooth muscle cell proliferation
A balloon catheter, polymer technology, applied in cardiovascular system diseases, catheters, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve problems such as lack of drug-eluting balloons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
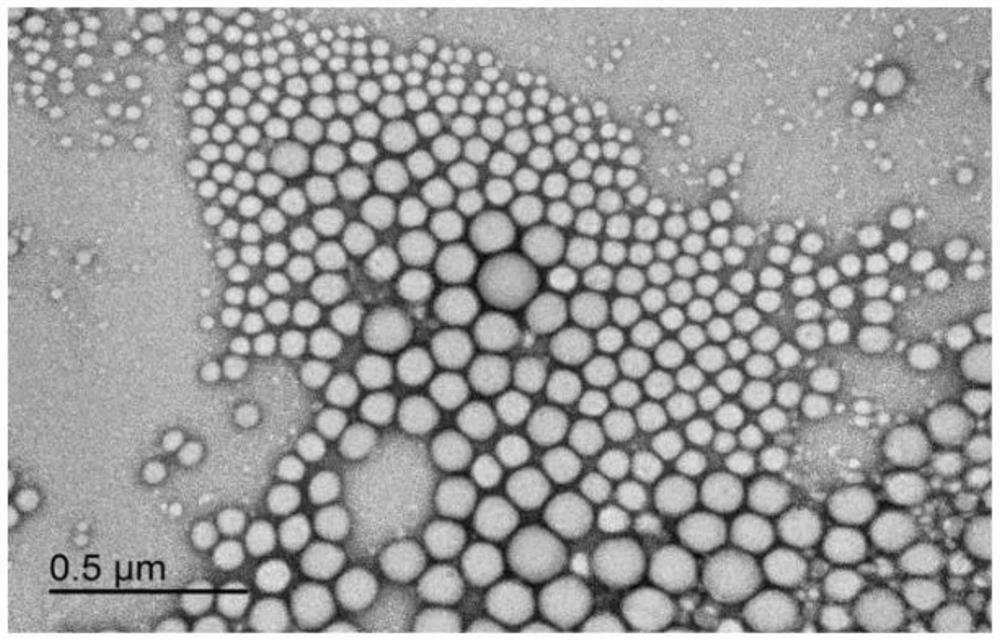
[0203] Embodiment 1. nanoparticle synthesis method
[0204] In the examples described herein and other examples described herein below, certain materials were used in the studies and the following results were obtained: RG504H poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) PLGA50:50, quercetin (QUER) and acetonitrile were obtained from Sigma Aldrich Corp. (St. Louis, MO); ethyl acetate, Tween 80, resveratrol (RESV) and Triacetyl resveratrol (TAR) was obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA); Eudragit RL100 was obtained from Evonik Industries AG (Essen, Germany). Polymer nanoparticles were synthesized using single emulsion solvent evaporation technique (Astete C.E. and Sabliov C.M.J. Biomater Sci Polym Edi. 2006; 17(3):247-89).
[0205] Briefly, the organic phase was prepared by mixing Eudragit RL100 (60 mg) and PLGA (200 mg) in a mixed solution of ethyl acetate and acetone (8:2) (6 mL) and stirring gently at room temperature for 30 min. Next, quercetin and triacetyl resveratrol ...
Embodiment 2
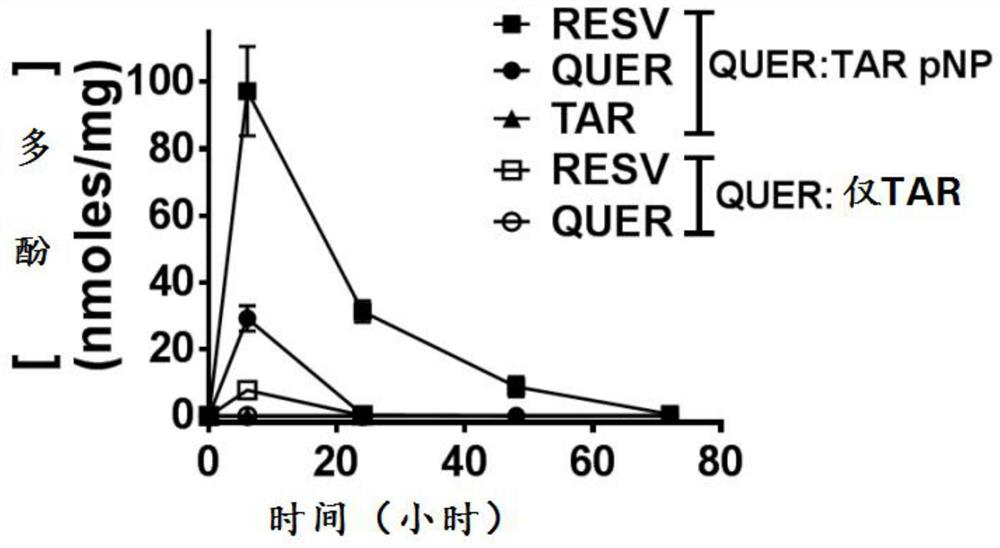
[0206] Example 2. Drug loading and encapsulation efficiency assay method
[0207] The drug loading and encapsulation efficiency were determined using HPLC. A standard curve was first prepared in the extraction solvent dimethylformamide (DMF). Preliminary tests showed that quercetin needs to be added with ascorbic acid to reduce its degradation, and quercetin was analyzed in DMF without adding ascorbic acid. Drug loading was measured by suspending drug-loaded polymer nanoparticles in DMF at a concentration of 3.9 mg / mL. Collect 200 µL of samples and add 80 µL of ascorbic acid to each. Samples were clarified by centrifugation and analyzed by HPLC. The samples containing ascorbic acid were analyzed for quercetin, while the samples without ascorbic acid were analyzed for triacetyl resveratrol and resveratrol. Analysis was performed in triplicate. Calculate the theoretical loading based on the initial amounts of quercetin and tar added during the synthesis.
Embodiment 3
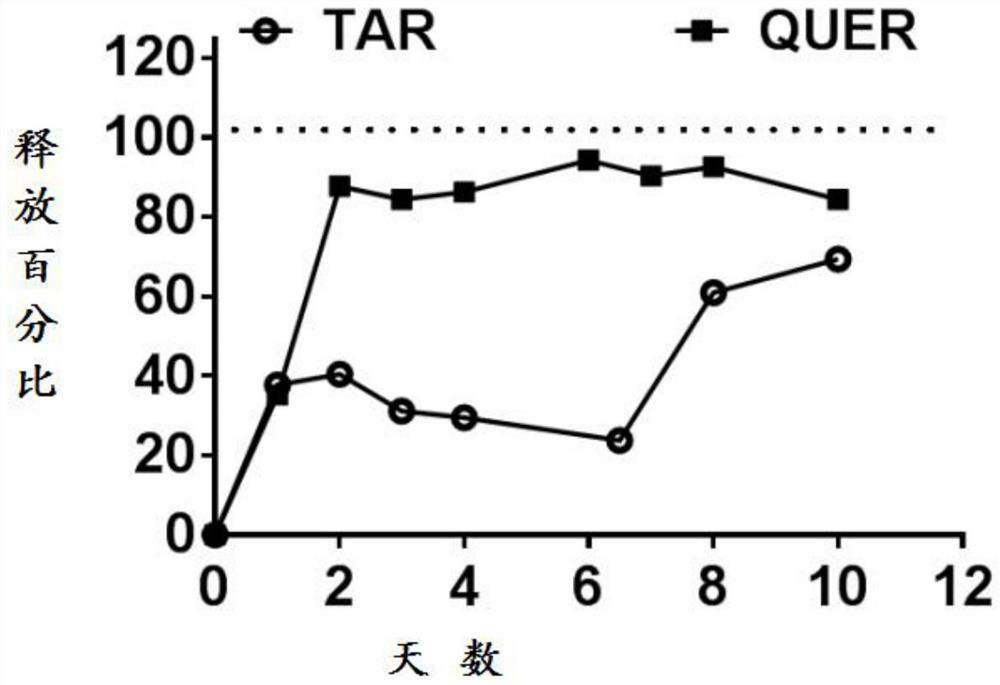
[0208] Example 3. Evaluation method of drug release curve.
[0209] Drug release profiles were used to measure the release of both drugs from pNPs over 10 days. Release studies were performed in a simulated blood solution at pH 7.4 to simulate physiological conditions. Nanoparticles were suspended at a concentration of 19.5 mg / L, and the suspension was transferred to a dialysis bag that was sealed and placed in a simulated blood solution. Place the whole system in a shaking incubator for 10 days. Samples were collected from the dialysis bag every day and analyzed by HPLC, which was similar to the method used to determine the drug loading.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com