Application of tga7 Gene in Regulating Plant Flowering Period
A gene and plant technology, applied in the application field of TGA7 gene in regulating the flowering period of plants, to achieve the effect of delaying flowering period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Obtaining of embodiment 1 homozygous mutant
[0025] 1. Obtaining Mutants
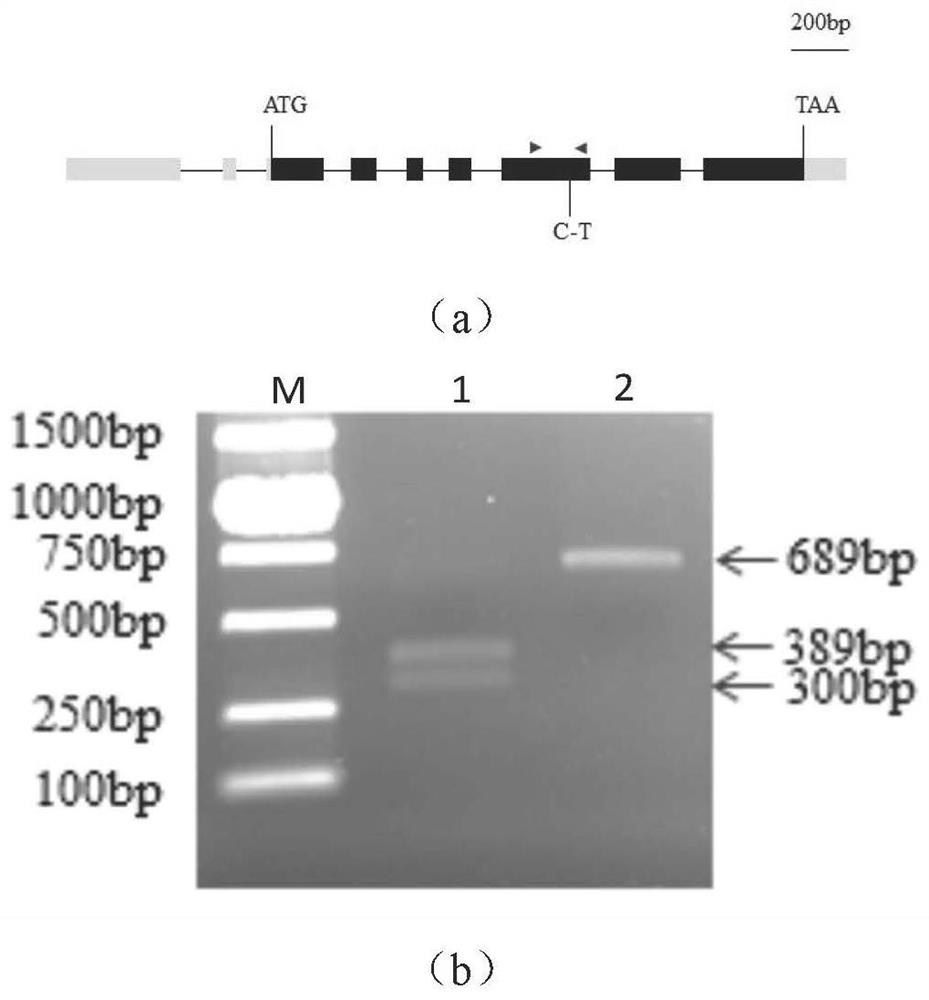
[0026] The TGA7 mutant seeds used were purchased from the Arabidopsis Resource Center (ABRC, the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center, http: / / www.arabidopsis.org / ). Among them such as figure 1 (a) The number of tga7 is CS89835, and the construction method of the mutant is point mutation; the C in the EcoRV restriction site of the wild-type genome is mutated to T, so that the EcoRV restriction site in the genome of tga7 is deleted, so that it can be carried out Homozygous mutants were obtained by enzyme digestion after PCR reaction. The full-length gene coding (CDS) sequence of the tga7 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1.
[0027] 2. DNA Extraction from Arabidopsis Plant Leaves
[0028] Take an appropriate amount of seeds on wet filter paper, place them in a refrigerator at 4°C for 48 hours in the dark, and after the seeds break and end dormancy, move them into the soil and place them in a greenh...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2 flowering time and rosette leaf number statistical analysis
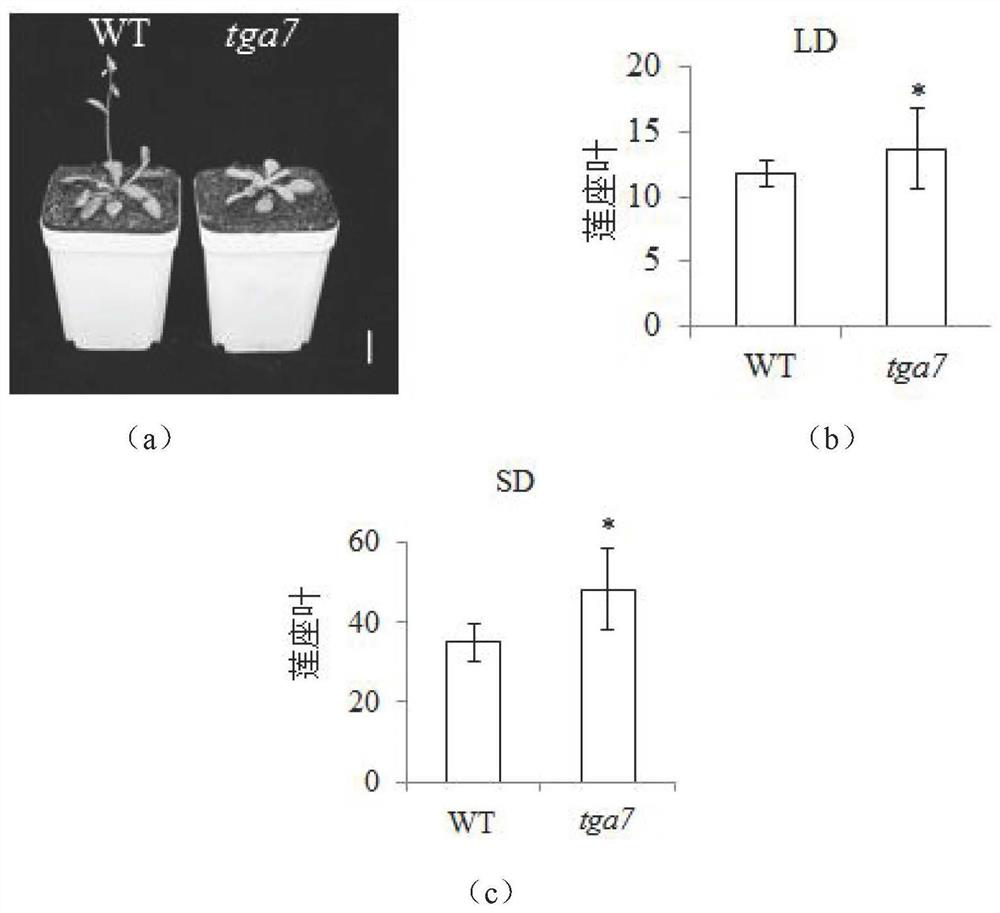
[0057] Under the condition of 23°C, grow under the condition of long light (16h / 8h, light / dark) or short light (8h / 16h, light / dark) 10000Lux light conditions. 20 wild-type plants of Arabidopsis thaliana WT and tga7 plants with normal growth were selected, and the number of rosette leaves after flowering of the plants was counted.
[0058] Statistical results such as figure 2 As shown in (a-c), the flowering time of the tga7 plant was later than that of the wild type, and the number of rosette leaves was more than that of the wild type, which indicated that the TGA gene mutation in Arabidopsis plants delayed flowering. The tga7 mutant showed delayed flowering under both long-light and short-light conditions, suggesting that TGA7 may not be involved in the photoperiodic pathway.
Embodiment 3
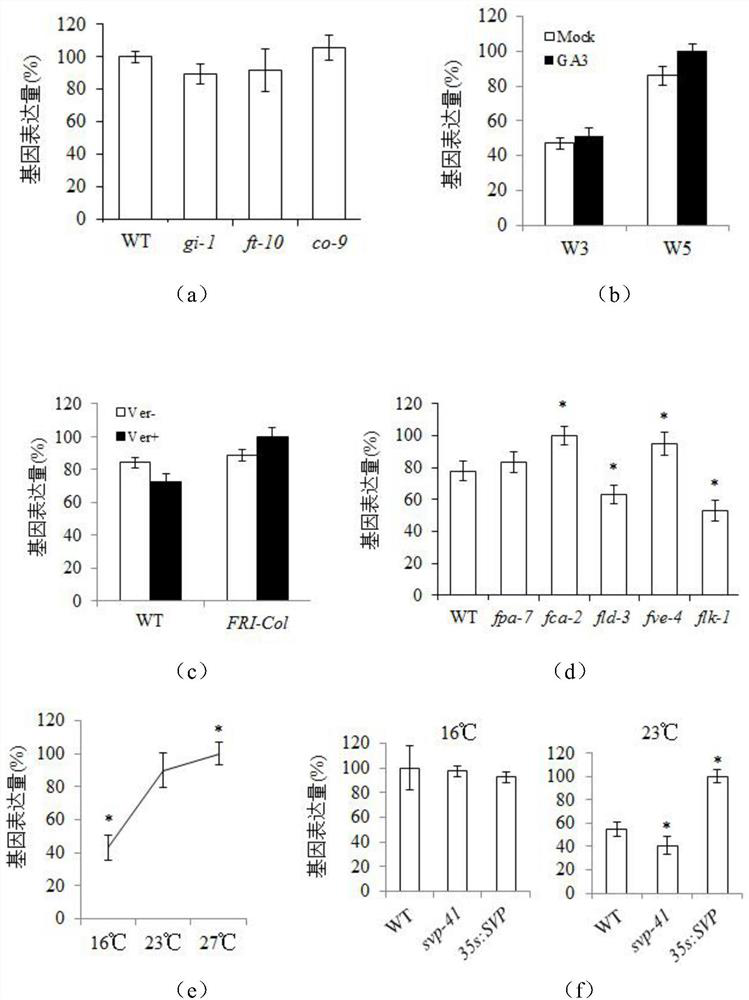
[0059] Example 3 Expression analysis of genes related to processing of five flowering regulatory pathways in TGA mutants and wild type
[0060] 1. Processing of five flowering regulatory pathways
[0061] (1) Vernalization: Plants: Col, FRI
[0062] ①Treatment group: plant in 1 / 2MS of no-antibiotic medium, place at 4°C for 2 days to break dormancy, place in the greenhouse for 4 days, place at 4°C for 6 weeks, place in the greenhouse for 5 days, and then plant in the soil (LD / SD).
[0063] ②Control: 36 days after the start of dormancy breaking treatment in the treatment group, 1 / 2MS in the non-antibiotic medium was planted at 4°C for 2 days to break dormancy, placed in the greenhouse for 9 days, and then planted in soil (LD / SD).
[0064] ③ Sampling was taken 9 days after seedling transplantation, and the expression level of TGA7 gene was quantitatively analyzed.
[0065] (2) Gibberellin: Plants: Col, tga7
[0066] ①Treatment group: SD 100μM GA3, spray once a week from the 7t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com