Sitagliptin key intermediate impurity as well as preparation method and application thereof
A sitagliptin and intermediate technology, applied in the field of medicinal chemistry, can solve the problems of poor stability of key intermediates, quality decline, and affecting the quality of sitagliptin products, and achieve the goals of simple method, quality control and quality control Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] The present invention provides the preparation method of sitagliptin key intermediate impurity described in above-mentioned technical scheme, comprises the following steps:
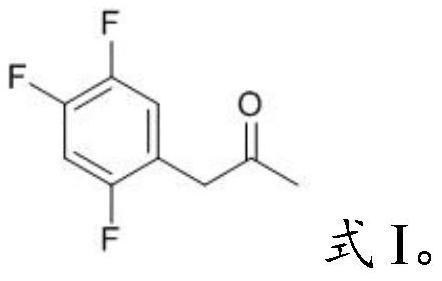
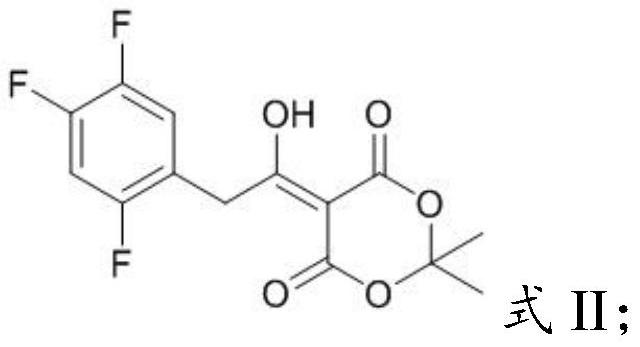
[0031] Mixing the acetylmycorrhizinic acid derivative having the structure shown in formula II with an organic solvent and performing pyrolysis to obtain the key intermediate impurity of sitagliptin having the structure shown in formula I;
[0032]
[0033] The organic solvent is one or more of toluene, xylene, chlorobenzene, chloroform, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, DMF, DMSO and acetonitrile; the pyrolysis temperature is 100-120°C.
[0034] In the present invention, unless otherwise specified, the required preparation materials are commercially available products well known to those skilled in the art.
[0035] In the present invention, the chemical name of the acetyl-Merfuran's acid derivative having the structure shown in formula II is 5-(1-hydroxyl-2-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)ethylene)- 2,2-Dimet...
Embodiment 1
[0046]Take 1.4g of 5-(1-hydroxy-2-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)ethylene)-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxacyclo-4,6-di Ketone) (II) was dissolved in 45mL (39g) of toluene, and after reflux at 110°C for 8h, the TLC detection should be completed, cooled to room temperature, and the solvent was recovered by distillation under reduced pressure, and the solvent was recovered with petroleum ether / ethyl acetate (volume ratio of 10: 1) Eluting with an eluent, and separating the obtained residue by column chromatography to obtain compound I-1.
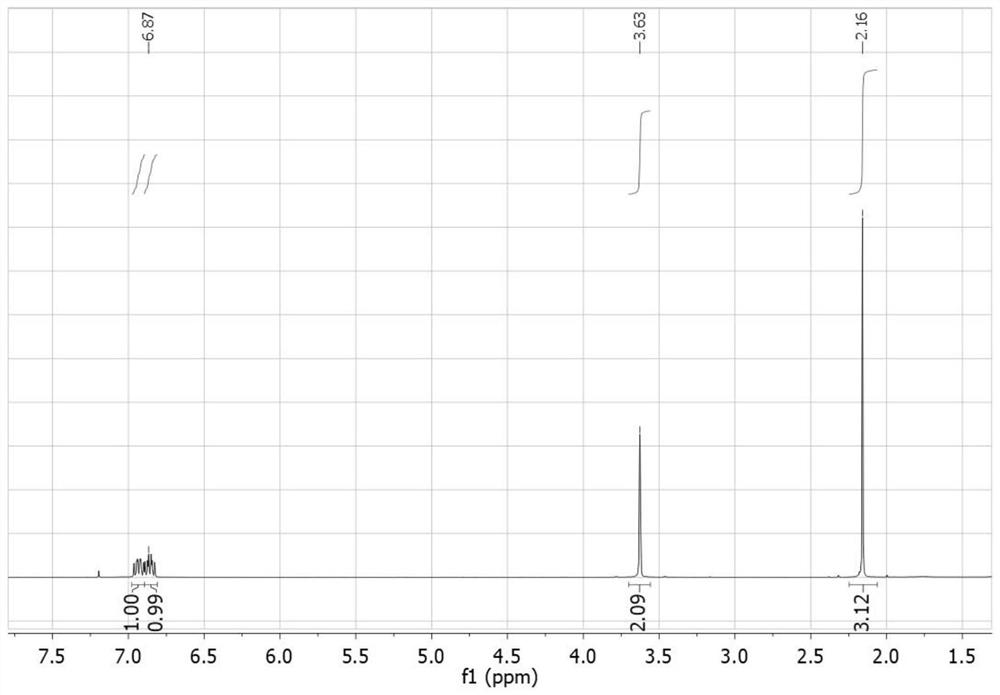
[0047] The compound I-1 prepared in embodiment 1 is carried out nuclear magnetic characterization, and the characterization data of its proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum are as follows: 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ6.94(m,1H),6.87(m,1H),3.63(s,2H),2.16(s,3H). The chemical name of this compound is 1-(2,4,5-trifluoro phenyl)-2-propanone.
Embodiment 2
[0049] Take 1.0g of 5-(1-hydroxy-2-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)ethylene)-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxacyclo-4,6-di Ketone) (II) was dissolved in 25mL (22g) of xylene, and after pyrolysis at 120°C for 6h at reflux, after the reaction was detected by TLC, it was cooled to room temperature, and the solvent was recovered by distillation under reduced pressure, and the solvent was extracted with petroleum ether / ethyl acetate (volume The ratio is 10:1) as the eluent for elution, and the obtained residue is separated by column chromatography to obtain compound I-2.
[0050] The compound 1-2 prepared in embodiment 2 is carried out nuclear magnetic characterization, and the characterization data of its proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum are as follows: 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ6.94(m,1H),6.87(m,1H),3.63(s,2H),2.16(s,3H). The chemical name of the compound is 1-(2,4,5-trifluorobenzene base)-2-propanone.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com