Rhodococcus gene editing method using phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase gene mutant as reverse selection marker
A phenylalanyl and gene editing technology, applied in the field of gene editing, can solve the problems of antibiotic resistance gene leakage, affecting cell traits, etc., and achieve the effect of efficient screening and high specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
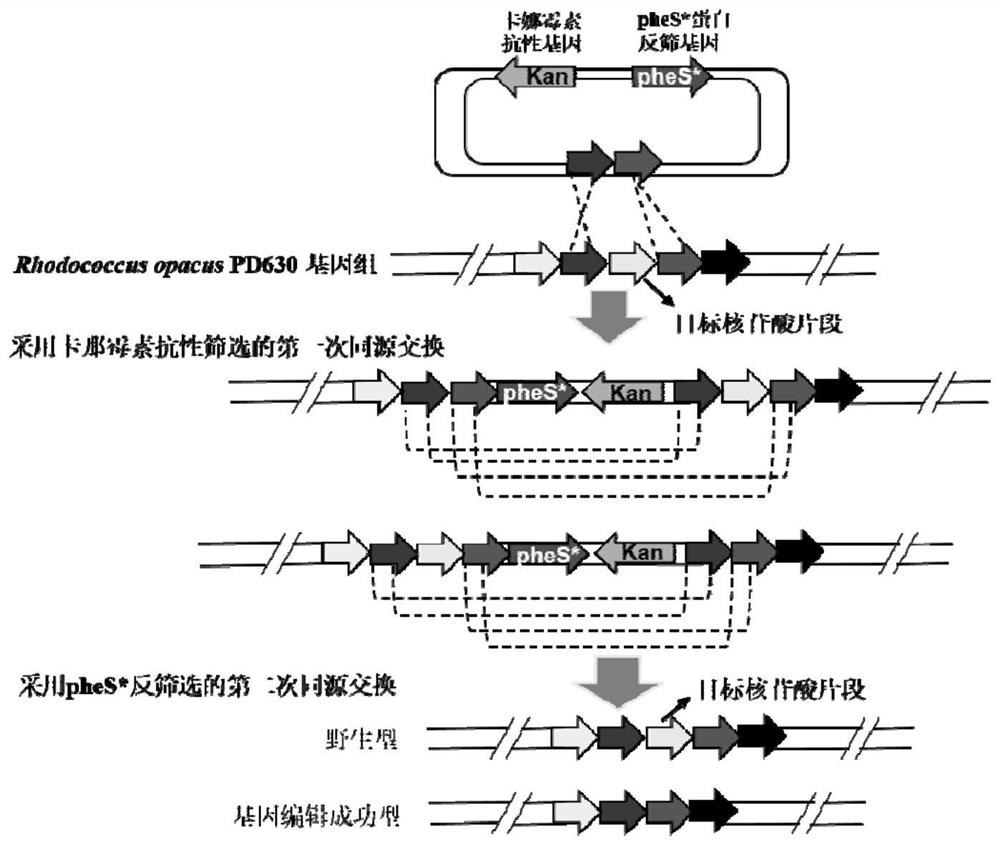
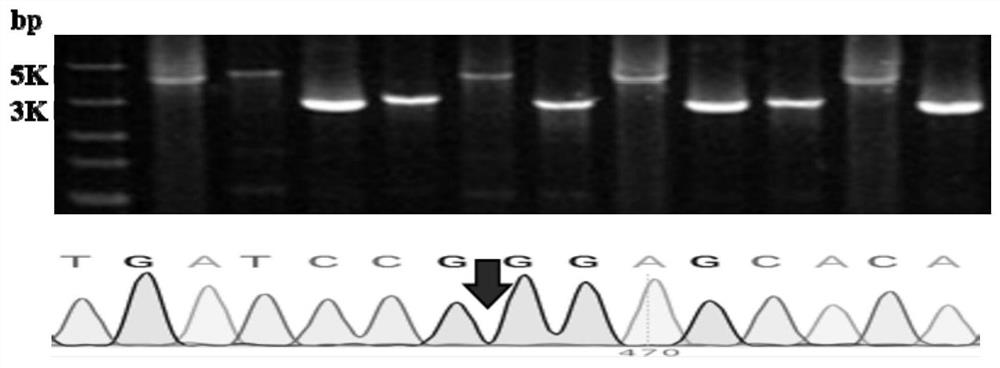
[0029] Example 1. Rhodococcus opacus Deletion of the mucofuroate cycloisomerase gene (GenBank:AHK33752.1) in PD630
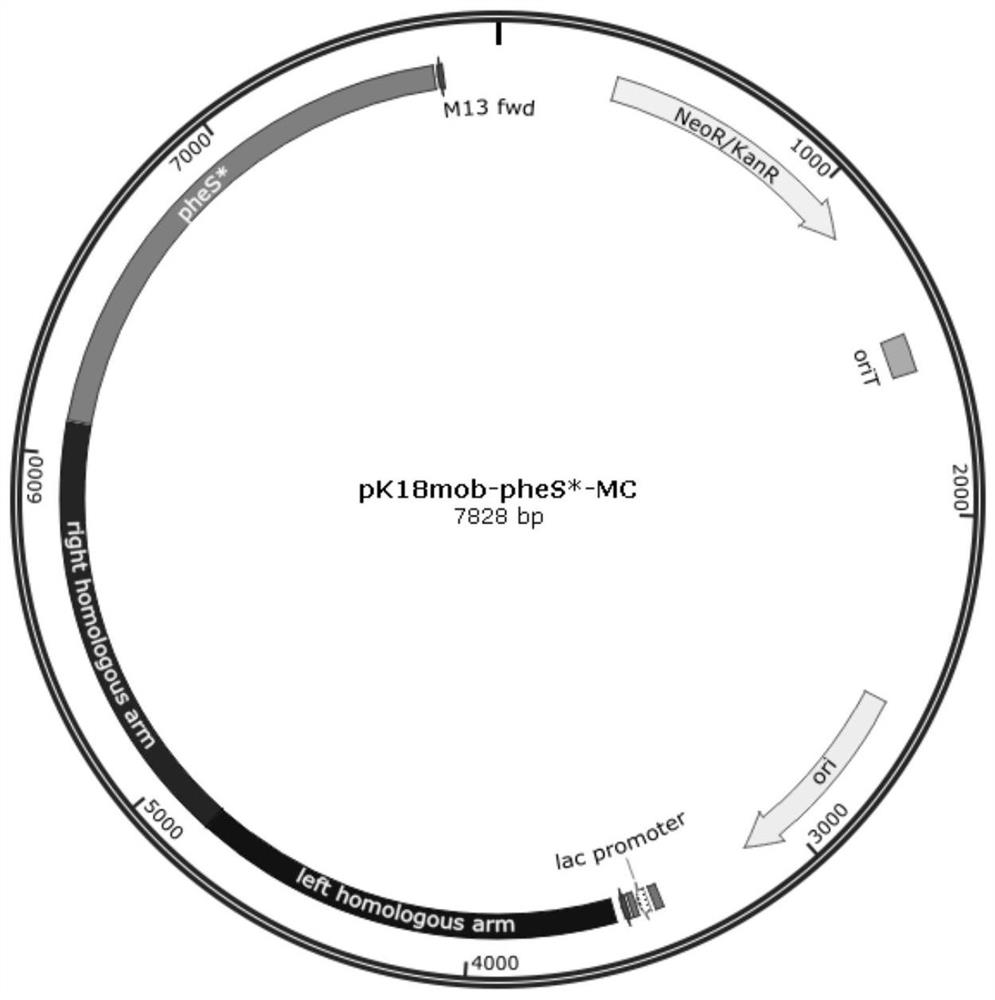
[0030] (1) Construction of pk18mob-pheS plasmid
[0031] extract R. opacus PD630 genome, and design specific primers to clone the nucleotide fragment containing phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase gene (AHK32253.1) and its own promoter, wherein the upstream primer is SEQ ID NO: 1: tacccggggatcctctagaTGCGGTCCTCGACAGCATCAGCG; downstream The primer is SEQ ID NO: 2: aacgacggccagtgccaagcttATTGCGCTACTCGCACGTCTGC, and the PCR reaction is carried out according to the following system:
[0032] 5×Reaction buffer 10.0 μL dNTPs (10 mM) 1.0 μL Upstream primer SEQ ID NO: 1 (10 μM) 1.0 μL Downstream primer SEQ ID NO: 2 (10 μM) 1.0 μL Rhodococcus opacus PD630 Genome
1.0 μL Taq enzyme (5 U / μL) 1.0 μL ddH 2 O
35.0 μL Overall system 50 μL
[0033] The reaction system was performed as follows: pre-denaturat...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Rhodococcus opacus Deletion of the catechol 2,3 dioxygenase gene in PD630 (GenBank: AHK27425.1)
[0047] (1) The construction of pk18mob-pheS* plasmid is the same as steps (1) and (2) in Example 1.
[0048] (2) Insert the nucleotide fragments on both sides of the catechol 2,3 dioxygenase gene locus into the pk18mob-pheS* anti-screening plasmid
[0049] 通过设计特异性引物:SEQ ID NO:11:acgaattcgagctcggtaccGGCCAACGGCGTGAAGCCGGC;SEQ ID NO:12:caggcccccacaccgaggacaactcGACACGGGACGCACCGTCGAAAGGGAC;SEQID NO:13:gtccctttcgacggtgcgtcccgtgtcGAGTTGTCCTCGGTGTGGGGGCCTG;SEQ ID NO:14:tgtcgaggaccgcatctagaGAGCGGGACGACCTCCTGCTGCG,通过PCR及上述引物获得邻苯二酚2,3 A nucleotide fragment of approximately 1000 bp upstream and downstream of the dioxygenase gene. The nucleotide fragments on both sides were ligated together by overlapping PCR method, and then the ligated nucleotide fragments were inserted into the pk18mob-pheS* plasmid using an assembly kit to obtain a suicide plasmid containing homology a...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Rhodococcus opacus Deletion of the protocatechuate 3,4 dioxygenase gene in PD630 (GenBank: AHK32653.1)
[0055] (1) The construction of pk18mob-pheS* plasmid is the same as steps (1) and (2) in Example 1.
[0056] (2) Insert the nucleotide fragments on both sides of the protocatechuate 3,4 dioxygenase gene locus into the pk18mob-pheS* counter-screening plasmid
[0057] 通过设计特异性引物:SEQ ID NO:17:acgaattcgagctcggtaccCGGCCCGACCCCGAGGATGC;SEQ ID NO:18:gcgcgacacctttctgggttgtgaccgaGGAAAAAGATCCTCACGTTCTCGATGTGAACAGTC;SEQ ID NO:19:gactgttcacatcgagaacgtgaggatctttttccTCGGTCACAACCCAGAAAGGTGTCGCGC;SEQ ID NO:20:gcctgcaggtcgactctagaGCGCGACGGCTCCGCCGG,通过PCR及上述引物获得原儿茶酸3, 4 Nucleotide fragments of about 1000 bp upstream and downstream of the dioxygenase gene. The upstream and downstream fragments of the protocatechuate 3,4 dioxygenase gene were ligated together by overlapping PCR method, and then the ligated nucleotide fragments were inserted into the pk18mob-pheS* plasmid us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com