Method for preparing heart valve endothelial cells by inducing pluripotent stem cell differentiation, and application of heart valve endothelial cells
A technology for pluripotent stem cells and heart valve, applied in the field of stem cell differentiation, can solve the problems of cumbersome process, difficult to guarantee, complicated operation, etc., and achieve the effect of simple differentiation operation, short time-consuming and high differentiation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] The method for inducing the differentiation of human embryonic stem cell line H9 to prepare heart valve endothelial cells comprises the following steps:
[0102] 1) The human embryonic stem cell line H9 was tiled and planted in a matrigel-coated culture dish to make it adhere to the wall; wherein, the tile density of pluripotent stem cells was 30,000 / cm 2 ; Human embryonic stem cell line H9 comes from Wicell Laboratory in the United States;
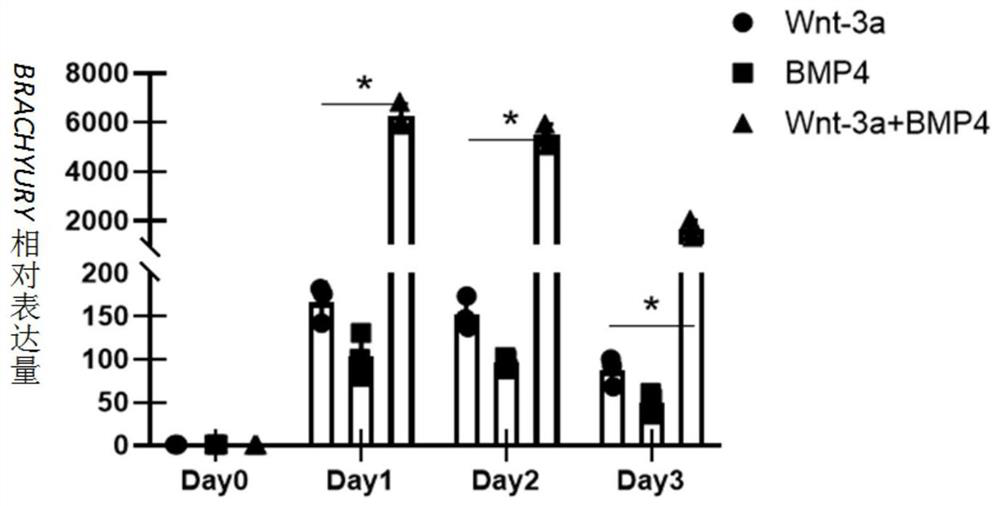
[0103] 2) The pluripotent stem cells were placed in the differentiation medium Essential 6 (Gibco Company) containing Wnt3a and bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) for 1 day, and then placed in the differentiation medium containing epidermal growth factor (bFGF) and bone morphogenetic protein 4(BMP4) Differentiation medium Essential 6 was cultured for 2 days to obtain cardiac mesoderm cells (LPM); wherein, in the differentiation medium Essential 6 containing Wnt3a and BMP4, the final concentration of Wnt3a was 25ng / mL and the conce...
Embodiment 2
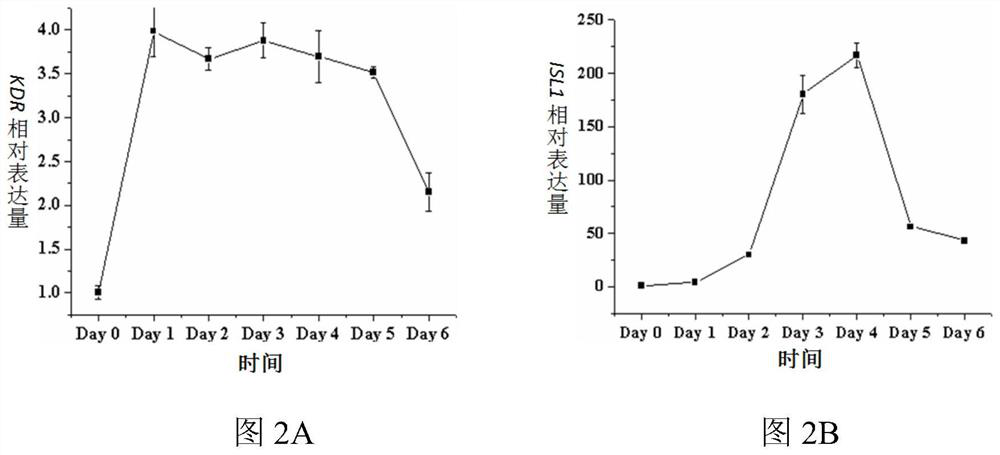
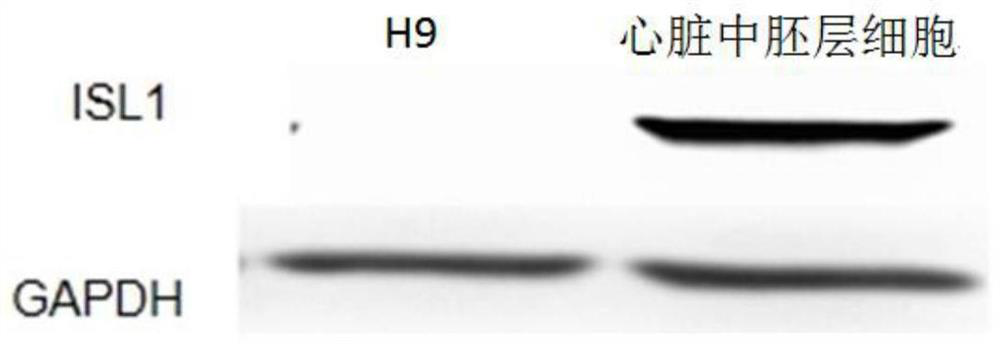
[0149] Morphological and molecular verification of H9-derived heart valve endothelial cells in the above-mentioned Example 1
[0150] 1. Cells and culture conditions
[0151] Heart valve endothelial cells (VEL) derived from H9 obtained in Example 1;
[0152] Umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD, USA);
[0153] Human aortic endothelial cell line (HAEC) was purchased from Shanghai Cell Bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences;
[0154] Isolated human heart valve endothelial cells (VEC), from Wuhan Union Hospital;
[0155] Isolation of human heart valve endothelial cells Culture conditions: 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cell incubator, EGM-2BulletKit culture, EGM-2BulletKit purchased from Lonza Company of the United States.
[0156] 2. Experimental method
[0157] 2.1 Adhesive isolated human heart valve endothelial cells and H9-derived heart valve endothelial cells were photographed and recorded using a microscope.
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0173] Verification of the function of the H9-derived heart valve endothelial cells in the above example 1
[0174] 1. Materials
[0175] Matrigel and all culture dishes were purchased from Corning Company of the United States; Alexa Fluor 594AcLDL fluorescent dye of acetylated low-density lipoprotein was purchased from Invitrogen Company of the United States; nuclear dye DAPI was purchased from Sigma Company of the United States; normal saline DPBS was purchased from BI Company; EBM-2BulletKit was purchased from American Lonza Company; trypsin was purchased from BI Company.
[0176] 2. Cells
[0177] Human embryonic stem cell line H9, from Wicell Laboratory, USA; heart valve endothelial cells prepared in Example 1.
[0178] 3. Experimental method
[0179] 3.1 In vitro low-density lipoprotein uptake test method:
[0180] H9-derived heart valve endothelial cells were cultured to 30-40% confluency with H9 (as a negative control). After cells were serum starved for 12 hours,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com