Grape hard branch grafting method
A hard branch grafting and grape technology, applied in the field of grafting, can solve the problems of long survival rate breeding cycle, unsuitable environmental conditions, poor survival rate of grafted seedlings, etc., and achieve the effect of improving grafting efficiency, reducing planting costs, and firm grafting interface
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
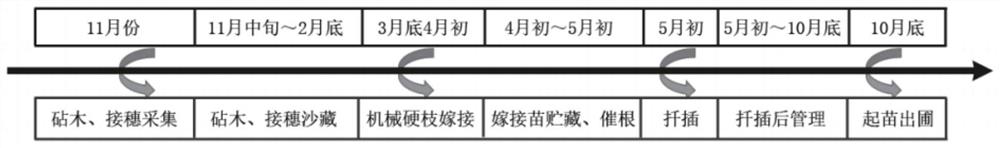
[0045] 1 rootstock and scion preparation
[0046]Rootstock collection and storage: Rootstocks are generally collected during winter pruning (November-December) of the previous year. The branches are required to be fresh, fully mature, full of buds, free from pests, mechanical damage, and frost damage. Rootstock diameter is generally 0.7 ~ 1.1cm. The upper part of the terminal bud should be cut horizontally to leave more than 3cm, and the lower part should be cut obliquely under the bud, and all the bud eyes of the branches should be cut off to prevent the germination of rootstock buds from affecting the survival rate of grafting. The length is about 30cm. bundle. The cut rootstocks are to be stored in sand. Sand storage requires filling in a ditch about 50cm deep. First, spread 5-10cm thick wet sand or fine sand on the bottom of the ditch. For each bundle of rootstock branches, a layer of sand is buried. , to ensure that each branch can be in contact with wet sand. Rootstoc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com