Ceramic bonding area surface modification method suitable for ceramic/metal connection
A technology of metal connection and ceramic bonding, applied in the field of ceramic metal connection, to achieve the effect of broadening the selection range, enhancing bonding, and enhancing surface energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] This embodiment is carried out by adopting the above-mentioned scheme 2, including: step 1, magnetron sputtering coating, step 2, vacuum sintering and step 3, titanium trihydride sintering, which are three stages;
[0047] Step 1, magnetron sputtering coating, through DC magnetron sputtering technology, the metal target (that is, the material of magnetron sputtering coating) selects NiTi35 alloy, its nominal melting point is 1141 ° C, and the target is installed in the magnetron sputtering equipment On the cathode, in argon vacuum (vacuum degree not greater than 10 -3 Pa) and direct current and room temperature (25°C), the target atoms are sputtered onto the surface of the SiC ceramic sample, and the film thickness is controlled at 100nm;
[0048] Step 2, vacuum sintering, using a -3 Pa) in the sintering furnace of the component NiTi alloy, which is 90% of the melting point of the NiTi alloy (calculated according to the thermodynamic temperature scale K) and kept at 10...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The process of this embodiment is the same as that of embodiment 2, except that no titanium sponge is placed during the vacuum sintering in step two and the titanium hydride sintering in step three.
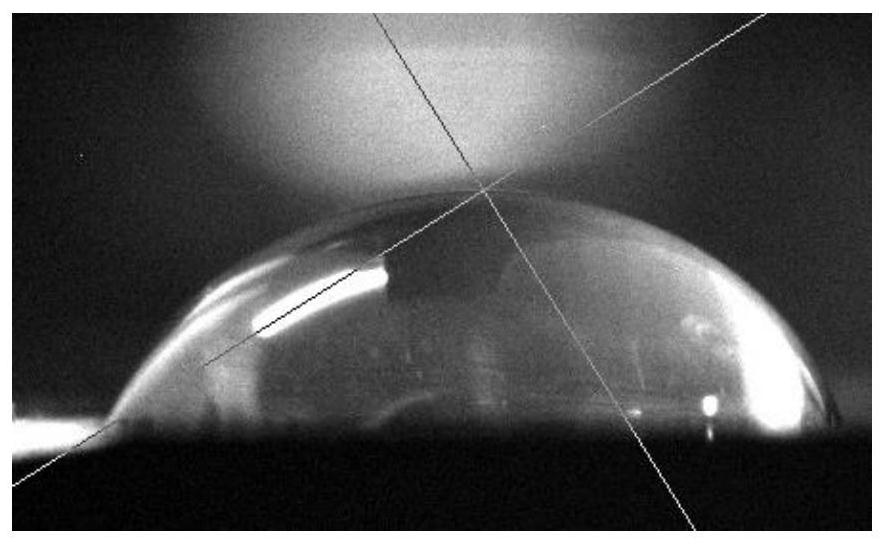
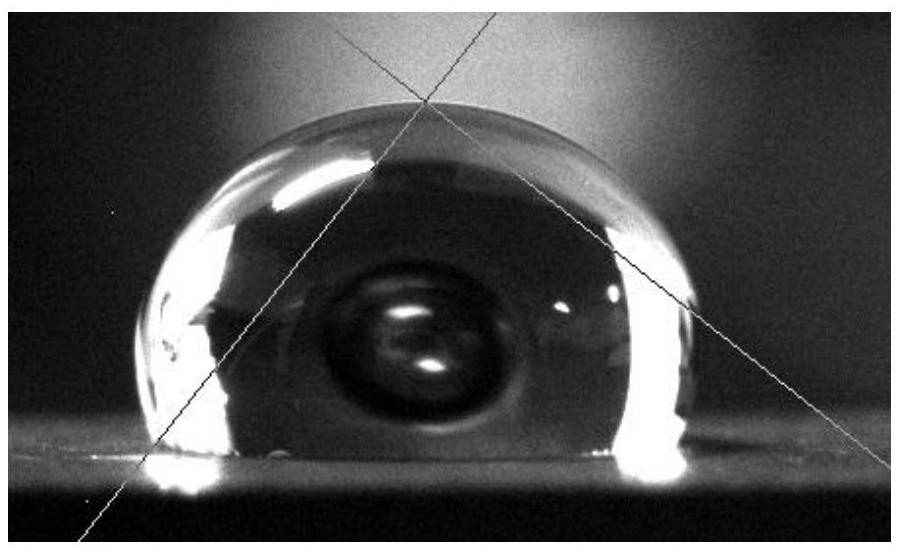
[0052] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the wettability of the surface of SiC ceramic samples to pure water is poor, and the surface energy of SiC ceramic samples is low.
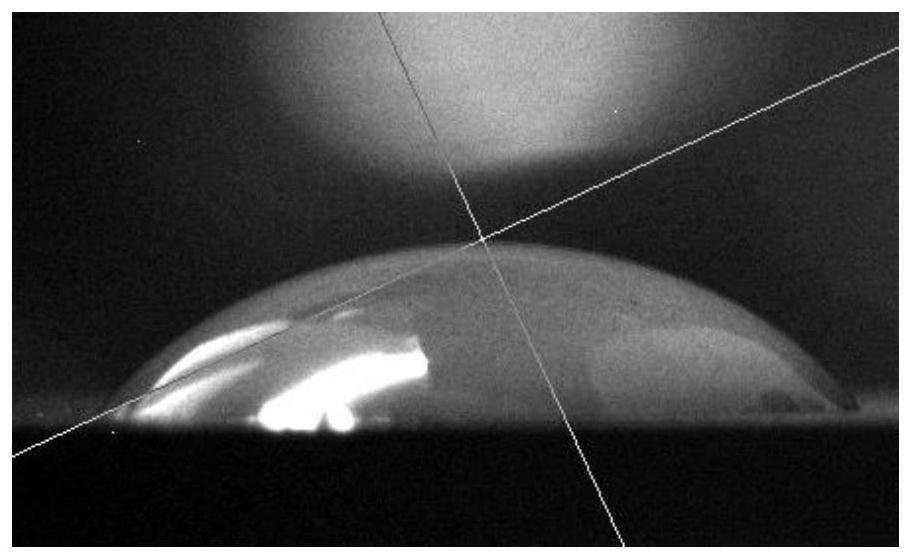
[0053] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that after the magnetron sputtering coating, due to the existence of the NiTi coating, the surface energy of the NiTi coating is lower, and the wettability to pure water is significantly reduced.
[0054] As can be seen from Figure 3(a) and Figure 3(b), after vacuum sintering, in Example 1, due to the addition of titanium sponge for protection, the surface oxidation of the NiTi coating was prevented, and the NiTi coating was crystallized at the same time. The surface energy of the NiTi coating is greatly improved, and the wettability with water is signif...
Embodiment 3
[0057] This embodiment is carried out using the above scheme 1, including the two stages of step 1 magnetron sputtering coating and step 2 vacuum sintering;
[0058] Step 1, magnetron sputtering coating, through DC magnetron sputtering technology, the metal target (that is, the material of magnetron sputtering coating) selects NiTi35 alloy, its nominal melting point is 1141 ° C, and the target is installed in the magnetron sputtering equipment On the cathode, in argon vacuum (vacuum degree not greater than 10 -3 Pa) and direct current and room temperature (25°C), the target atoms are sputtered onto the surface of the SiC ceramic sample, and the film thickness is controlled at 300nm;
[0059] Step 2, titanium hydride sintering, place the SiC ceramic sample in a corundum crucible, and use titanium hydride powder with a particle size of 38-250 microns to fill the gap between the sample and the corundum crucible until the relative density of the powder is 60%. The corundum crucib...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com