Method for removing solid impurities of catalytic slurry oil through low-temperature coalescence
A technology for catalyzing oil slurry and solid impurities, applied in the field of petroleum refining and production, can solve the problems of concentrated liquid hazardous waste, poor separation effect, short operation cycle, etc., and achieve the effect of easy removal, fast speed and moderate process conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
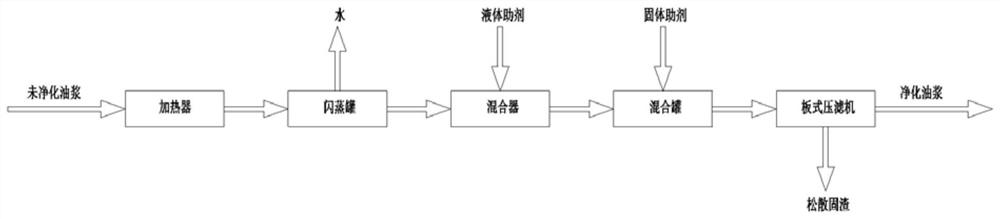
[0038] A method for removing solid impurities from catalytic oil slurry by low-temperature coalescence, comprising the following steps:
[0039] (1) Heat treatment: use a heat exchanger to heat the catalytic oil slurry to 170°C;
[0040] (2) Dehydration treatment: Use a flash tank under the pressure of -0.03MPa to remove trace water in the catalytic oil slurry;
[0041] (3) Mixing by adding liquid additives: transfer the catalytic oil slurry to the mixer, and add 0.1% liquid additives into the pipeline, mix through the mixer, so that the liquid additives can be evenly dispersed in the catalytic oil slurry, and wrapped in tiny The colloid and asphaltene around the catalyst solid particles dissolve and diffuse, making the catalyst solid particles reveal polarity;
[0042] (4) Adding solid additives for mixing: Add 0.8% solid additives into the mixing tank, and carry out moderate stirring, and mix for 15 minutes, so that the polar catalyst solid particles and the solid additives...
Embodiment 2
[0052] A method for removing solid impurities from catalytic oil slurry by low-temperature coalescence, comprising the following steps:
[0053] (1) Heat treatment: use a heat exchanger to heat the catalytic oil slurry to 180°C;
[0054] (2) Dehydration treatment: use a flash tank to remove trace water in the catalytic oil slurry under slight negative pressure;
[0055] (3) Mixing by adding liquid additives: transfer the catalytic oil slurry to the mixer, and add 0.3% liquid additives into the pipeline, mix through the mixer, so that the liquid additives can be evenly dispersed in the catalytic oil slurry, and wrapped in tiny The colloid and asphaltene around the catalyst solid particles dissolve and diffuse, making the catalyst solid particles reveal polarity;
[0056] (4) Mixing with solid additives: add 3% solid additives into the mixing tank, and stir moderately, mix for 30 minutes, so that the polar catalyst solid particles and solid additives collide and coalesce into l...
Embodiment 3
[0065] The difference between this embodiment 3 and embodiment 2 is only:
[0066] In step (1), the heating temperature is 170°C;
[0067] In step (3), the addition amount of the liquid auxiliary agent is 0.2%, and the weight proportions of the dispersant, oil repellant, and diluent in the liquid auxiliary agent are respectively 20%, 20%, and 60%.
[0068] In step (4), the addition amount of the solid auxiliary agent is 1.5%, and the weight ratios of the nucleating agent, particle trapping agent and filter aid in the solid auxiliary agent are respectively 23%, 37%, and 40%.
[0069] In step (4), the stirring and mixing time is 20 minutes, and the ejection velocity of the jetting fluid is 20 m / s.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Ash content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com