Film type resistance strain gauge used in high-pressure hydrogen sulfide environment
A resistance strain gauge, thin-film technology, applied in the field of sensors, can solve problems affecting measurement accuracy and stability, strain gauge hysteresis and creep, adhesive failure, etc., to avoid strain transmission errors and pressure effects, and eliminate zero drift and creep, to achieve the effect of temperature self-compensation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
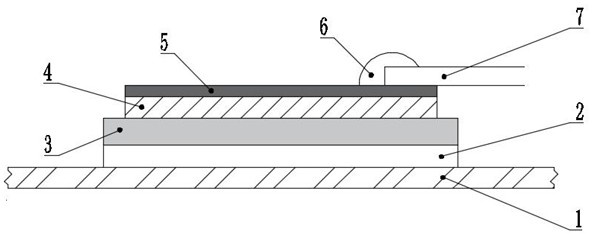
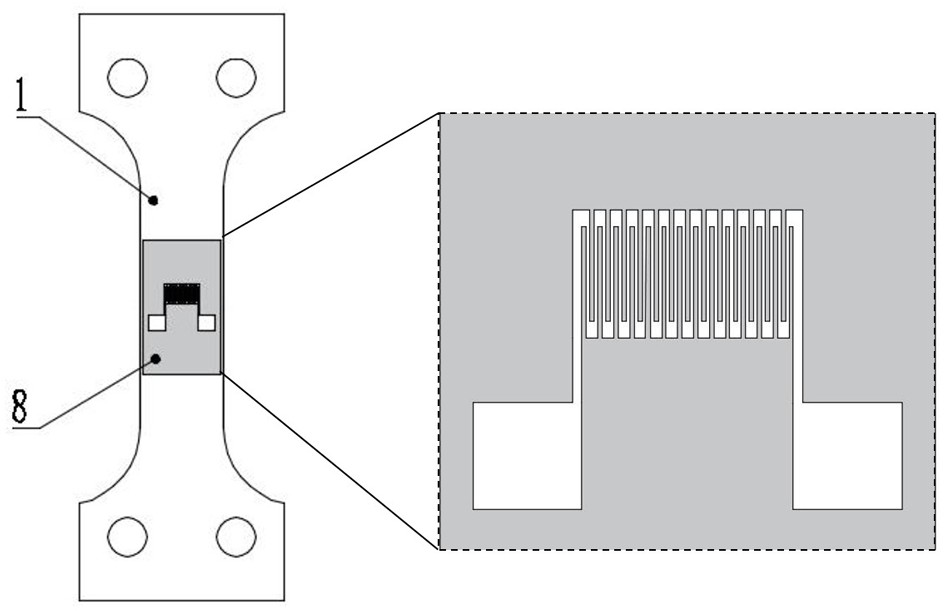
[0041] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, a thin-film resistance strain gauge used in a high-pressure hydrogen sulfide environment includes a substrate 1, a transition buffer layer 2 arranged on the upper surface of the substrate, an insulating layer 3 arranged on the upper surface of the transition buffer layer, and a The functional layer 4 on the upper surface of the insulating layer, the protective layer 5 on the upper surface of the functional layer; the base is made of 316L stainless steel, the transition buffer layer is Cr film, and the insulating layer is AlN film. The functional layer is a FeNi alloy film. Two lead wires 7 are connected to the protective layer 5 through solder 6;
[0042] A preparation method of a thin-film resistance strain gauge, comprising the steps of:
[0043] (3-1) Place the pretreated substrate in the sputtering chamber of the magnetron sputtering apparatus for fixing and finishing;
[0044] The upper surface of the substrate is polished...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0066] The Cr film is used as a transitional buffer layer with a thickness of 300nm.
[0067] Vacuum the sputtering chamber to 5.0×10 -4 Pa, the substrate temperature of the sample turret is raised to 100°C by heating the substrate to transfer heat, adjust the bias voltage to 80V, feed argon into the sputtering chamber, control the argon flow rate to 25 sccm, and raise the air pressure in the sputtering chamber to 1.8Pa, raise the voltage of A target seat to 350V for glow discharge, ionize the argon gas, generate argon gas ions, and argon gas ions bombard the Cr target material, causing sputtering of the target material; adjust the working pressure in the sputtering chamber to 0.15Pa , carry out pre-sputtering for 10 min; after the pre-sputtering process, after the voltage and current of A target base are stabilized, control the rotation speed of the sample turntable at 2r / min, adjust the voltage and current...
Embodiment 3
[0070] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0071] Sputtering an AlN film on the upper surface of the Cr film with a thickness of 400nm as an AlN insulating layer;
[0072]Adjust the temperature controller of the sputtering instrument so that the substrate temperature of the sample turntable rises to 300°C, and the flow rate of nitrogen gas is 25 sccm, so that Ar:N 2 1:1.2, the air pressure in the sputtering chamber is 0.5Pa during the sputtering process, the power of the C target seat is 150W during the sputtering process, and the continuous sputtering is 120min, forming an AlN film on the surface of the sputtered Cr film;
[0073] sputtering grid-shaped FeNi film on the mask with a thickness of 1000nm as a functional layer;
[0074] The sputtering parameters in the process of sputtering FeNi film are: vacuumize the sputtering chamber to 1.0×10 -4 Pa, the substrate temperature is heated to 200°C, the flow rate of argon gas is 22sccm, the air pressur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com