Application of hypoxanthine nucleotide in preparation of anti-infective drugs
A hypoxanthine nucleotide and anti-infection technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory effect, and achieve the effect of reducing bacterial drug resistance and improving anti-infection effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 sample preparation
[0033]Pick a single bacterial colony and inoculate it in 5mL LB medium at 37°C (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, and sexual streptococcus or cultured at 30°C (Aeromonas hydrophila, Edwardsiella tarda, Vibrio alginolyticus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus) at 200rpm for 16 hours; Or cultivate to OD at 30℃200rpm 600 1.0, take an appropriate amount of bacterial liquid at 8000rpm, centrifuge for 5min to collect the bacterial cells, remove the supernatant and wash the bacterial cells with an equal volume of 0.85% saline for 3 times, suspend in 1×M9 (containing 10mM sodium acetate, 2mM MgSO 4 , 0.1 mM CaCl 2 ), and adjust the concentration of the bacterium solution to 10 in the M9 medium 6 CFU / mL (diluted 1000 times); aliquot into 5mL test tubes for later use.
Embodiment 2
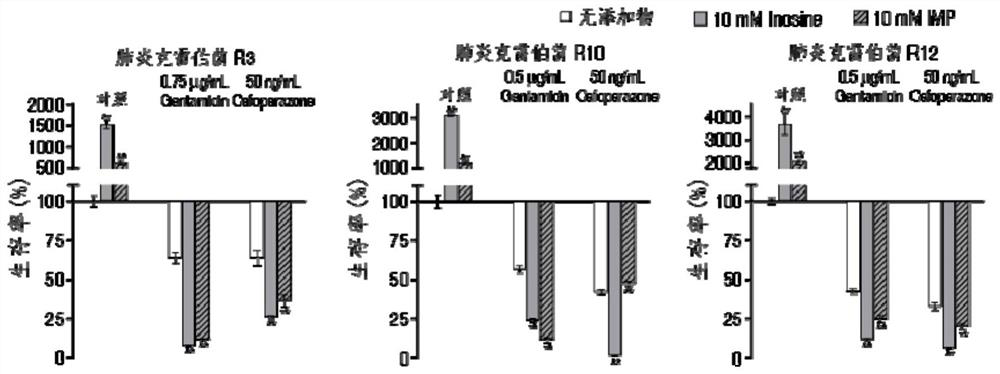
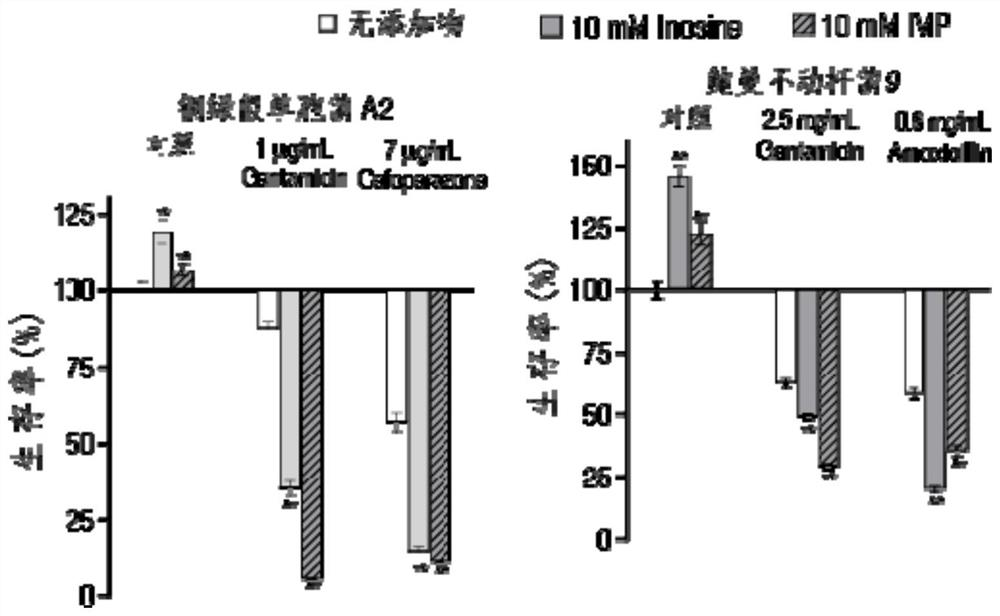
[0034] Embodiment 2 xanthine nucleotides and inosine improve bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics effect determination
[0035] Every kind of bacterial sample prepared in embodiment 1 is divided into 3 groups, 2 experimental groups add 10mM inosine nucleotide (IMP) and inosine (Inosine) respectively, another control group adds equal volume normal saline; Add corresponding antibiotics to all test tubes, three biological repetitions; incubate in a shaker at 37°C 200rpm for 6 hours, then take 100 μL and use serial dilution method, take 10 μL respectively for plate counting, and calculate bacterial CFU / mL (colony forming unit Bacterial colony number at 20-200 data can be used for statistical analysis; Bacterial survival rate (percent survival) is the bacterium CFU / the bacterium quantity that only adds antibiotic × 100%.
[0036] See results Figure 1~2 , it can be seen from the figure that for Klebsiella pneumoniae R10, inosine can increase its sensitivity to gentamicin by about...
Embodiment 3
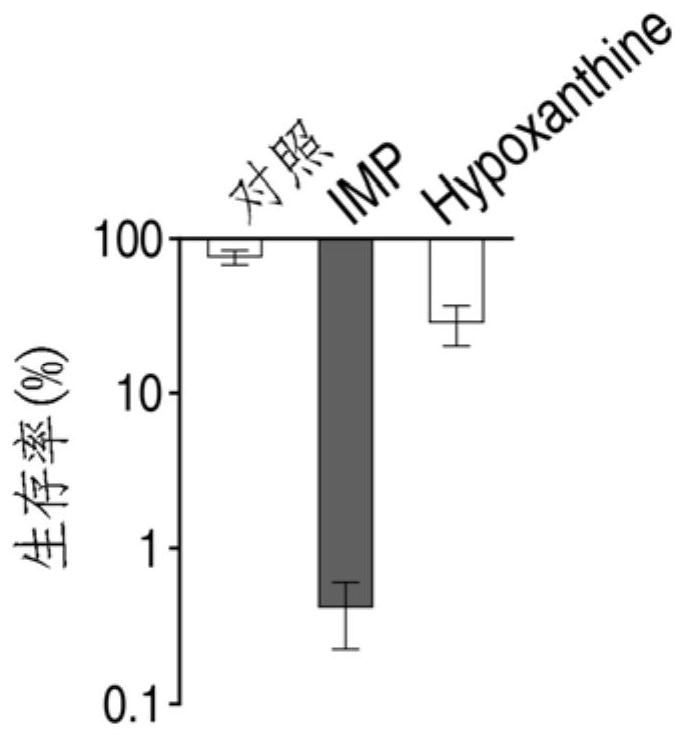
[0039] Example 3 hypoxanthine nucleotides can improve the sensitivity of Escherichia coli to ampicillin
[0040] The prepared Escherichia coli K12 samples were divided into 3 groups, 7.5mM inosine nucleotide (IMP) and hypoxanthine (Hypoxanthine) were added to the 2 experimental groups, and an equal volume of normal saline was added to the control group, each Add 100 μg / ml ampicillin to all test tubes, three biological repetitions; incubate in a 200 rpm shaker at 37°C for 6 hours, then take 100 μL and use serial dilution method, take 10 μL respectively for plate counting, and calculate the bacterial CFU / mL (colony formation units / ml). The data with the number of bacterial colonies in the range of 20-200 can be used for statistical analysis. Bacterial survival rate (percent survival) is bacterial CFU after hypoxanthine compound and / or antibiotic treatment / initial bacterial number×100%.
[0041] See results image 3 , as can be seen from the figure, the survival rate of bacter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com