Insulating layer structure of thin film sensor based on metal substrate
A thin-film sensor, metal base layer technology, used in multilayer circuit manufacturing, cleaning/polishing of conductive patterns, printed circuits connected to non-printed electrical components, etc., can solve insulation failure, prone to pinholes, cleanliness The problem is not high, to achieve the effect of simple structure, solving short circuit, increasing time and cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
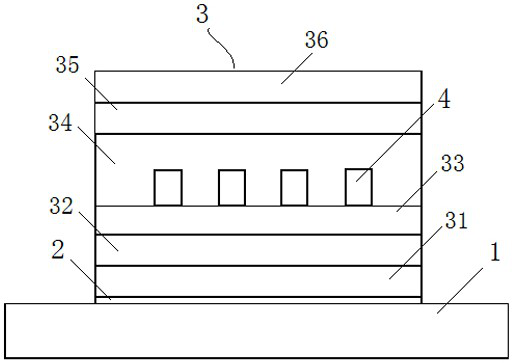
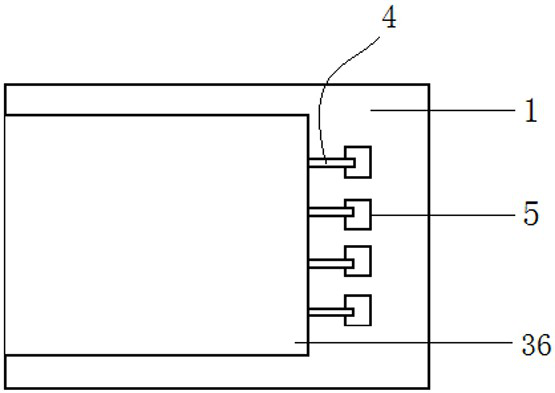
[0027] An insulating layer structure of a thin film sensor based on a metal substrate, comprising a metal substrate layer 1, an adhesive layer 2 arranged on the metal substrate layer, an insulating layer 3 arranged on the adhesive layer, and a sensor arranged on the insulating layer 3 The circuit layer 4, the insulating layer 3 is formed by layer-by-layer deposition of aluminum oxide by different processes.
Embodiment 2
[0029] As a preferred design, the bonding layer 2 is a metal titanium layer with a thickness of 5-50 nm deposited on the metal substrate.
[0030] The insulating layer 3 is composed of three layers of aluminum oxide deposited layer by layer.
[0031] The first layer 31 of the insulating layer 3 is a layer of aluminum oxide with a thickness of 0.2-5 um deposited on the titanium metal layer by electron beam evaporation.
[0032] The second layer 32 of the insulating layer 3 is a layer of aluminum oxide with a thickness of 10-500 nm deposited on the first insulating layer 31 by atomic layer deposition.
[0033] The third layer 33 of the insulating layer 3 is a layer of aluminum oxide with a thickness of 0.2-5 um deposited on the second insulating layer 32 by electron beam evaporation.
Embodiment 3
[0035] As a preferred design, a protective layer may also be provided on the insulating layer 3 . The first protective layer 34 is a layer of aluminum oxide with a thickness of 0.2-5 um deposited on the third insulating layer 33 by electron beam evaporation, and the first protective layer does not cover the pad 5 of the sensor circuit layer.
[0036] The function of the first protective layer 34 is to protect the circuit layer of the sensor against external damage such as scratches and abrasions, and at the same time have a certain insulation capacity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com