Oxidoreductase GliT and application thereof in resisting mycotoxins
A technology of mycotoxins and reductases, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of unclear harm to human body, animals and plants, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1 Obtaining of novel oxidoreductase GliT gene sequence
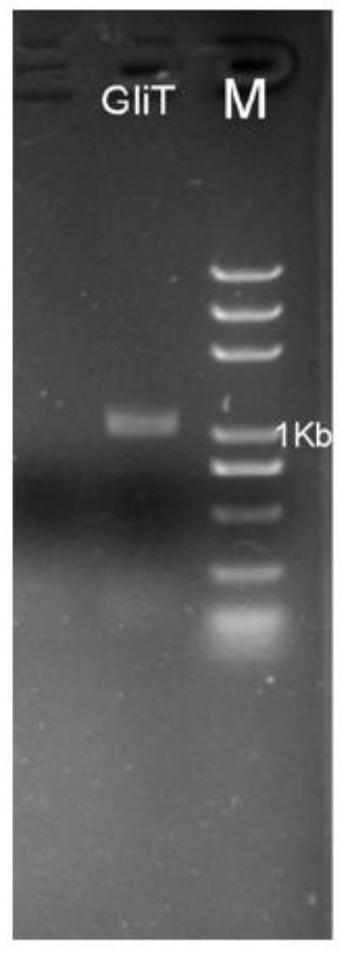
[0028] Amplification of the gene GliT: inoculate the deep-sea fungus Geosmithia pallida FS140 on the YPD medium plate, culture at 37°C for 72 hours, pick fresh mycelium, use the fungal RNA extraction kit to extract RNA, and then use the All-in-one RTMaster cDNA was obtained by reverse transcription with Kit. According to the transcriptome sequencing results, the GliT sequence of the gene encoding oxidoreductase was predicted, and the upstream and downstream primers GliT-F and GliT-R were designed. The primer sequences were GliT-F: 5'-ATGTCCATCGGAAAACTTCTCGC-3'; -3', using the cDNA library as template amplification to obtain the PCR product ( figure 1 ). The product was recovered and cloned by TA with pEASY-T1 kit, transformed into Escherichia coli competent cells, spread on the ampicillin resistance plate to screen out positive clones, and used universal primers M13-F (5'-GTAAAACGACGGCCAGT-3') and M1...
Embodiment 2
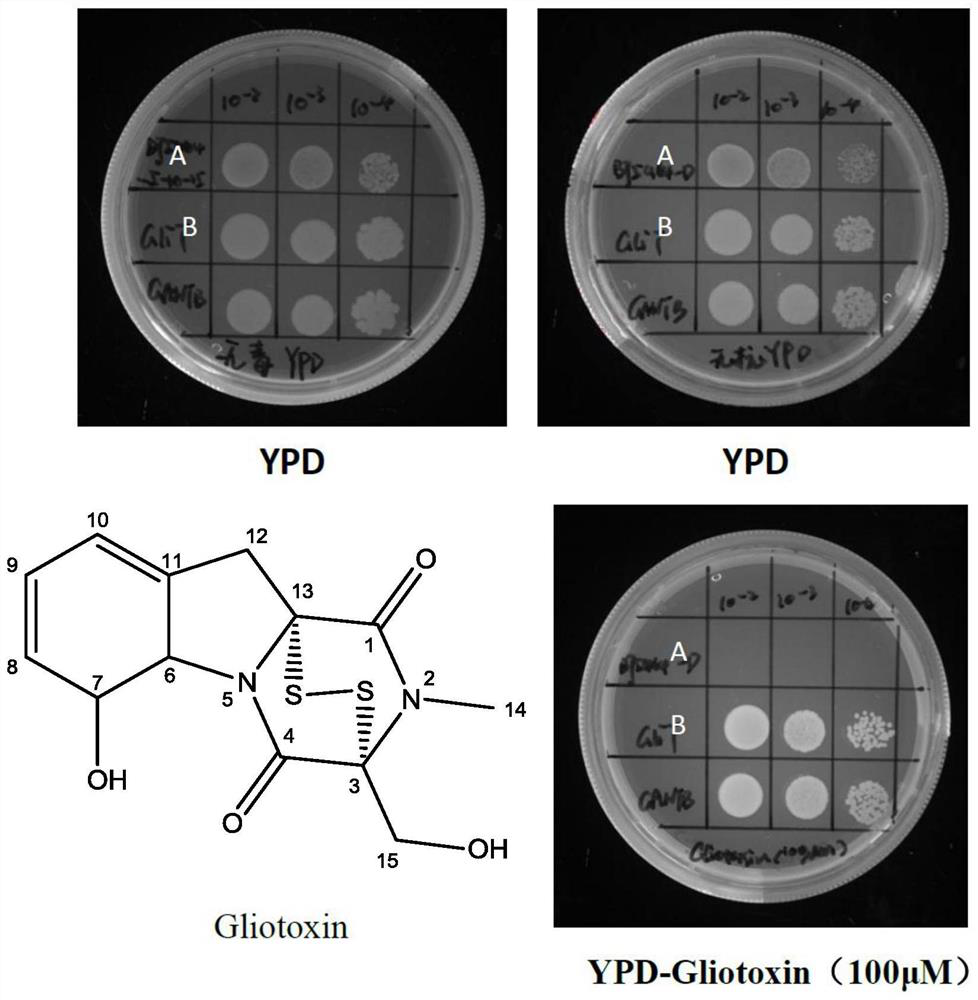
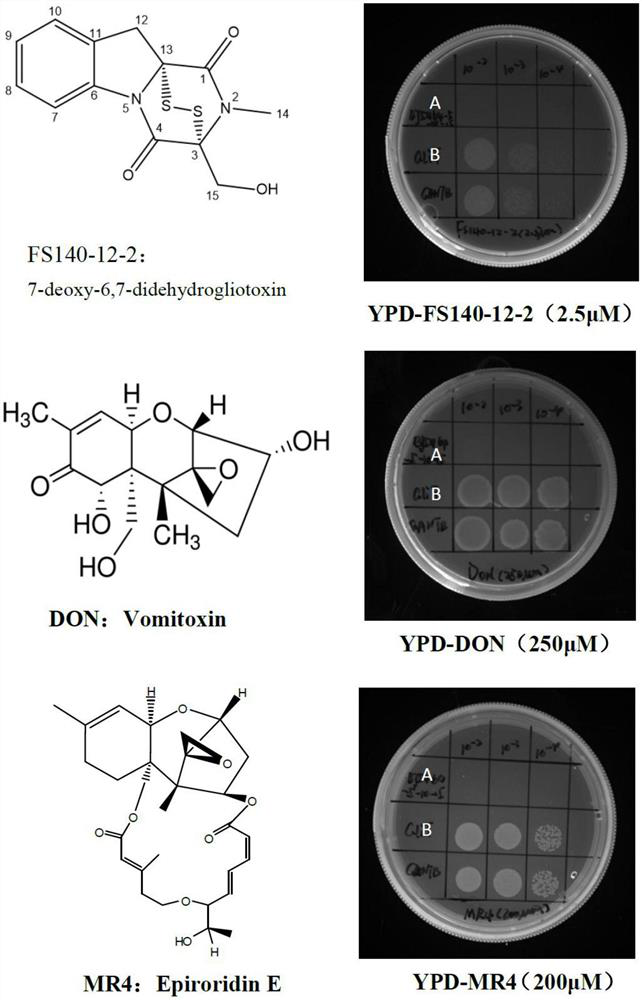
[0029] Example 2 Functional verification of novel oxidoreductase GliT
[0030] The new oxidoreductase gene GliT was inserted into the yeast vector YEp352-TEF1-CYC1 by homologous recombination (YEp352-TEF1-CYC1 is an early constructed plasmid, carrying a constitutive promoter TEF1 and a terminator CYC1, see the vector map image 3 A, known products in the prior art: Xiaodan Ouyang, Yaping Cha, Wen Li, Chaoyi Zhu, Muzi Zhu, Shuang Li, Min Zhuo, Shaobin Huang and Jianjun Li. Stepwise engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce(+)-valencene and its related sequiterpenes, RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 30171, DOI: 10.1039 / c9ra05558d). First design the upstream and downstream primers YEp352-GliT-F and YEp352-GliT-R for the amplification of gene GliT (SEQ ID NO.1), and the primer sequence is YEp352-GliT-F:5'- GCAATCTAATCTAAGTCTAGA ATGTCCATCGGAAAACTTCTCGC-3'; YEp352-GliT-R:5'- TACATGATGCGGCCCGTCGAC CTATGGCTCCCAATCAATCCCAAAT-3' (the underlined sequence is the homology arm fragment), usi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com