Biomedical porous Ti-Zn alloy and preparation method thereof
A biomedical, ti-zn technology, applied in medical science, tissue regeneration, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of no biological activity, bacterial infection, stress shielding, etc., to improve biological activity, promote growth and reproduction, and enhance mechanical properties. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The invention provides a method for preparing a biomedical porous Ti-Zn alloy, comprising the following steps:
[0031] S1: Mix titanium powder and zinc powder in a ratio of 90:10 by weight, and then place them in a stainless steel planetary ball mill for dry mixing. The controlled speed is 250r / min, and the time is 3h;
[0032] S2: Molding the dry-mixed powder in step S1 under a pressure of 800Mpa to form a compact;
[0033] S3: Put the compact and silicon carbide powder prepared in step S2 into a polycrystalline mullite fiber insulation barrel, and then place it in a microwave sintering furnace. It is 99.999% argon, the output power of the microwave sintering furnace is controlled to 2kW, the heating rate is 30°C / min, the sintering temperature is 800°C, and the sintering time is 20min. Microwave sintering is carried out, and biomedical porous Ti is obtained after cooling with the furnace. -Zn alloy.
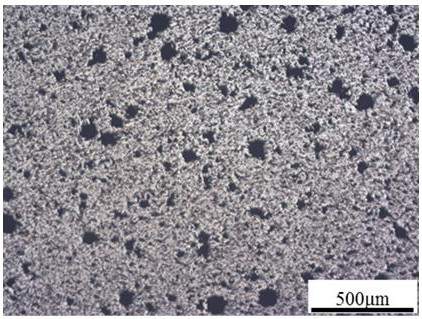
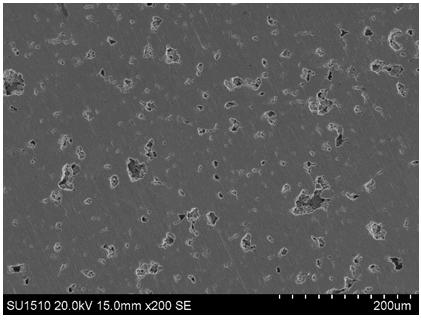
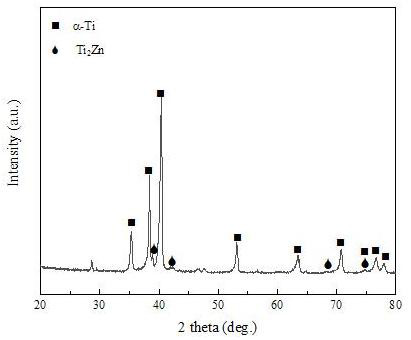
[0034] The porous Ti-Zn alloy prepared by the method provided in ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The invention provides a method for preparing a biomedical porous Ti-Zn alloy, comprising the following steps:
[0043] S1: Mix titanium powder and zinc powder in a ratio of 85:15 by weight and place them in a stainless steel planetary ball mill for dry mixing. The control speed is 220r / min, and the time is 3.5h;
[0044] S2: Molding the dry-mixed powder in step S1 under a pressure of 600Mpa to form a compact;
[0045] S3: Put the compact and silicon carbide powder prepared in step S2 into a polycrystalline mullite fiber insulation barrel, and then place it in a microwave sintering furnace. It is 99.999% argon, the output power of the microwave sintering furnace is controlled to 1.5kW, the heating rate is 25°C / min, the sintering temperature is 750°C, and the sintering time is 15min. Microwave sintering is carried out, and biomedical porous materials are obtained after cooling with the furnace. Ti-Zn alloy.
[0046] The porous Ti-Zn alloy prepared by the method provide...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The invention provides a method for preparing a biomedical porous Ti-Zn alloy, comprising the following steps:
[0049] S1: Mix titanium powder and zinc powder in a ratio of 75:25 by weight and place them in a stainless steel planetary ball mill for dry mixing. The control speed is 280r / min, and the time is 2.5h;
[0050] S2: Molding the powder after dry mixing in step S1 under a pressure of 900Mpa to form a compact;
[0051] S3: Put the compact and silicon carbide powder prepared in step S2 into a polycrystalline mullite fiber insulation barrel, and then place it in a microwave sintering furnace. It is 99.999% argon, the output power of the microwave sintering furnace is controlled to 2.5kW, the heating rate is 40°C / min, the sintering temperature is 900°C, and the sintering time is 25min. Microwave sintering is carried out, and biomedical porous materials are obtained after cooling with the furnace. Ti-Zn alloy.
[0052] The porous Ti-Zn alloy prepared by the method ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com