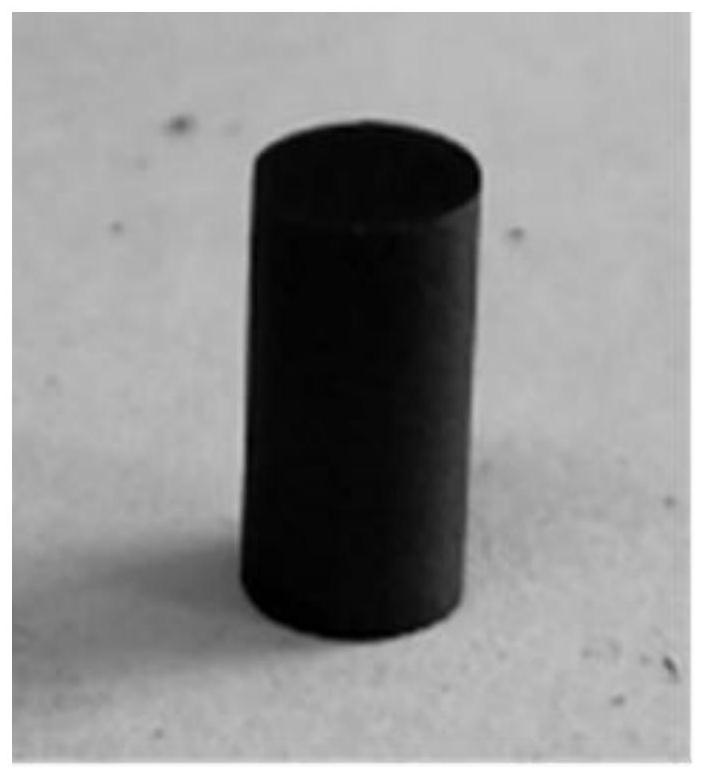
Low-temperature high-speed superplastic forming method for zirconium diboride-based superhigh-temperature ceramics
A technology of ultra-high temperature ceramics and zirconium diboride, which is applied in the forming field of ultra-high temperature ceramics, can solve the problems of inaccessible net forming of ultra-high temperature ceramics, and achieve the effect of improving the deformation ability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] 1) Configuration and grinding of raw materials
[0024] Weighing zirconium diboride and zirconium disilicide powders with a volume ratio of 70:30 and putting them into a ball mill jar, wherein the purity of zirconium diboride and zirconium disilicide is 99.9%, and the average particle size is 1-3 microns; Add large tungsten carbide balls and small tungsten carbide balls with a quantity ratio of 1:3 and keep the mass ratio of the mass of the grinding balls to the raw material powder at 10:1; Polyethylenimine anhydrous ethanol solution was used as the grinding medium; vacuum-filled with argon, and circulated for 3 times; finally, it was ball-milled on a planetary ball mill at a speed of 250 rpm for 48 hours to obtain a mixed slurry of nano-sized particles. The obtained mixed slurry was placed in a vacuum drying oven, vacuumed to 0 bar, vacuum-dried at a constant temperature of 30° C. for 5 hours and then cooled to room temperature for 3 hours to obtain a dry powder.
[0...
Embodiment 2
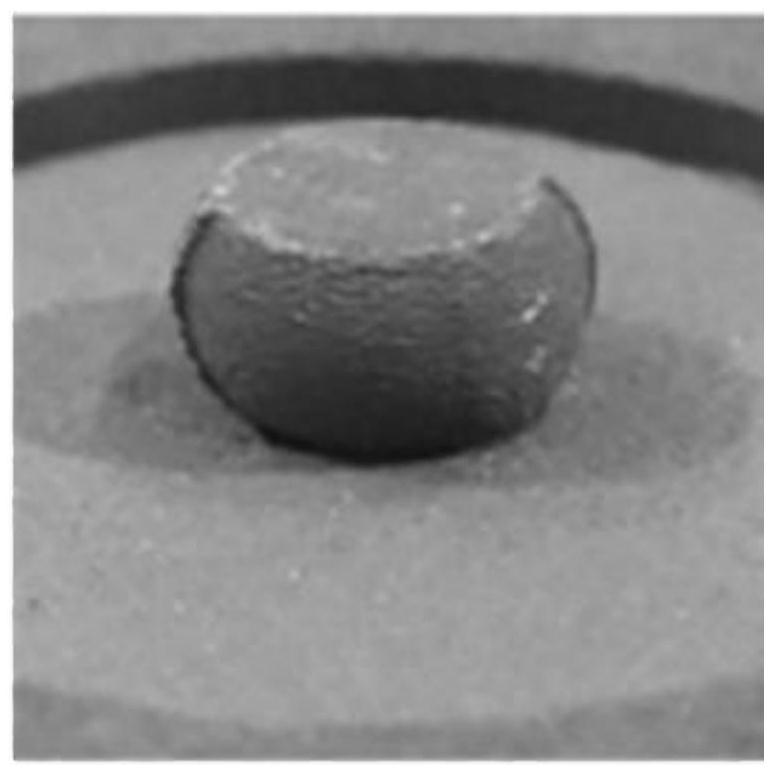
[0030] Similar to the steps in Example 1, the difference is that the volume ratio of zirconium diboride to zirconium disilicide is 80:20; sintering at 1400 ° C for 30 min; superplastic forming temperature is 1500 ° C, and the strain rate is 10 -4 , the applied load was 60MPa, and the forming time was 110min, resulting in a compression deformation of 65%. The surface of the product is smooth and without cracks.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Similar to the steps in Example 1, the difference is that the superplastic forming temperature is 1500 ° C, and the strain rate is 10 -3 , the applied load was 20MPa, and the forming time was 17min, resulting in a compression deformation of 101%. The surface of the product is smooth and without cracks.
[0033] In summary, a low-temperature, high-speed superplastic forming method for zirconium diboride-based ultra-high temperature ceramics introduces an appropriate amount of disilicide inside zirconium diboride to change the grain boundary morphology of zirconium diboride, thereby greatly improving The superplastic deformation ability of ultra-high temperature ceramics. enabling it to operate at higher initial strain rates (10 -4 -10 -1 the s -1), lower temperature (1300-1600°C), and lower stress (20-60MPa), in a shorter time (5-120min) to achieve more than 100% deformation and no cracks, for The near net shape process production of ultra-high temperature ceramic c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com