Method for selectively removing host nucleic acid in liquid biological sample
A biological sample and selective technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the efficiency of nucleic acid extraction of pathogenic microorganisms, reducing detection sensitivity and accuracy, crowding out the amount of sequencing data, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] A method for selectively removing host nucleic acid from a liquid biological sample, the method comprising the steps of:
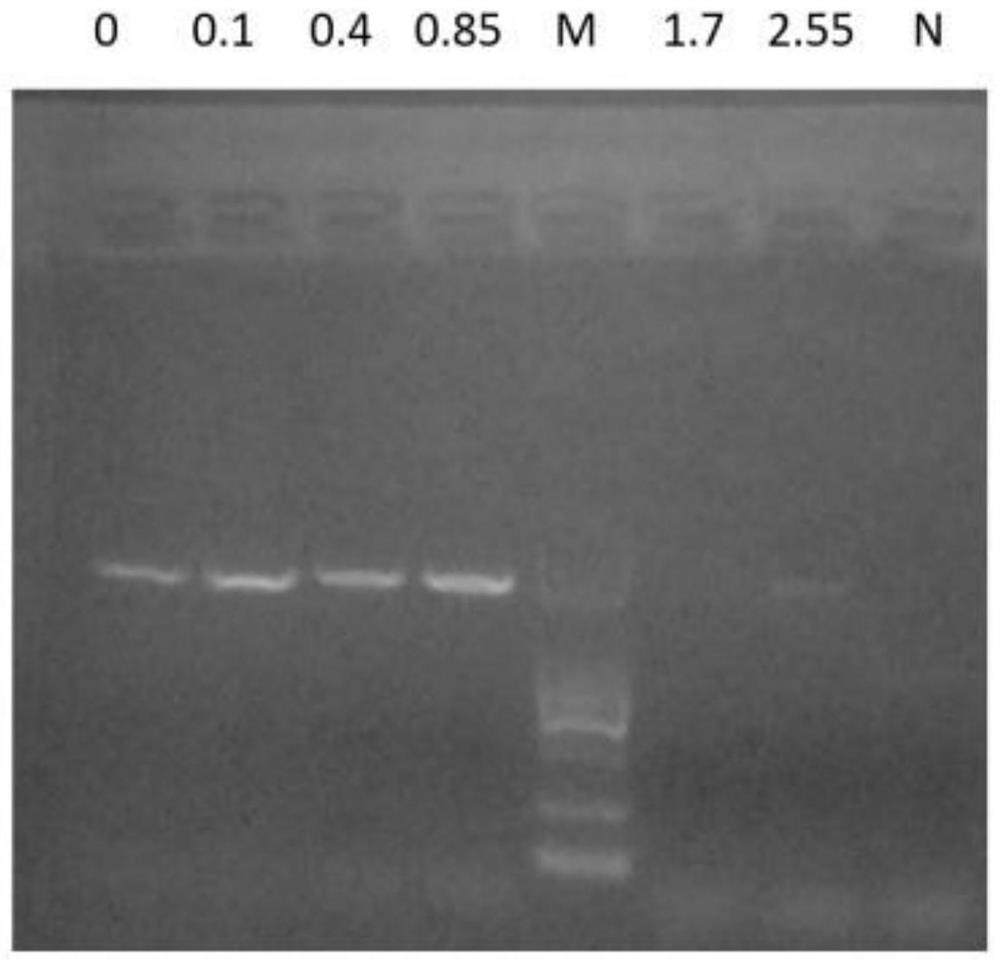
[0069] (1) Mix the liquid biological sample and the saponin solution evenly, and let stand at room temperature for 5 minutes to specifically lyse the cells of non-target components such as host cells to obtain a mixture, the final concentration of saponin in the mixture is 1.7%;
[0070] (2) The mixture is centrifuged at high speed, and the supernatant is discarded after centrifugation to obtain the first precipitate, the centrifugation speed is 4000rpm, and the time is 30 minutes;
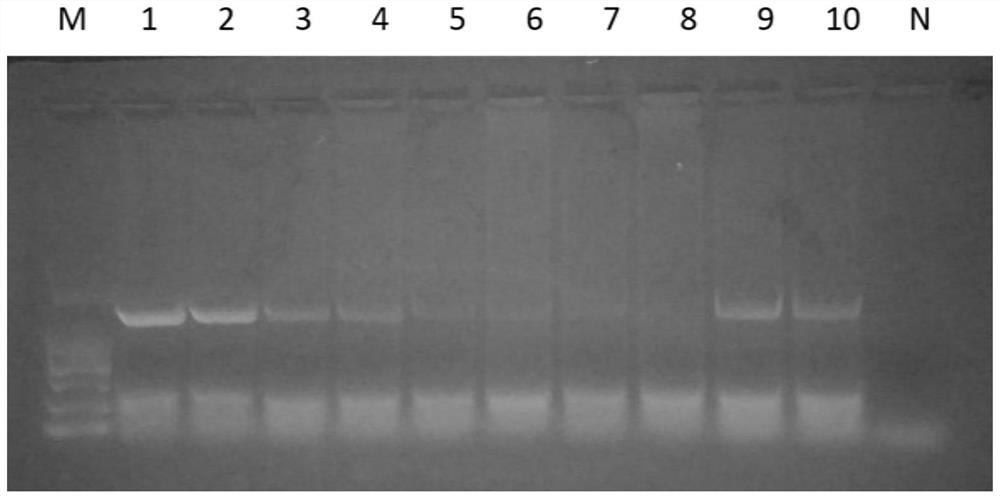
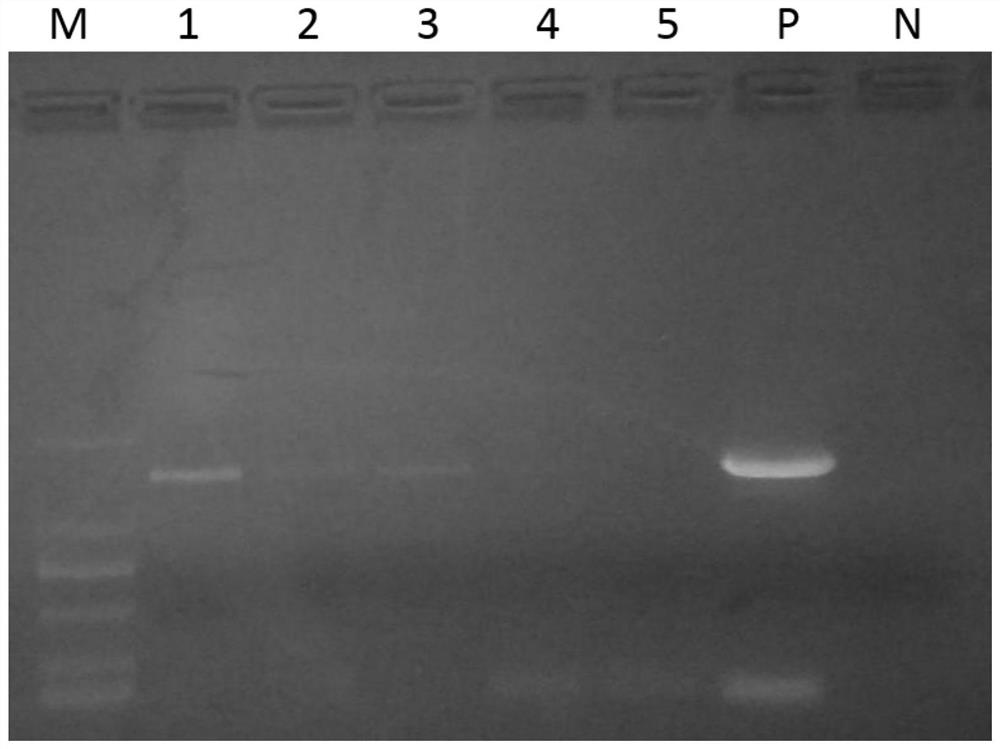
[0071] (3) Add nuclease reaction solution and nuclease to the first precipitation, nuclease contains 10 enzyme units, the purpose is to degrade the non-target components in the sample, mainly host nucleic acid; after step (3), enrich the target microorganism 1 , rinse target microorganism 1 with water and / or biological buffer, the biological buffer is PBS; repeat step (...
Embodiment 2
[0077] A method for selectively removing host nucleic acid from a liquid biological sample, the method comprising the steps of:
[0078] (1) Mix the liquid biological sample and the saponin solution evenly, and let stand at room temperature for 10 minutes to specifically lyse the cells of non-target components such as host cells to obtain a mixture, the final concentration of saponin in the mixture is 0.04%;
[0079] (2) The mixture is centrifuged at high speed, and the supernatant is discarded after centrifugation to obtain the first precipitate, the centrifugation speed is 4200rpm, and the time is 28 minutes;
[0080] (3) Add nuclease reaction solution and nuclease to the first precipitation, nuclease contains 50 enzyme units, the purpose is to degrade the non-target components in the sample, mainly host nucleic acid; after step (3), enrich the target microorganism 1 , use water and / or biological buffer to wash target microorganism 1, the biological buffer is PBS; repeat ste...
Embodiment 3
[0086] A method for selectively removing host nucleic acid from a liquid biological sample, the method comprising the steps of:
[0087] (1) Mix the liquid biological sample and the saponin solution evenly, and let stand at room temperature for 15 minutes to specifically lyse the cells of non-target components such as host cells to obtain a mixture. The final concentration of saponin in the mixture is 0.85%;
[0088] (2) Centrifuge the mixture at high speed, pour off the supernatant after centrifugation, and obtain the first precipitate, the centrifugation speed is 4500rpm, and the time is 26 minutes;
[0089] (3) Add nuclease reaction solution and nuclease to the first precipitation, nuclease contains 100 enzyme units, the purpose is to degrade the non-target components in the sample, mainly host nucleic acid; after step (3), enrich the target microorganism 1 , use water and / or biological buffer to wash target microorganism 1, the biological buffer is PBS; repeat step (3) 2 t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com