Method for recycling molybdenum from waste hydrogenation catalysts
A waste hydrogenation catalyst, ammonium molybdate technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, molybdenum compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of low recovery efficiency, less research, and large salt consumption in chemical precipitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
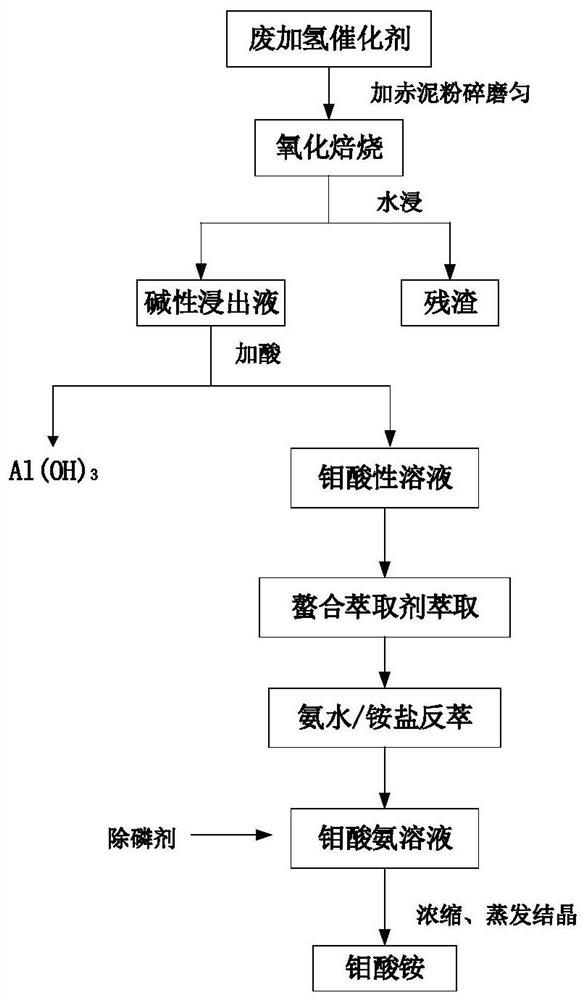
[0026] (1) Grind 50 g of spent hydrogenation catalyst and 100 g of red mud evenly, and roast them at 300°C for 1.5 h; after the calcination is cooled, leaching with water at 70°C for 40 min at a leaching liquid-solid ratio of 5:1, Molybdenum leaching rate was 95.72%.
[0027] (2) Use 30 wt.% sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the leaching solution in step (1) to 6~8, and precipitate aluminum hydroxide; extract the remaining liquid, and extract the organic phase component into Kelex 100 (10 wt.%)+ Sulfonated kerosene (90 wt.%), Acoega M5640 (10 wt.%) + sulfonated kerosene (90 wt.%), Acorga M5774 (10 wt.%) + sulfonated kerosene (90 wt.%), AcorgaOPT5540 ( 10 wt.%)+sulfonated kerosene (90 wt.%), the O / A ratio of the extracted organic phase to the aqueous phase is 1:1, the extraction time is 5min, the extraction temperature is 25°C, and the extraction of molybdenum after the primary extraction The rates were 64.52%, 86.21%, 87.12%, and 87.85%, respectively.
[0028] (3) Back-extra...
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) Grind 50 g of spent hydrogenation catalyst and 100 g of red mud evenly, and roast at 300 °C for 1 h; after the calcination is cooled, the leaching liquid-solid ratio is 5:1, and leaching with water at 70 °C for 60 min, the molybdenum leaching rate was 95.73%.
[0031] (2) Use 30 wt.% sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the leaching solution in step (1) to 6~8, and precipitate aluminum hydroxide; extract the remaining liquid, and extract the organic phase component into Mextral 84-1 (20 wt.% ) + sulfonated kerosene (80 wt.%), Mextral860N-1 (20 wt.%) + sulfonated kerosene (80 wt.%), Mextral 973N (20 wt.%) + sulfonated kerosene (80 wt.%) , Mextral 984N (20 wt.%) + sulfonated kerosene (80 wt.%), extract the organic phase compared with the aqueous phase O / A is 1:1, the extraction time is 5 min, the extraction temperature is 25 ° C, after the primary extraction The extraction rates of molybdenum were 12.11%, 15.54%, 15.78%, and 16.12%.
[0032] (3) Back-extract the organi...
Embodiment 3
[0034] (1) Grind 50 g of spent hydrogenation catalyst and 80 g of red mud evenly, and roast at 500°C for 1 h; after the calcination is cooled, the leaching liquid-solid ratio is 4:1, and leaching with water at 60°C for 40 min, the molybdenum leaching rate was 96.12%.
[0035](2) Use 30 wt.% sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the leaching solution in step (1) to 6~8, and precipitate aluminum hydroxide; extract the remaining liquid, and extract the organic phase component into Kelex 100 (30 wt.%)+ Sulfonated kerosene (70 wt.%), Acorga M5640 (30 wt.%) + sulfonated kerosene (70 wt.%), Acorga M5774 (30 wt.%) + sulfonated kerosene (70 wt.%), AcorgaOPT5540 ( 30 wt.%)+sulfonated kerosene (70 wt.%), the O / A ratio of the extracted organic phase to the aqueous phase is 1:1, the extraction time is 5min, the extraction temperature is 25°C, and the extraction rate of molybdenum after primary extraction 81.11%, 96.24%, 96.18%, 96.32%.
[0036] (3) Back-extract the organic phase extracted in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com