In-situ reinforced remediation method for chlorohydrocarbon-polluted underground water
A technology of in-situ strengthening and remediation methods, applied in the direction of contaminated groundwater/leachate treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problem of uneven distribution of halogenated hydrocarbon pollution, low efficiency of biodegradation, and remediation The materials are easy to agglomerate and other problems, to achieve the effect of increasing microbial diversity and activity, fast removal speed, and complete degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The present embodiment prepares a kind of nano colloidal activated carbon, concrete steps are as follows:
[0034] (1) The specific surface area is selected as 1050m 2 / g, 50 mg of coconut shell activated carbon with a particle size of 10 μm;
[0035] (2) Add the coconut shell activated carbon into the horizontal ball mill and grind it in the horizontal ball mill for 96 hours, so that the particle size range is 0.1-1.8 μm;
[0036] (3) Add 250mL of distilled water at 65°C to the ground activated carbon, put it into a high-pressure homogenizer, circulate and homogenize it for 10 times, the homogenization pressure is 80MPa, and cool it down to room temperature naturally to obtain nano colloidal activated carbon with a particle size of 50~ 150nm;
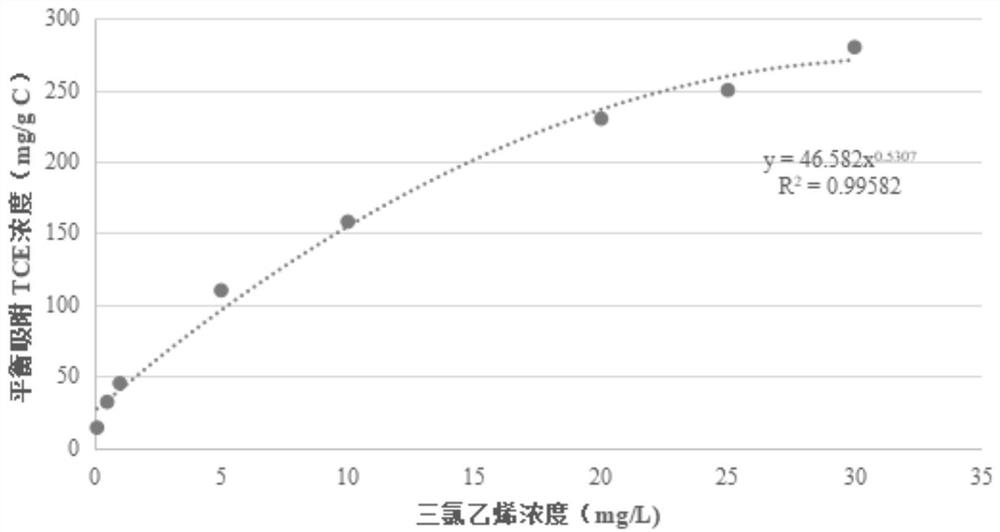
[0037] (4) Add 2.5mL, 5.0mL, 7.5mL, 12.5mL, 25mL, 37.5mL, 50mL, 62.5mL, 75mL of nano colloidal activated carbon into nine 500mL adsorption reaction flasks;
[0038] (5) Adding 500 mL of TCE water samples with a concentration of...
Embodiment 2
[0042] In this example, the nano colloidal activated carbon of Example 1 was used to prepare colloidal activated carbon-based composite bacteria. Specific steps are as follows:
[0043] (1) Preparation of inorganic medium: 1.650g NH 4 NO 3 , 1.9g KNO 3 , 0.440g CaCl 2 2H 2 O, 0.370gMgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 170mg KH 2 PO 4 , 37.3 mg Na 2 - EDTA, 27.8mg FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 6.2 mg H 3 BO 3 , 22.3mgMnSO 4 4H 2 O, 8.6mg ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.83mg KI, 0.25mg Na 2 MoO·2H 2 O, 0.025 mg CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O, 0.025 mg CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O was added to 1L deionized water, the pH value was adjusted to 7.0 with 0.1M NaOH solution, sterilized in a pressure cooker at a temperature of 121 °C for 20 minutes, and cooled in an ultra-clean bench to obtain an inorganic medium.
[0044] (2) Add 8 g of groundwater polluted by chlorinated hydrocarbons to the inorganic medium in step (1), at 30° C., under the condition of a rotating speed of 180 r / min, keep away from light, shake at a constant temperature, ...
Embodiment 3
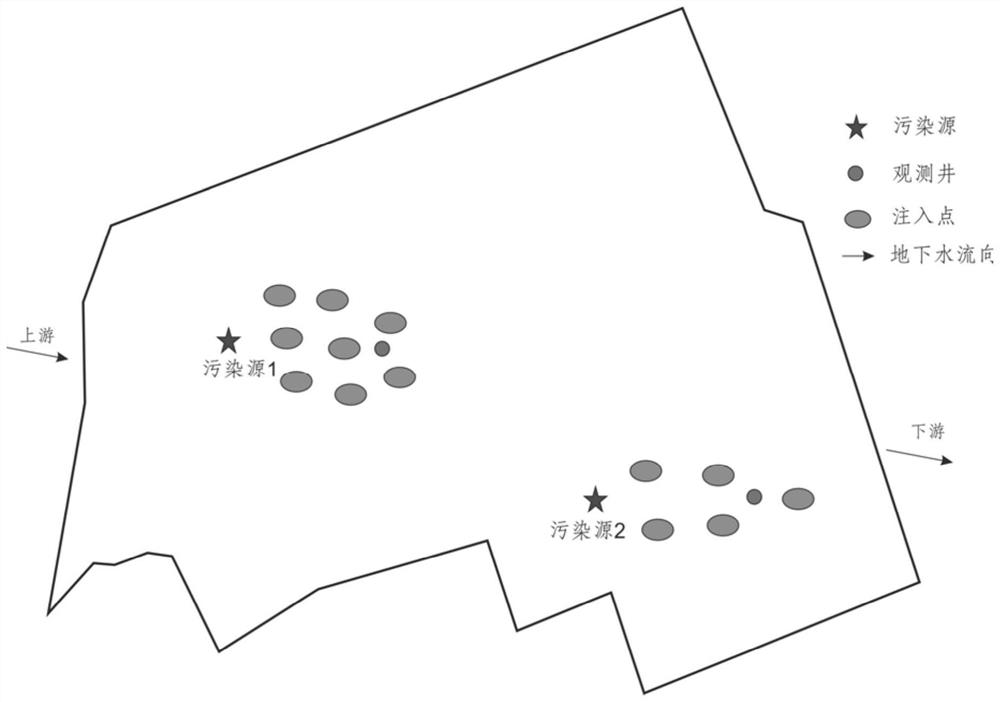
[0049] For an industrial site, two chlorinated solvent pollution plumes were detected below it, and the main pollution factors were trichlorethylene and 1,2-dichloroethylene. Using the nano-colloid activated carbon-based composite bacterial solution prepared in Example 2 of the present invention, a direct-push injection system was used to remediate the groundwater of the polluted site.
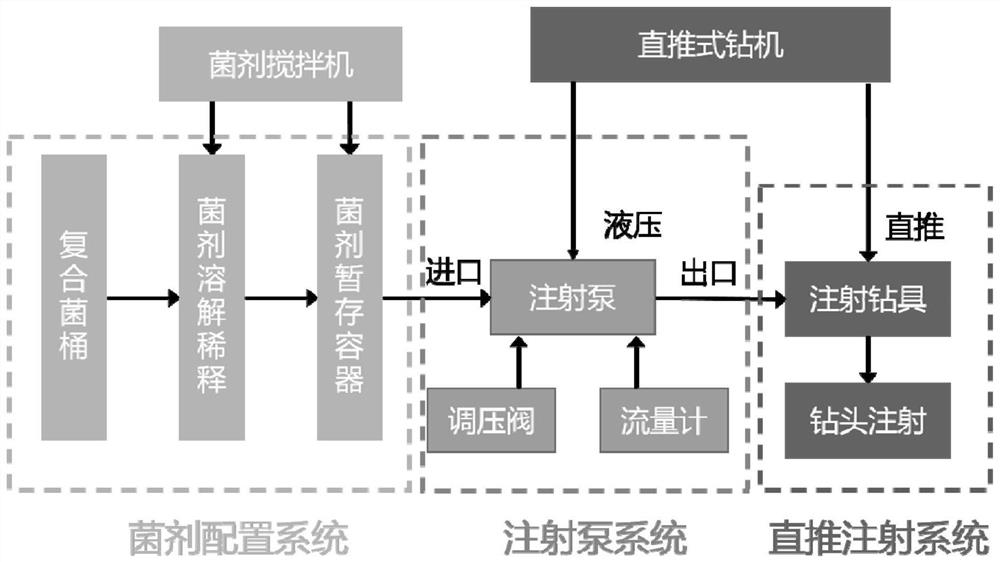
[0050] The direct-push injection system includes a bacterial agent configuration system, a syringe pump system and a direct-push injection system. The bacterial agent configuration system transports the mixed bacterial agent to the bacterial agent barrel through a diaphragm pump, and then dissolves, dilutes and mixes the mixed bacterial agent through the bacterial agent mixer. Stirring configuration work; the injection pump system is powered by the hydraulic system of the drilling rig, pressurizes the mixed bacterial agent and pushes it into the pressure pipeline, and then pushes the injection ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com