Zero-discharge treatment process for printing and dyeing wastewater
A technology of printing and dyeing wastewater and treatment process, which is applied in textile industry wastewater treatment, water/sewage treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high biochemical cost, secondary pollution, and difficulty in meeting national discharge standards, and achieve Low cost and high water reuse rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
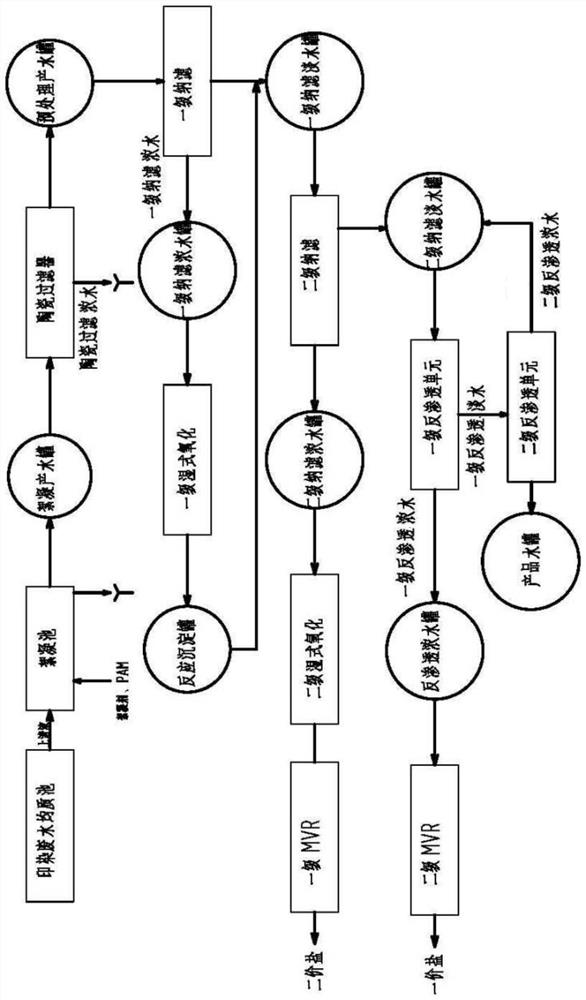
[0023] like figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a zero-discharge treatment process for printing and dyeing wastewater, including the following steps:
[0024] Step 1. The raw water of printing and dyeing wastewater enters the homogenization tank first, and then is pumped into the air flotation flocculation tank. The water produced in the air flotation flocculation tank passes through the self-cleaning filter and then enters the ceramic filter membrane. The ceramic filtered fresh water is sent to the first-level nanometer filter unit, the concentrated water filtered by ceramics is sent to the first-stage nanofiltration concentrated water tank;
[0025] Among them, a micro-nano bubble generator is installed in the air flotation flocculation tank. The material of the micro-nano bubble generator is PP. The micro-nano bubble generator can generate a large number of nano-scale tiny bubbles, and the nano-scale small bubbles can stay in water longer. Long, the air flotation e...
Embodiment 2
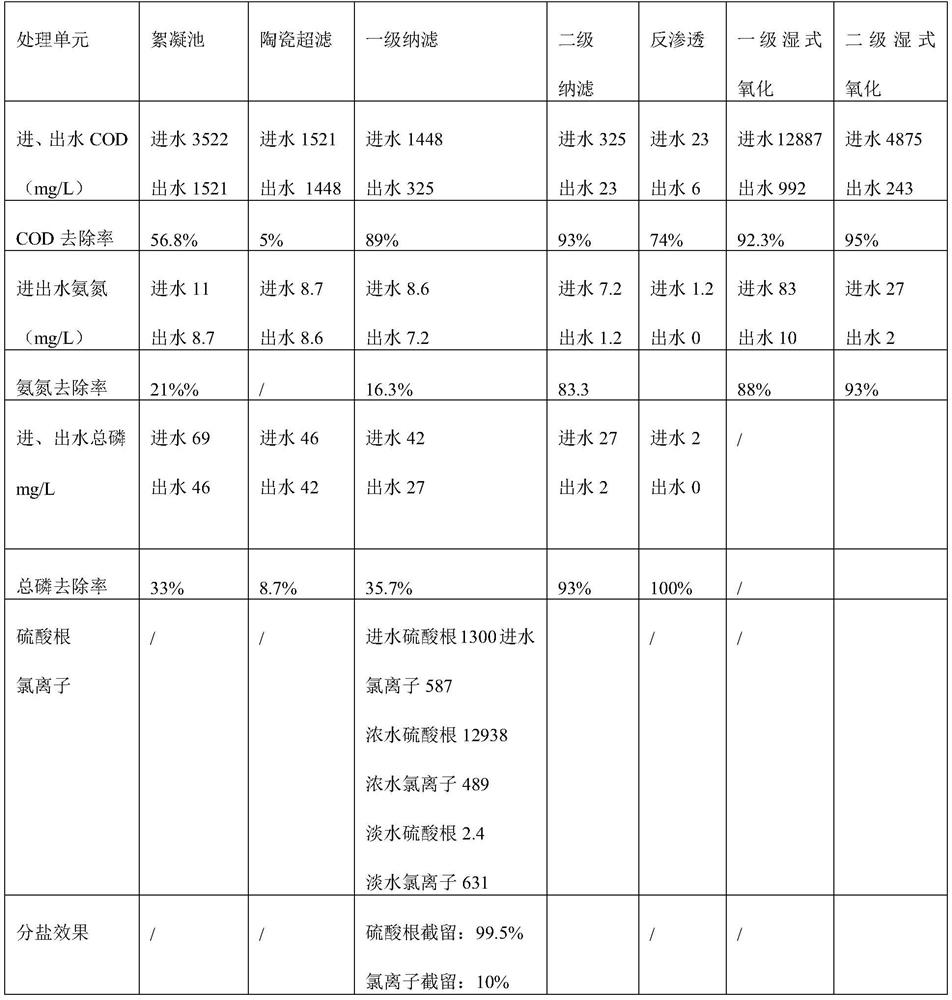
[0036] A certain printing and dyeing wastewater in Guangdong needs to be treated with zero discharge. The pollutant content in the wastewater before treatment: COD3522mg / L, ammonia nitrogen 11mg / L, total phosphorus 69mg / L, SS: 1175mg / L, sulfate radical 1300mg / L, chloride ion 587mg / L; It is required to be zero discharge, and the effluent is required to meet the production and reuse requirements of the factory area. TDS is less than or equal to 25mg / L.
[0037] Adopt the technique of embodiment 1, this technique comprises the following steps;
[0038] Step 1. The raw water of printing and dyeing wastewater enters the homogenization tank first, and then is pumped into the air flotation flocculation tank. The water produced in the air flotation flocculation tank passes through the self-cleaning filter and then enters the ceramic filter membrane. The ceramic filtered fresh water is sent to the first-level nanometer filter unit, the concentrated water filtered by ceramics is sent t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com