Visual and modular detection of nucleic acids with enzyme-assisted nanotechnology
A nucleic acid and target nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid detection, can solve problems such as high cost, expensive usage of probes, and complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0123] method
[0124] Identifying Nanostructure Characterization
[0125] All sequences can be found in Tables 1-7 and were purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT). To prepare recognition nanostructures, in 50mM NaCl, 1.5mM MgCl 2 and 50mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.5) were mixed with DNA aptamer and reverse body oligonucleotides in equimolar ratio. The mixture was incubated at 95°C for 5 minutes and cooled slowly at 0.1°C / s until the reaction reached 25°C, after which Taq DNA polymerase ( Promega) to form a hybrid complex. To characterize the assembly and activity of the recognition nanostructures in the presence of the DNA target, different concentrations of the target oligonucleotides were added to this mixture. The real-time association and dissociation kinetics of the complexes were measured by biolayer interferometry (Pall Fortebio). Briefly, preassembled biotin-aptamers were immobilized on streptavidin-functionalized interferometric sensors. After a brief wa...
Embodiment 2
[0168] enVision platform
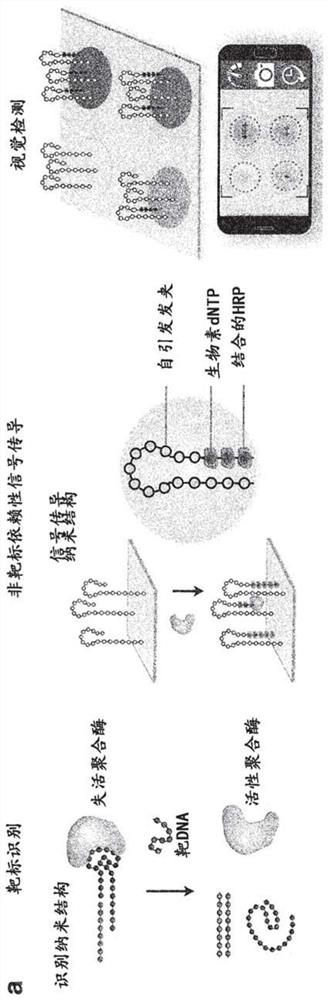
[0169] The enVision platform consists of a series of enzyme-assisted DNA nanostructures to enable three functional steps: DNA target recognition, target-independent signal enhancement, and visual detection ( figure 1 a). Target recognition is decoupled from signal enhancement through orthogonal sequence design of nanostructures. In the recognition step, the recognition element is a unique hybrid nanostructure. It consists of a modified aptamer bound to a TaqDNA polymer [Dang, C. & Jayasena, S.D.J Mol Biol 264:268-278 (1996); Park, K.S. et al. Sci Adv 2:e1600300 (2016)]. In the absence of target DNA, the aptamer binds firmly to the polymerase to inhibit the polymerase activity. Following target hybridization in the presence of complementary target DNA, the hybrid dissociates to activate polymerase activity. During the signaling step, the active polymerase elongates the universal self-initiating nanostructure in a target-independent manner. By inc...
Embodiment 3
[0172] Optimized Assay for Visual Quantification of Nucleic Acids
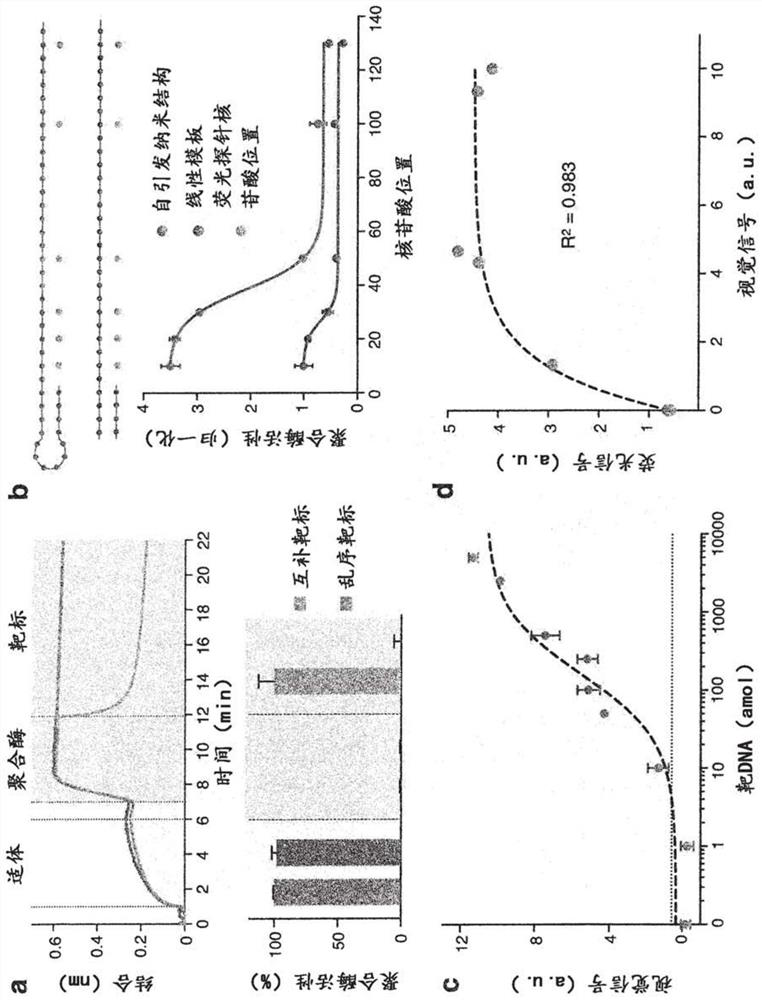
[0173] The performance of DNA nanostructures as functional recognition and signaling elements were evaluated, respectively. For recognition of nanostructures, polymerases associate with modified aptamers to form hybrid complexes ( figure 2 a, above). This optimized complex exhibited negligible polymerase activity ( Figure 8 a). In the presence of complementary target DNA, the hybrid structure dissociates and polymerase activity is fully restored ( figure 2 a, the figure below). This recognition and activation was found to exhibit high sequence specificity, as only complementary targets resulted in strong polymerase activity, whereas scrambled oligonucleotide sequences produced negligible activity ( Figure 8 b).
[0174] The universal recognition element is further designed as a self-initiated nanostructure. The structure exhibits enhanced polymerase occupancy and activity compared to its similarly s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com