Method for preparing agricultural enzyme from kitchen waste, prepared agricultural enzyme and application of agricultural enzyme
A kitchen waste and enzyme technology, applied in application, fertilization method, agriculture, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable stable degradation of kitchen waste, complex composition of kitchen waste, excessive acidification, etc., to improve crop yield and quality, and realize waste. The effect of resource utilization and growth promotion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] In the present embodiment, a kind of method utilizing food waste to make agricultural enzyme comprises the steps:
[0035] Step 1: Preparation of fermentation accessories:
[0036] The proportioning of each component of the fermentation stock solution by mass percentage is as follows:
[0037] 2 parts of brown sugar, 20 parts of tap water, 6 parts of kitchen waste, 1-2 parts of baking powder;
[0038] Among them, food waste includes all kinds of vegetable scraps and edible meat removed from the kitchen, as well as vegetables, rice, meat and other substances left on the dining table and bowls. Food waste contains oil and salt; baking powder contains lactic acid bacteria and yeast Bacterial flora;
[0039] Rinse the food waste with clean water, desalinate and reduce fat, mix the food waste evenly, and crush it into 10-20mm pieces to obtain a food waste mixture;
[0040] Step 2: Add the above-mentioned tap water into the fermentation barrel, add it to the enzyme barrel,...
Embodiment 2
[0047] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, especially in that:
[0048] The agricultural enzyme prepared by the method of this embodiment was diluted 100 times and applied between the rows of small green vegetables. See Table 1-3.
Embodiment 3
[0050] This embodiment is basically the same as the previous embodiment, and the special features are:
[0051] The agricultural enzyme prepared by the method of this embodiment was diluted 200 times and applied between the rows of small green vegetables. See Table 1-3.
[0052] Experimental test analysis:
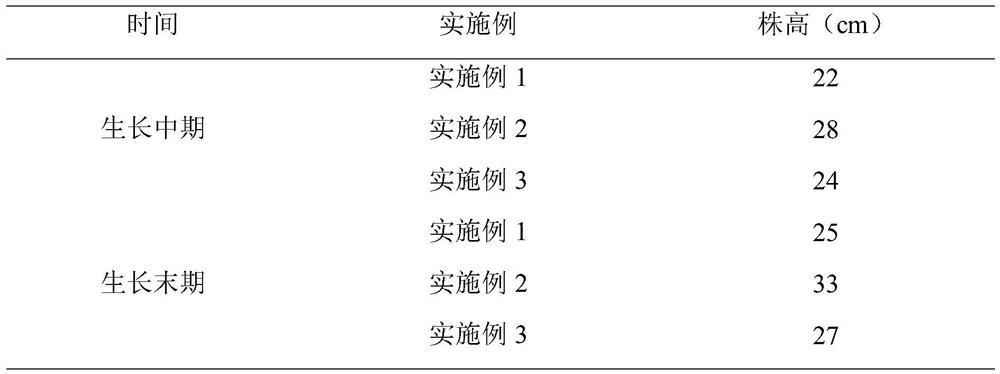
[0053] After the above-mentioned embodiment 1,2,3, agricultural enzymes are used to irrigate the small green vegetables, and the growth conditions of the small green vegetables are compared as follows:
[0054] Table 1. Plant height of pakchoi under different concentrations of enzymes
[0055]
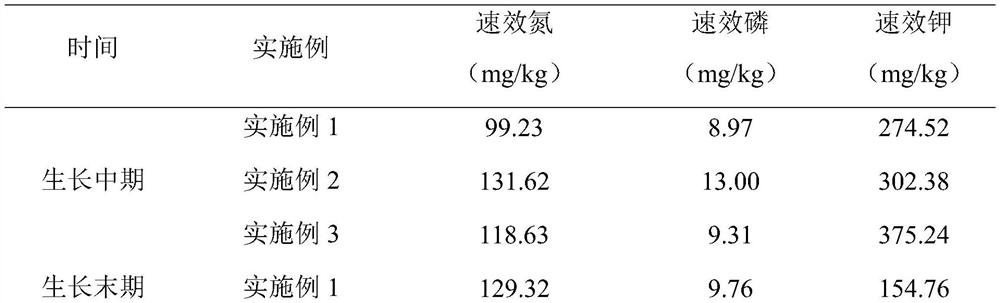
[0056] After the small green vegetables were irrigated with agricultural enzymes in Examples 1, 2, and 3, the soil available nutrients were compared as follows:
[0057] Table 2. Soil available nutrients under different concentrations of enzymes
[0058]
[0059]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com