Positive electrode material and preparation method thereof, positive plate and lithium ion battery
A technology of positive electrode material and positive electrode sheet, which is applied in the field of positive electrode sheet and lithium-ion battery, positive electrode material and its preparation, can solve the problems of aggravating the irreversible side reaction between electrolyte and positive electrode material, unstable material structure, and affecting battery performance, etc., to achieve Improving electrochemical performance, improving ion and electronic conductivity, and high Fermi level effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] 2. A method for preparing a cathode material.
[0033] A method for preparing a positive electrode material, comprising the steps of:
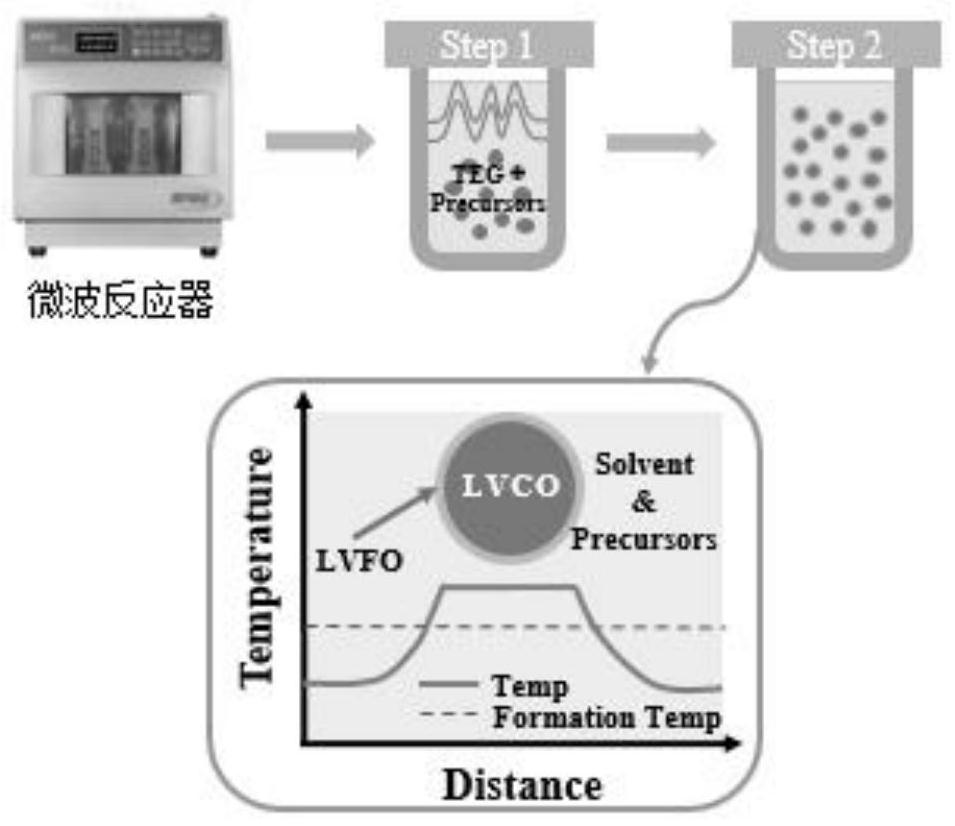
[0034] Step (A), dissolving the first lithium source, cobalt source, and first vanadium source in deionized water at a mass fraction ratio of 1-3:0.01-2.5:1-3, adding a chelating agent, adjusting the pH, and evaporating to form Gel, the gel is dried and sintered to form vanadium-doped lithium cobaltate;
[0035] Step (B), the vanadium-doped lithium cobalt oxide prepared in step (A), the second lithium source, the iron source, the phosphorus source, and the second vanadium source are 1-3:0.01-5 in parts by mass: 0.01-2.5: 0.01-2.5: 0.01-2.5 were added to the reagent and mixed, added to a microwave reactor, stirred and ultrasonically treated, and heated to obtain a mixture.
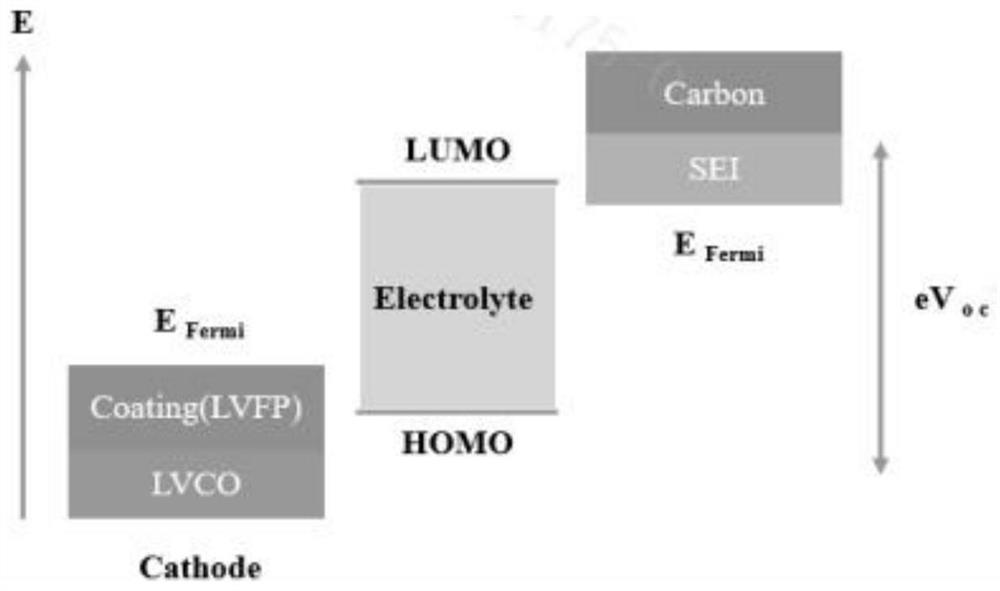
[0036] Step (C), washing the mixture prepared in step (B), vacuum drying, and vacuum calcination to obtain a core-shell structure with vanadium-doped lithium cobal...
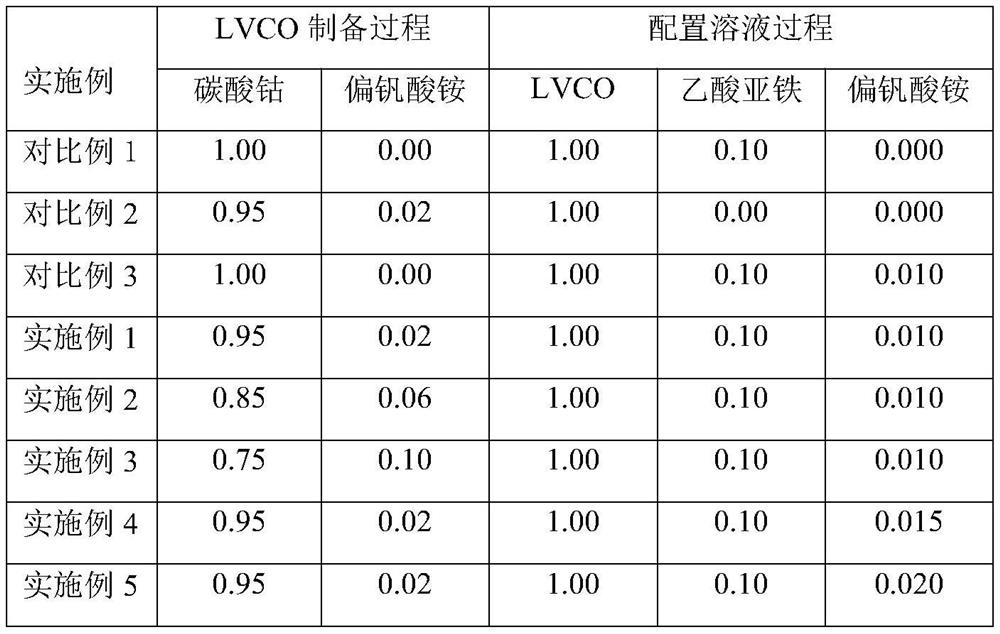
Embodiment 1
[0055] 1. A method for preparing a positive electrode material, comprising the following steps:
[0056] Step (A), dissolving the first lithium source, cobalt source, and first vanadium source in deionized water at a ratio of 1:0.95:0.02 in parts by mass, adding a chelating agent, adjusting the pH, and evaporating to form a gel. drying and sintering to form vanadium-doped lithium cobaltate;
[0057] Step (B), the vanadium-doped lithium cobalt oxide prepared in step (A), the second lithium source, the iron source, the phosphorus source, and the second vanadium source are in a ratio of 1:1:0.1:0.1 in parts by mass: 0.01 was added to the reagents and mixed, added to a microwave reactor, stirred and ultrasonically treated, and heated to obtain a mixture.
[0058] Step (C), washing the mixture prepared in step (B), vacuum drying, and vacuum calcination to obtain a core-shell structure with vanadium-doped lithium cobaltate as the core and vanadium-doped lithium iron phosphate as th...
Embodiment 2
[0074] The difference between Example 2 and Example 1 is that the ratio of the first lithium source, the cobalt source, and the first vanadium source in parts by mass is 1:0.85:0.06.
[0075] The rest are the same as in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com