A detection kit for porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus antibody
An antibody detection and kit technology, applied in the field of swine infectious gastroenteritis virus antibody detection kits, can solve the problems of numerous epitopes, low specificity, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc. low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
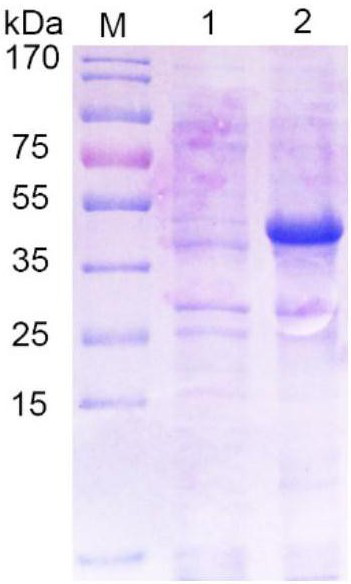
[0041] Example 1 Expression and purification of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus N protein
[0042]The recombinant vector was transformed into BL21(DE3), and 1.5 μL of the plasmid was added to 100 μL of competent cells, and the EP tube was placed on ice for 30 minutes, then heat-shocked in a water bath at 42°C for 90 seconds, and 1 mL of anti-LB was added to the EP tube Incubate on a shaker at 37°C for 1 hour, spread 150 μL of bacterial solution on the plate with a spreader and place it in a constant temperature incubator overnight. Pick a single colony with a regular shape on the plate, add 30mL Amp+LB liquid medium to culture, 210r / min 37°C, when the OD600nm value of the bacterial solution is 0.6-0.8, add a final concentration of 1mM / L IPTG inducer, and induce at 37°C After 6h, the recombinant N protein was successfully expressed by SDS-PAGE analysis ( figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Construction of phage display library and panning of Nanobodies
[0044] 2.1 Immunization of experimental animals
[0045] 2.1.1 N protein immune Bactrian camels
[0046] Mix 1 mL of recombinant N protein (1 mg / mL) purified by affinity chromatography with an equal volume of Freund's complete adjuvant, emulsify completely to form a water-in-oil state, and inject it into the camel's neck. The injection method is subcutaneous injection. Freund's incomplete adjuvant was used for the second to fifth immunizations, and the interval between each immunization was two weeks. After the fifth immunization, 200 mL of peripheral blood was collected through the jugular vein.
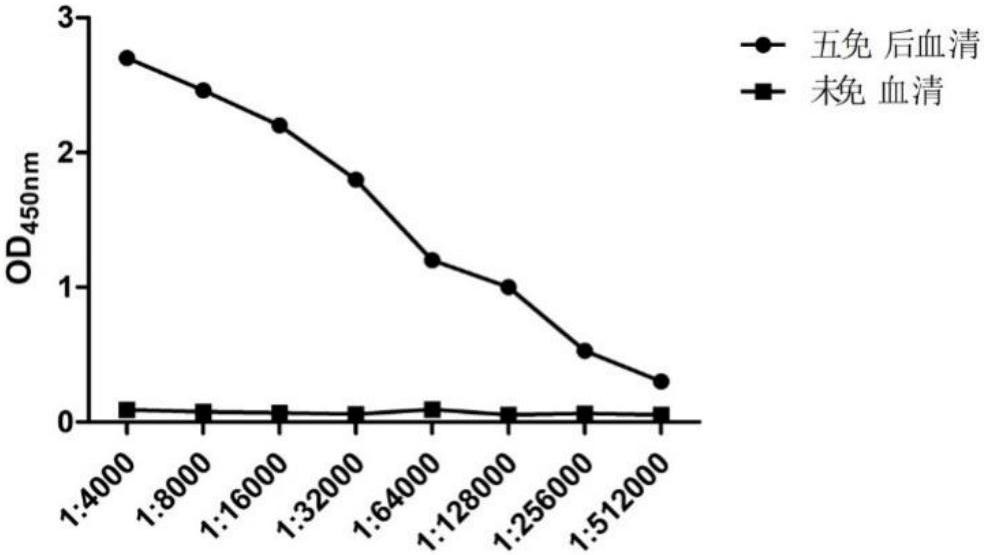
[0047] 2.1.2 N protein antibody titer determination
[0048] The serum was separated from the collected blood to detect the antibody titer against the N protein, and the serum before immunization was used as a control. Through indirect ELISA detection, the antibody titer against the N protein in the...
Embodiment 3
[0065] The establishment of embodiment 3 competition ELISA method
[0066] 3.1 Determine the concentration and dilution of biotin-labeled nanobody and optimal coating antigen by checkerboard titration
[0067] Use biotin-labeled Nb9 at a concentration of 1 mg / ml as the primary antibody, and HRP-labeled streptavidin as the secondary antibody, and find the concentration of the antibody with an OD value around 1.0. The concentration of Nb9 was 10 μg / mL-1 ng / mL, and 96-well plates were coated with N protein at different dilutions (0.5, 1, 2, 4 μg / mL), each well was blocked with 200 μL of blocking solution, and incubated at room temperature for 1 h. After washing 3 times, 100 μL of biotinylated Nb9 of different concentrations was added to each well of the enzyme-labeled plate, incubated for 1 h, after washing 3 times, 100 μL of horseradish peroxidase-labeled streptavidin was added and incubated for 30 min. After washing 3 times, 100 μL of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine was added a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com