RET IGBT device structure with separation gate structure and manufacturing method thereof
A device structure and separation gate technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of reducing blocking ability, reducing device switching speed, increasing switching loss, etc., and reducing leakage current. , the effect of reducing charging and reducing switching loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
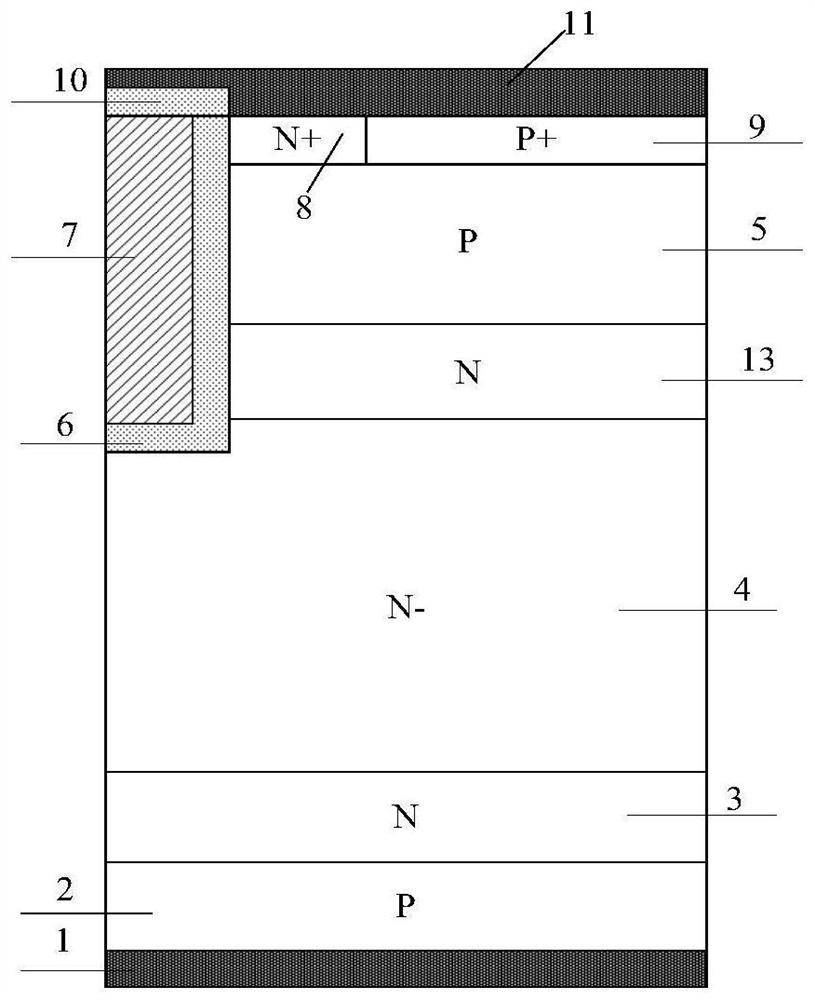
[0086] An embodiment of a RET IGBT device with a split gate structure, such as figure 2 As shown, it includes: collector metal 1, P-type collector region 2, N-type field stop layer 3 and N-drift region 4 stacked in sequence from bottom to top, and the trench gate located above N-drift region 4 structure and a trench emitter structure, the trench gate structure includes a separation gate dielectric layer 6, a separation gate electrode 17 above the separation gate dielectric layer 6, a gate dielectric layer 18 above the separation gate electrode 17, and a gate dielectric layer 18 in the gate dielectric layer 18 The polysilicon gate electrode 7 and the isolation dielectric layer 10 above the polysilicon gate electrode 7, the trench emitter structure includes a trench emitter dielectric layer 14 and a polysilicon trench emitter electrode 15 in the trench emitter dielectric layer 14;
[0087] There is an N-type buried layer 16 between the trench gate structure and the trench emitte...
Embodiment 2
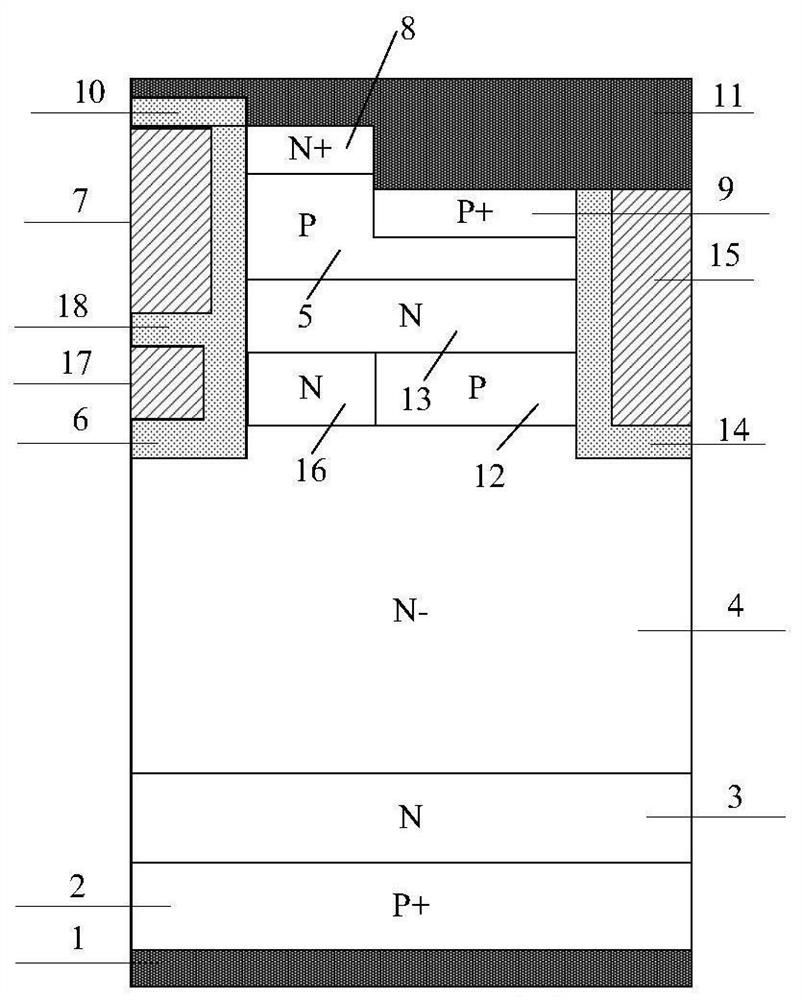
[0125] An embodiment of a RET IGBT device with a split gate structure, such as image 3 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the polycrystalline trench emitter electrode 15 includes a P-type doped polysilicon electrode 151 and an N-type doped polysilicon electrode 152 below the P-type doped polysilicon electrode 151, so The doping concentration of the N-type doped polysilicon electrode 152 is less than the concentration of the P-type doped polysilicon electrode 151, the thickness of the N-type doped polysilicon electrode 152 is less than the thickness of the P-type doped polysilicon electrode 151, and the N-type Doped polysilicon is fully depleted.
[0126] By doing different doping to the polysilicon electrode of the trench emitter structure, when the device is turned off, the PN junction formed by the trench emitter is reverse-biased, and the N-type doped polysilicon electrode 152 has a lower doping concentration and a smaller thickness. ...
Embodiment 3
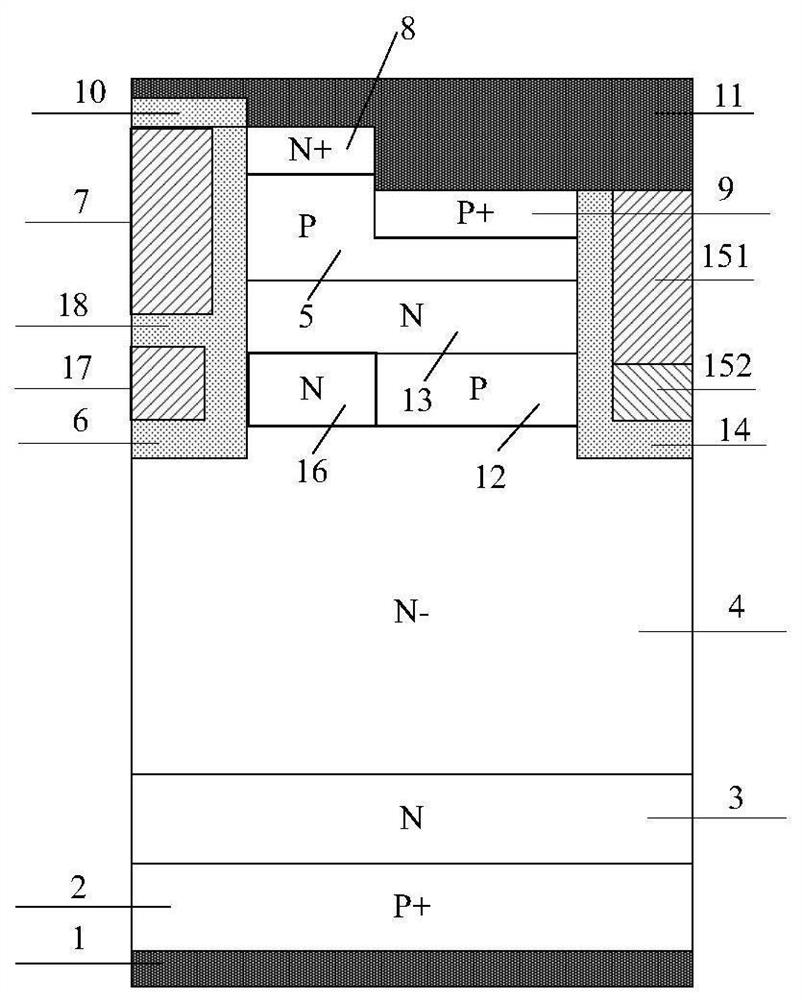
[0128] An embodiment of a RET IGBT device with a split gate structure, such as Figure 4As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the polysilicon gate electrode 7 includes a P-type doped polysilicon electrode 71, an N-type doped polysilicon electrode 72 below the P-type doped polysilicon electrode 71, and an N-type doped polysilicon electrode 72. The concentration of 72 is less than that of the P-type doped polysilicon electrode 71 , and the thickness of the N-type doped polysilicon electrode 72 is less than the thickness of the P-type doped polysilicon electrode 71 .
[0129] When the device is turned off, the PN junction in the trench gate is reverse-biased, and the N-type region is completely depleted, reducing the gate capacitance Cge.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com