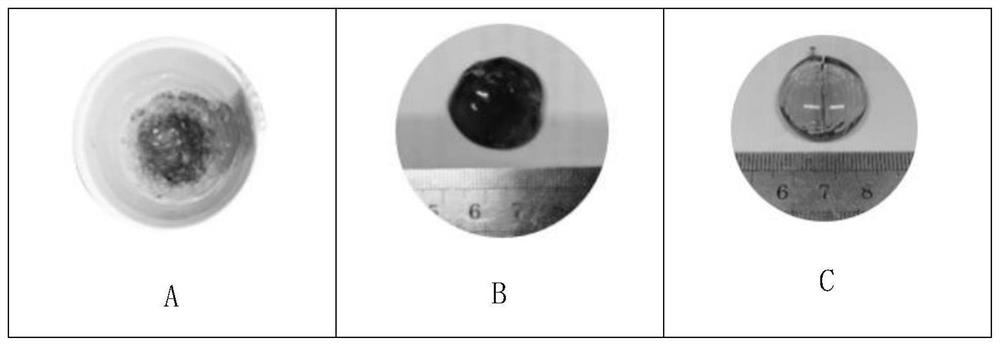
Glass solidification body of incombustible radioactive waste and synergistic glass solidification method
A technology of radioactive waste and glass solidification, which is used in radioactive purification, glass forming, glass furnace equipment, etc. It can solve the problems of glass fiber and resource waste without considering it, so as to improve the waste containment rate, reduce the processing cost, and make the raw materials easy to use. the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0188] Embodiment 1. Waste source item component test
[0189] The oxide composition of the waste source item plays a vital role in the glass formulation design, which directly affects the applicability of the formulation and the performance of the cured body, and the overall consideration of the oxide composition in radioactive waste. Using X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF, PANalytical.B.V, Zetium) and full-spectrum direct-reading plasma emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, LEEMAN LABS, Prodigy) to test the composition of non-combustible waste (glass fiber, soil, concrete), radioactivity Nuclides mainly consider fission products 137 Cs, 90 Sr and activation products 60 Co.
[0190] The waste sources used in the specific examples include fiberglass, soil, and concrete. The test results are shown in Table 1.
[0191] Table 1. Main oxide components of non-radioactive waste (glass fiber, soil, concrete)
[0192] Element glass fiber soil concrete SiO 2
...
Embodiment 2
[0195] Embodiment 2. Preparation of glass fiber+concrete non-combustible waste (binary combination) hybrid glass solidified body
[0196] 2.1 Preparation of glass solidified body
[0197] (1) Pretreatment: The large-volume glass fiber in the non-combustible radioactive waste is crushed or sheared, and the soil is dried to facilitate the accuracy of the measurement results.
[0198] (2) Ingredients (preparation of the mixture to be melted): Weigh 70wt% of glass fiber, 25wt% of concrete, and the weight of non-combustible waste accounts for 95wt% of the mixture to be melted. Weigh glass additive Na 2 O is used as a glass matrix composition, and the weight ratio in the mixture to be melted is 5wt%, and Na 2 O to Na 2 CO 3 Form introduction. Weigh 0.2wt% of CoO and 0.2wt% of Cs in the glass solidified body 2 O, 0.2 wt% SrO simulated radionuclide. The glass fiber, the concrete, the glass matrix composition and the simulated radionuclide are evenly mixed to obtain the mixture ...
Embodiment 3
[0224] Example 3. Preparation of Soil+Concrete Vitrified Body as a Binary Combination Waste Source
[0225] 3.1. Preparation of glass solidified body
[0226] (1) Pretreatment: The large volume of concrete in the non-combustible radioactive waste is crushed or sheared so that the maximum size of the concrete raw material does not exceed 2mm, and the soil drying treatment facilitates the accuracy of the measurement results.
[0227] (2) Ingredients (preparation of the mixture to be melted): 50wt% of concrete and 40wt% of soil are weighed, and the weight of non-combustible waste accounts for 90wt% of the mixture to be melted. Weigh glass additive B 2 o 3 As a glass matrix composition, the weight proportion in the mixture to be melted is 10wt%, B 2 o 3 with H 3 BO 3 Form introduction. Weigh 0.2wt% of CoO and 0.2wt% of Cs in the glass solidified body 2 O, 0.2 wt% SrO simulated radionuclide. The concrete, the soil, the glass matrix composition and the simulated radionuclid...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com