Pharmacokinetic analysis method for covalent drug and metabolite thereof
A technology of pharmacokinetics and metabolites, which is applied in the field of pharmacokinetic analysis of covalent drugs and their metabolites, can solve problems such as complicated and difficult operation processes, hindering the detection of adducts, and achieve simplified operation processes, Increased abundance, accurate separation, and detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Example 1. Establishment and verification of UHPLC-QQQ-MS quantitative analysis method based on amino acid level
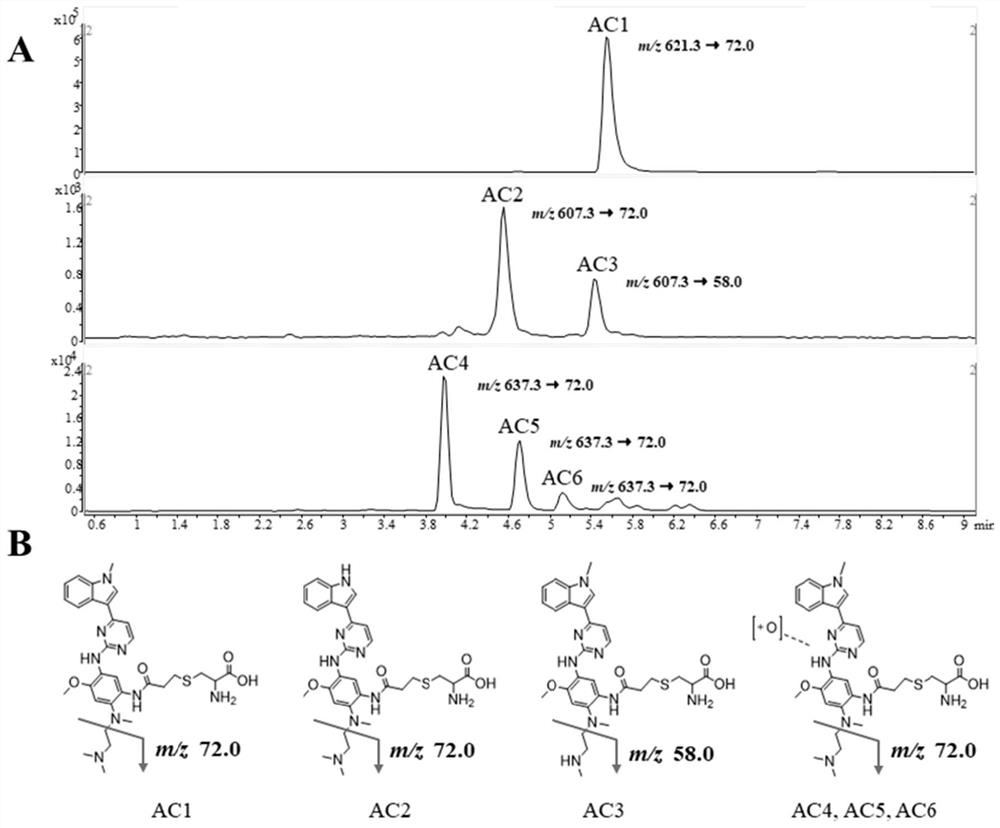
[0059] 1. In vitro incubation of covalent drugs and identification of adducts
[0060] Osimertinib stock solution was prepared with DMSO as solvent, the concentration was 4 mg / mL. The stock solution of osimertinib was diluted to a final concentration of 10.0 mmol / L with potassium phosphate buffer solution (PBS, pH7.4, 0.1 mol / L) containing NAPDH generating solution A, B and cysteine. Pre-incubated at 37°C for 2 min, then added 1.0 mg / mL human liver microsomes to start the metabolic reaction, with a total incubation volume of 400 μL. An equal amount of 50 μL incubation solution was collected at 0, 10, 30, 60, 120, 180, and 240 min, respectively. The samples were centrifuged at 15000 g for 10 min, and the supernatant was collected and dried with nitrogen. The residue was redissolved with 50 μL of 50% aqueous methanol, and the supernatant was collected afte...
Embodiment 2
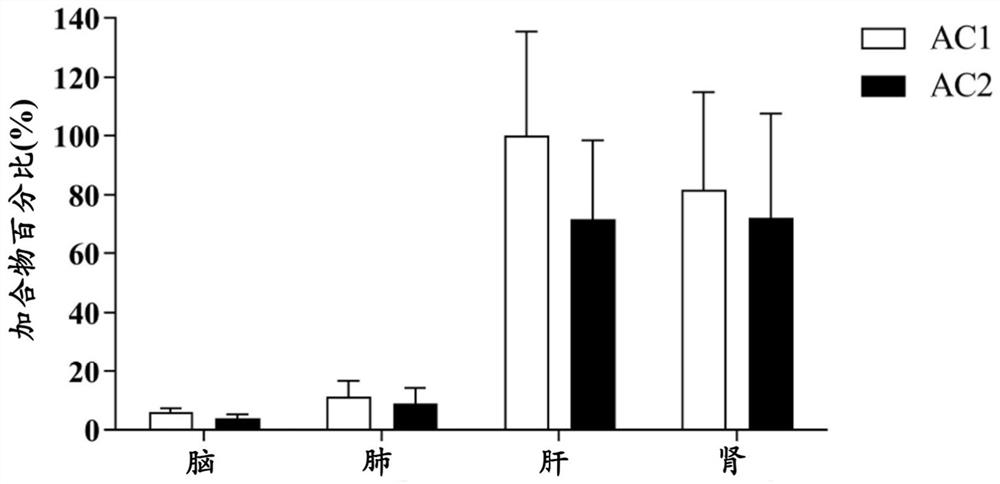
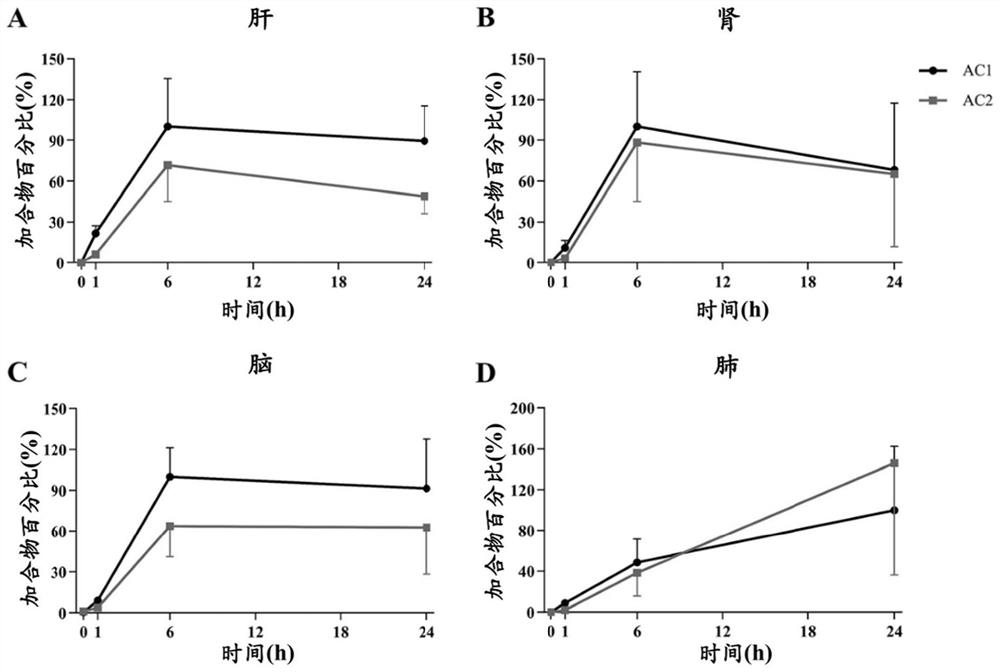
[0082] Example 2. Quantitative analysis of in vivo samples in rats after covalent drug administration
[0083] 1. Optimization of complete enzymatic hydrolysis method
[0084] By comparing the peak areas of AC1 obtained under different enzyme mixing ratios and enzymatic hydrolysis time, it was concluded that the optimal enzyme ratio required to detect 1500 μg protein was 8.4 units of pronase E and 16 units of chymotrypsin, and the optimal enzymatic hydrolysis time was 20 hours.
[0085] 2. Animal administration and sample processing
[0086] 16 SD rats, weighing about 200g (male) and 180g (female), were randomly divided into 4 groups (n=4, half male and half male). Groups 2, 3, and 4 were given osimertinib with 1% polysorbate 80 suspension (36 mg / kg), and group 1 was given 1% polysorbate 80 as a control. The rats in groups 1 and 2 were killed 1 hour after administration, and the rats in groups 3 and 4 were killed 6 hours and 24 hours after administration and blood was collec...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Elution gradient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com