Copper interconnection polishing solution with pressure buffering effect and preparation method of grinding material of copper interconnection polishing solution
A technology of buffering effect and polishing fluid, applied in chemical instruments and methods, polishing compositions containing abrasives, other chemical processes, etc., can solve problems such as adverse effects on the ecological environment and difficulties in post-cleaning, and achieve improved mechanical grinding rate, Effect of reducing mechanical damage and increasing specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The composition and weight percent of this example polishing liquid are as follows: Porous SiO 2 Hollow microspheres (60-120nm in particle size), 12%; H 2 o 2 (30% solution), 6%; EDTA, 3%; Betaine, 3%.
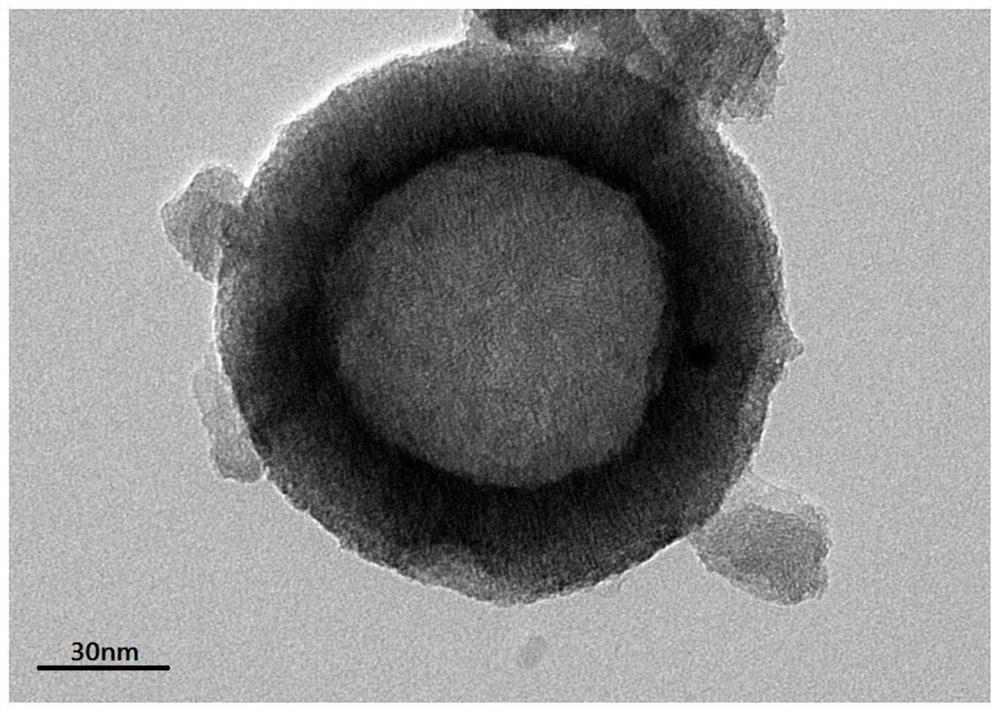
[0036] The porous SiO 2 The preparation method of the hollow microsphere abrasive is: 100mL of distilled water, 2.2g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), stirring at 45°C for 30 minutes; then adding 2.8mL of ammonia water and 3mL of orthosilicate Tetraethyl ester, 0.85mL ethyl acetate, and the resulting mixed system was rapidly and continuously stirred at 40°C for 12 hours; the product was centrifuged, then ultrasonically dispersed in hot water and washed repeatedly to remove the added CTAB to obtain nano-porous SiO 2 hollow microspheres. Porous SiO 2 Transmission electron microscope images of hollow microspheres as figure 1 As shown, the particle size is about 120nm.
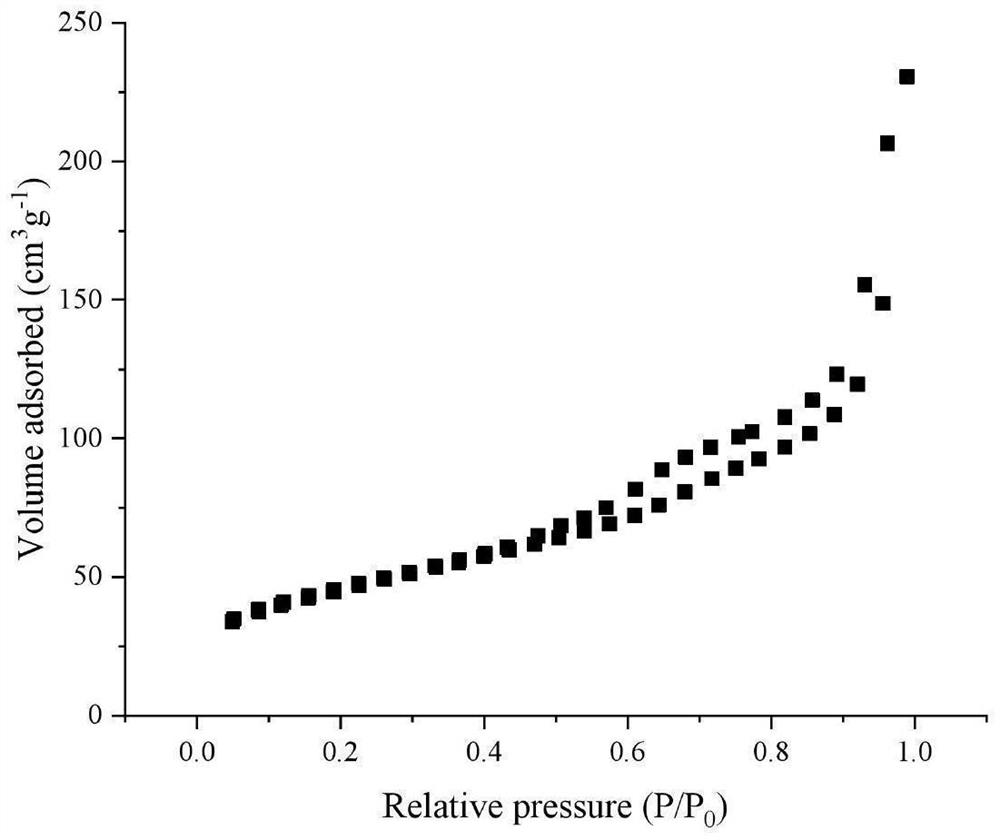
[0037] figure 2 Porous SiO 2 N of hollow microspheres 2 Adsorption / desorption isoth...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The composition and weight percent of this example polishing liquid are as follows: Porous SiO 2 Hollow microspheres (particle size 60-120nm), SiO 2 Sol (30-60nm particle size), mixed 2:1, 12%; H 2 o 2 (30% solution), 6%; EDTA, 3%; Betaine 3%.
[0041] Corresponding experimental data: Polishing conditions: rotating speed of upper and lower polishing head: 97 / 103rpm; flow rate of polishing liquid: 300mL / min; polishing pressure: 2.5psi; removal rate: 7739A / min, surface roughness Sq: 3.3nm.
Embodiment 3
[0043] The composition and weight percent of this example polishing liquid are as follows: SiO 2 Sol (particle size 60-120nm), SiO 2 Sol (30-60nm particle size), mixed 2:1, 12%; H 2 o 2 (30% solution), 6%; EDTA, 3%; Betaine 3%.
[0044] Corresponding experimental data: Polishing conditions: rotating speed of upper and lower polishing head: 97 / 103rpm; flow rate of polishing liquid: 300mL / min; polishing pressure: 2.5psi; removal rate: 9334A / min, surface roughness Sq: 23.1nm.
[0045] Comparing Examples 1-3, it can be seen that under the same conditions, porous SiO 2 In the presence of hollow microspheres, the surface roughness can be significantly reduced, SiO 2 The introduction of sol can increase the removal rate, and in porous SiO 2 Hollow microspheres and SiO 2 Under the premise of ensuring the removal rate, the polished sample with lower roughness can be obtained under the appropriate proportion of sol.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com