Construction method and application of homoserine and threonine biosynthetic pathway
A kind of homoserine, homoserine kinase technology, applied in industrial bio-economy and manufacturing, amino acid industrial production field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] Example 1 - construction scheme of synthetic pathway
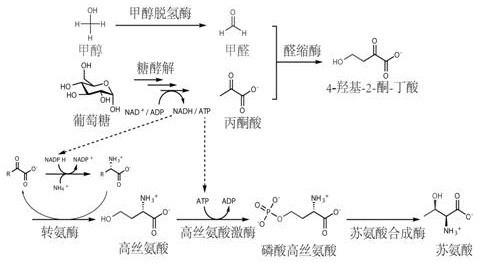
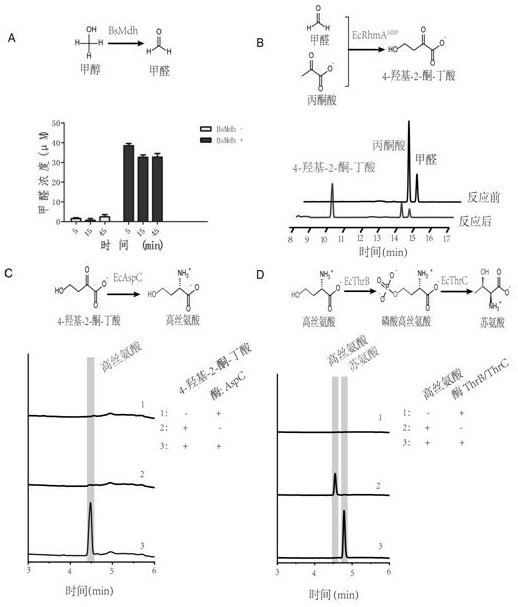
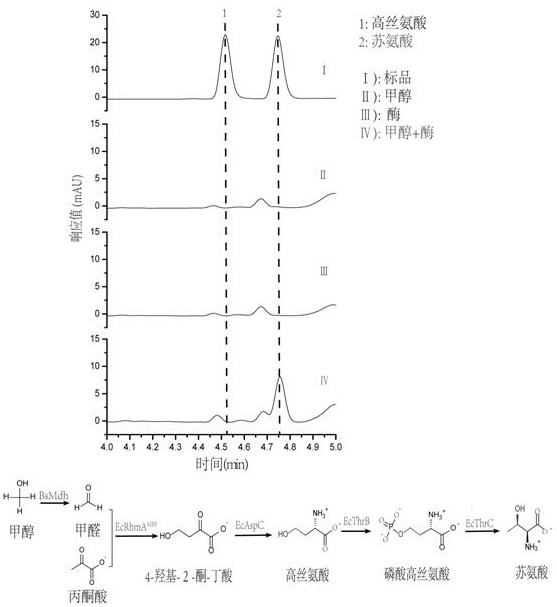
[0082] This new approach innovatively replaces low-energy CO with high-energy-density methanol / formaldehyde one-carbon compounds. 2 Introduced into the synthesis pathway of homoserine and threonine, it still uses glucose as the main carbon source for amino acid fermentation, and uses methanol as a one-carbon raw material to synthesize the intermediate metabolite 4-hydroxy- 2-ketobutyric acid, which then synthesizes homoserine through a transamination reaction, and homoserine can then synthesize threonine through natural pathways. see new route figure 1 . The unnatural nature of this new pathway is mainly reflected in the design and combination of different reactions in the first three steps to generate homoserine, while the latter two steps come from the natural threonine synthesis pathway to convert homoserine into threonine. Methanol and pyruvate can be converted into threonine through an in vitro multi-enzyme...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Example 2 Screening of Methanol Dehydrogenase
[0084] Methanol dehydrogenases from different sources were selected for enzyme kinetics characterization. It mainly includes seven NAD-dependent methanol dehydrogenases and two mutants that have been reported: derived from methylotrophic Bacillus methanolica ( Bacillus methanolicus ) of methanol dehydrogenase: B m Mdh (SEQ ID NO.28), B m Mdh2 (SEQ ID NO.29), B m Mdh3 (SEQID NO.31) and B m Mdh2 mutants: B m Mdh2 mut (SEQ ID NO.30); derived from Bacillus stearothermophilus ( B. stearothermophilus ) of alcohol dehydrogenase Bs Mdh (SEQ ID NO.32); derived from methylotrophic bacteria ( Cupriavidus necator ) of alcohol dehydrogenase Cn Mdh2 (SEQ ID NO.33) and its mutant CT4-1 (SEQ ID NO.34); derived from Lysinobacillus xylan ( Lysinibacillus xylanilyticus ) of methanol dehydrogenase Lx Mdh (SEQ IDNO.35); Derived from Corynebacterium glutamicum ( Corynebacterium glutamicum R) methanol dehydrogena...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3 - Screening of aldolase
[0090] Different types of aldolases were selected for enzyme kinetics characterization. Mainly including Escherichia coli ( Escherichia coli ) of 2-keto-3-deoxy-L-rhamnolate aldolase Ec RhmA (type II aldolase), 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate aldolase Ec YagE (EC:4.1.2.51 Gene ID:944925) and dihydrodipicolinate synthase EcYjhH (SEQ ID NO. 37). The above three aldolases were constructed on the expression vector pET16b, because 2-keto-3-deoxy-L-rhamnolate aldolase Ec RhmA has the problem of inclusion bodies, so the MBP-RhmA method expressed as a fusion protein was designed: connect maltose binding protein (MBP) to the N-terminal of the RhmA sequence, and finally obtain the corresponding vector: pET16b- Ec RhmA MBP ,pET16b- Ec YagE, pET16b- Ec YjhH.
[0091] Then, the above-mentioned expression vectors were respectively transformed in Escherichia coli expression hosts E .coli BL21(DE3), cultured at 37℃ to OD 600 Whe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com