Synthesis and application of high-order superlattice
A superlattice, high-level technology, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve the problems of atomic thin crystal degradation, unrealized, limited stability, etc., to achieve the effects of improved performance, excellent structural advantages, and simple and easy operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
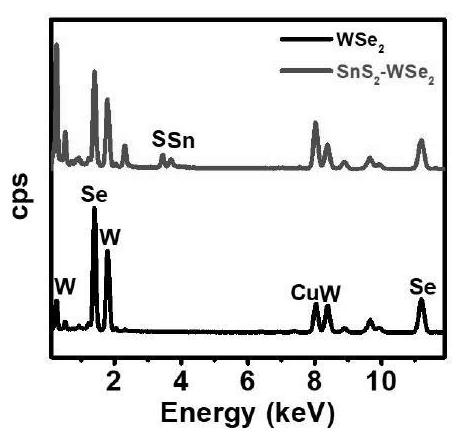
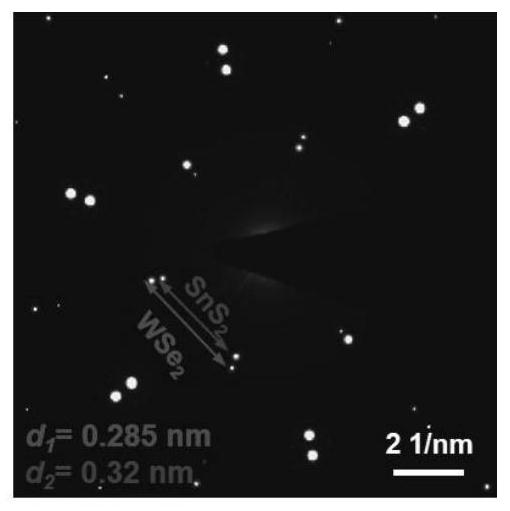
[0137] double-layer SnS 2 / WSe 2 Preparation of vertical heterogeneity:
[0138] Place the porcelain boat filled with S powder in the constant temperature zone upstream of the tube furnace (the temperature is about 180°C, which is the volatilization temperature), and the SnO 2 and tilted wafers (with single-layer WSe 2 nanosheets) porcelain boat placed in the center of the downstream constant temperature zone (temperature is 590 ° C. SnO 2 The mass ratio of powder and S powder is 1:2 (0.05g / 0.1g). Before heating, the air in the quartz tube was purged with 1215 sccm flow rate of argon. Then the constant temperature zones 3 were respectively heated to 590° C. (deposition temperature), and the argon gas flow rate was 120 sccm, and the temperature was kept constant for 8 minutes. There will be a double layer of SnS on the silicon wafer 2 / WSe 2 Vertical heterojunction generation. Generate SnS 2 / WSe 2 The schematic diagram of the vertical heterojunction device is shown i...
Embodiment 2
[0144] Compared with Example 1, the difference is that the volatilization temperature of S powder is 210°C, and the substrate temperature (SnO 2 The volatilization temperature) is 590°C (deposition temperature is 590°C), SnO 2 The mass ratio of powder and S powder is 1:2 (0.05g / 0.1g). The flow rate of Ar is 120 sccm, and the deposition time is 8 min. Figure 11 For the prepared SnS 2 / WSe 2 Optical schematic diagram of a vertical heterojunction, SiO 2 The / Si substrate is light red, and it can be clearly seen that some impurities and defects are generated on the surface of the heterojunction (yellow dots).
Embodiment 3
[0146] Compared with Example 1, the difference is that the S powder volatilization temperature is 150°C, and the substrate temperature (SnO 2 The volatilization temperature) is 590°C (deposition temperature is 590°C), SnO 2 The mass ratio of powder and S powder is 1:2 (0.05g / 0.1g). The flow rate of Ar is 120 sccm, and the deposition time is 8 min. Figure 12 For the prepared SnS 2 / WSe 2 Optical schematic diagram of a vertical heterojunction, SiO 2 / Si substrate is light red, SnS can be seen clearly 2 / WSe 2 The number of heterojunctions is reduced, and most of the samples in the picture are single-layer WSe 2 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com