Method for combined treatment of hard alloy grinding waste and scheelite
A technology for hard alloys and grinding waste, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, non-metallic elements, etc., can solve problems such as methods to be studied
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
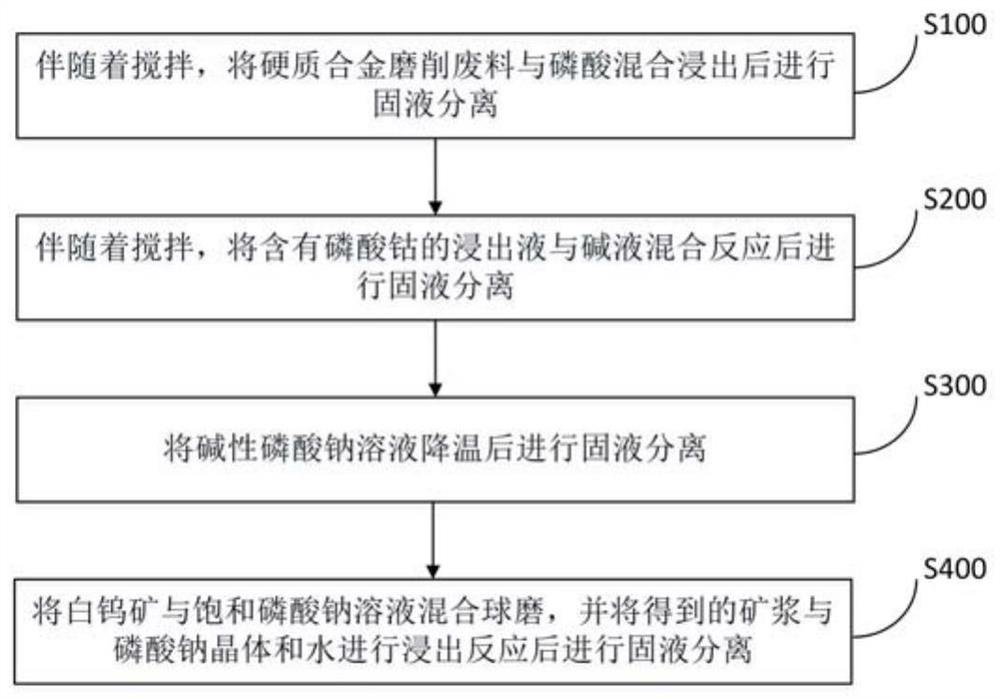
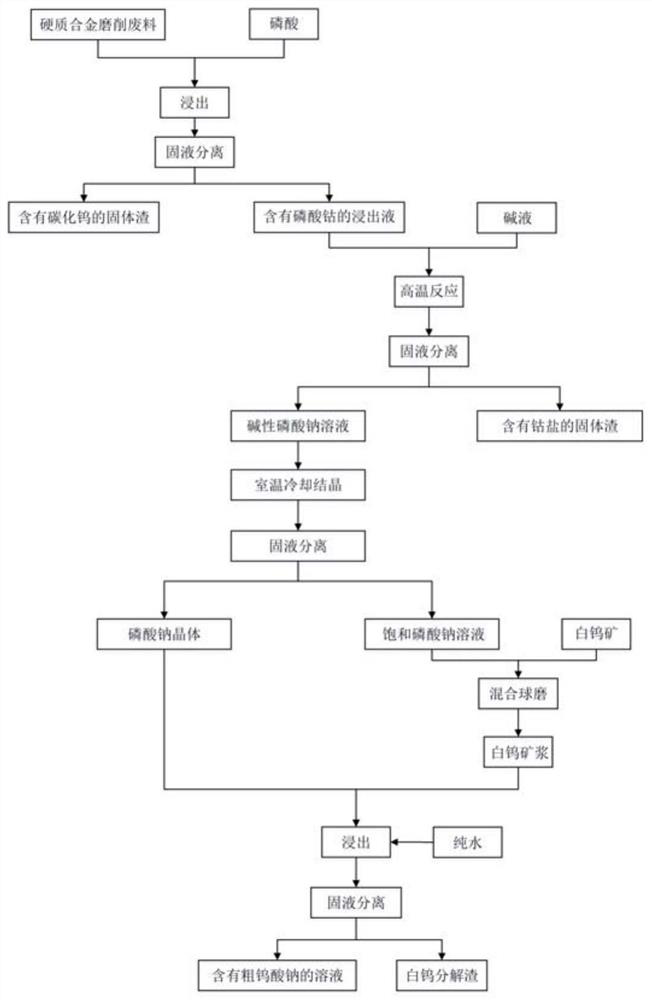
[0048] Step 1. Weigh 1 kg of cemented carbide grinding waste, add phosphoric acid that is 1.3 times the total theoretical amount required for leaching impurity elements such as cobalt, and add an appropriate amount of water to make the liquid-solid ratio 1L:1kg, stir and mix at room temperature for leaching for 10 hours, stirring speed 200 rpm, solid-liquid separation after the reaction is completed to obtain solid slag containing tungsten carbide and leachate containing cobalt phosphate, the leaching rate of cobalt element is 96.5%.
[0049] Step 2. Add 3.5 times the amount of phosphoric acid sodium hydroxide and 1.8 L of pure water to the leach solution obtained in the above-mentioned cobalt phosphate, and stir for 2 hours at 80° C. at a stirring rate of 300 rpm. After the reaction is completed, filter while hot for solidification. The liquid is separated to obtain a solid slag containing cobalt hydroxide and an alkaline sodium phosphate solution.
[0050] Step 3. After the ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Step 1. Weigh 1 kg of hard alloy grinding waste, add phosphoric acid twice the total theoretical amount required for leaching impurity elements such as cobalt, and add an appropriate amount of water at the same time to make the liquid-solid ratio 2L:1kg, stir and mix at room temperature for leaching for 6 hours, stirring speed 400rpm, solid-liquid separation after the reaction is completed to obtain solid slag containing tungsten carbide and leachate containing cobalt phosphate, the leaching rate of cobalt element is 98.8%.
[0054] Step 2. Add sodium hydroxide and 2.8L pure water of 4.4 times the amount of phosphoric acid added in step 1 to the leaching solution containing cobalt phosphate obtained above, stir and react at 90°C for 1h, and the stirring rate is 200rpm. After the reaction is completed, filter while hot for solidification. The liquid is separated to obtain a solid slag containing cobalt hydroxide and an alkaline sodium phosphate solution.
[0055] Step 3....
Embodiment 3
[0058] Step 1. Weigh 1 kg of cemented carbide grinding waste, add phosphoric acid that is 2.5 times the total theoretical amount required for leaching impurity elements such as cobalt, and add appropriate amount of water at the same time to make the liquid-solid ratio 2.5L:1kg, stir and mix at room temperature for leaching for 8 hours, stir The speed is 300rpm. After the reaction is completed, solid-liquid separation is performed to obtain a solid slag containing tungsten carbide and a leaching solution containing cobalt phosphate, and the leaching rate of cobalt element is 99.2%.
[0059] Step 2. Add sodium carbonate 4.9 times the amount of phosphoric acid added in step 1 and 2L of pure water to the leaching solution containing cobalt phosphate obtained above, stir and react at 85°C for 3 hours, and the stirring rate is 300rpm. After the reaction is completed, filter while hot for solid-liquid separation , to obtain solid slag containing cobalt carbonate and alkaline sodium ph...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com