Astragalus stem and leaf water and preparation method thereof
A technology of astragalus stems and leaves and astragalus, applied in the field of astragalus stems and leaves water and its preparation, to achieve the effects of improving planting enthusiasm, increasing income, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Preparation of Radix Astragali Stem and Leaf Water
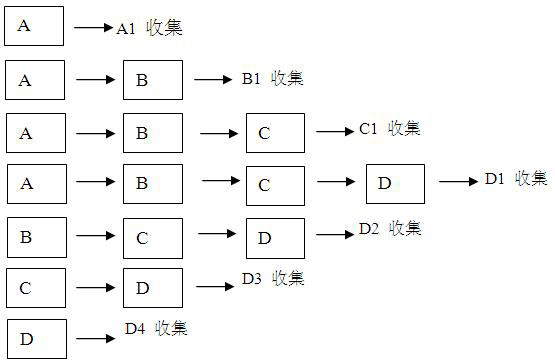
[0041] (1) Weigh 0.4 kg of the aerial parts of Astragalus membranaceus (stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus), wash, divide into four parts, put each 0.1 kg into filter bags, put them into stainless steel extraction tanks, and mark tanks A, B, C and D respectively;
[0042] (2) Divide 100L of purified water into 7 parts, add 1 part of the purified water to the countercurrent extraction tank A, extract the aerial parts of Astragalus membranaceus (Astragalus stem, leaf) in tank A, and then separate the solid and liquid, and collect the tank A Extract the solution to obtain A1, then add the second part of pure water to tank A to extract the aerial part of Astragalus membranaceus, obtain A2 after solid-liquid separation, put the separated extract solution A2 into the countercurrent extraction tank B, and extract the astragalus membranaceus in tank B The aboveground part is extracted, and then solid-liquid...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Preparation of Astragalus Stem and Leaf Water Rich in γ-aminobutyric acid
[0047] Steps (1) and (2) are the same as (1) and (2) in Example 1;
[0048] (3) The extracted liquid part is filtered through two stages, the first stage is coarse filtration with a filter aperture of 200 mesh, the second stage is fine filtration with a filter aperture of 2 microns, and the clarified water extract of Astragalus stems and leaves is obtained after filtration. Add 80g gamma-aminobutyric acid to the clarified astragalus stem and leaf water extract, and mix well;
[0049] (4) Astragalus stem and leaf water is sterilized at 138°C for 4 seconds, then cooled to 93°C for hot filling, sterilized by inverting the bottle, inspected by light, and packaged. The stem and leaf of Astragalus membranaceus rich in γ-aminobutyric acid water.
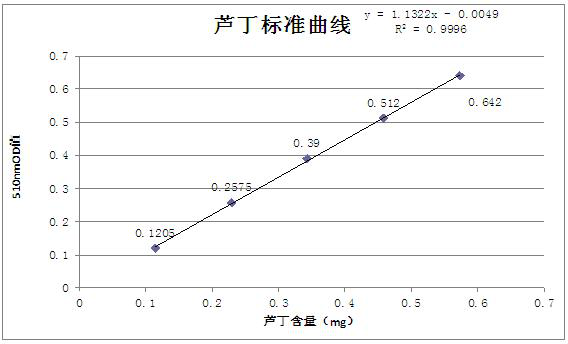
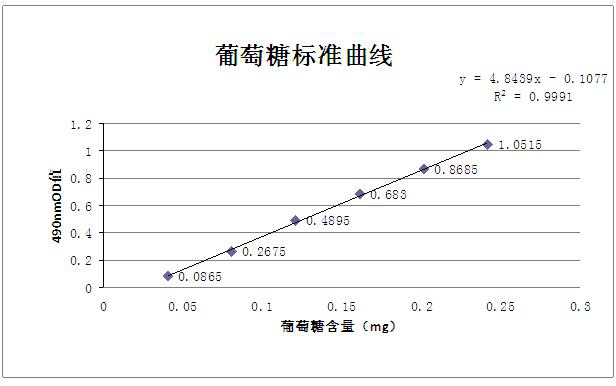
[0050] The stem and leaf water of Astragalus membranaceus was tested, and the polysaccharide content was 0.1679 mg / mL, and the total flavonoids w...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3 Determination of polysaccharides and total flavonoids in Astragalus stem and leaf water
[0052] 1 Experimental materials
[0053] 1.1 Raw material
[0054] The aerial parts of Astragalus membranaceus (stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus) were collected in Qiqihar City, Heilongjiang Province from September to October 2018; fresh and dried stems and leaves of Astragalus membranaceus;
[0055] 1.2 Reagents
[0056] Rutin was purchased from Dr. Ehrenstorfer in Germany, and glucose was purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.; concentrated sulfuric acid, ethanol, phenol, vanillin, and sodium hydroxide were all purchased as commercially available analytical grades;
[0057] 1.3 Instruments
[0058] Electronic Analytical Balance Mettler Toledo (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
[0059] SSW-600-2S electric heating constant temperature water tank Shanghai Boxun Industrial Co., Ltd.
[0060] Visible Spectrophotometer Hach Water Quality Analyzer (Shanghai) Co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com