Alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehyde in-situ selective hydrogenation reaction process taking water as cheap hydrogen donor
A technology for hydrogenation reaction and aldehyde selectivity, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, reduction preparation of oxygen-containing functional groups, and metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, etc., can solve problems such as high cost and achieve a simple preparation process. and controllable and excellent catalytic hydrogenation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
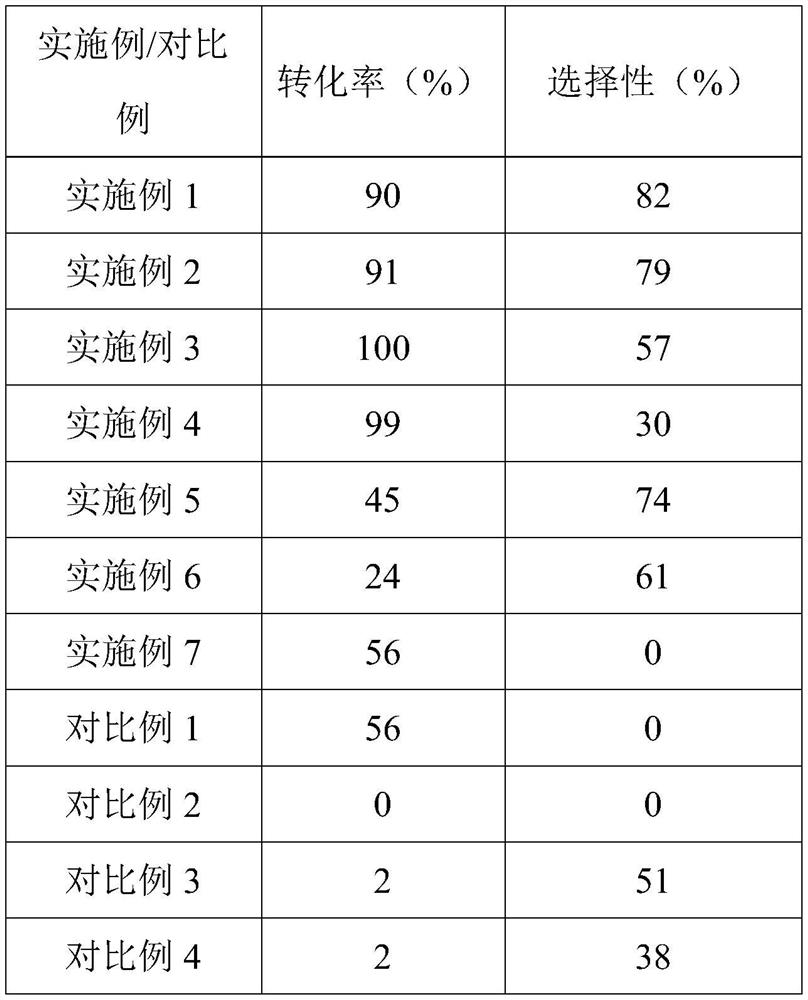
[0020] Weigh 25mg 1Au@MoC x Catalyst is loaded in 100mL autoclave, adds 0.5mmol α, β-unsaturated aldehyde, adds 15mL 1,4-dioxane aqueous solution (V H2O :V 1,4-Dioxane =1:3), and then the reaction system was replaced with carbon monoxide gas, accumulatively five times. Then charge 3MPa carbon monoxide. After that, the reaction device was placed in the heating mantle, and the heating was started at 800 rpm, and the reaction was carried out for 5 h to carry out the in-situ hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehyde to prepare unsaturated alcohol and its by-products. The reaction products were filtered through organic microporous membranes and analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively by nuclear magnetic resonance and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The specific reaction properties are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Weigh 25mg 1.5Au@MoC x Catalyst is loaded in 100mL autoclave, adds 0.5mmol α, β-unsaturated aldehyde, adds 15mL 1,4-dioxane aqueous solution (V H2O :V 1,4-Dioxane =1:3), and then the reaction system was replaced with carbon monoxide gas, accumulatively five times. Then charge 3MPa carbon monoxide. After that, the reaction device was placed in the heating mantle, and the heating was started at 800 rpm, and the reaction was carried out for 5 h to carry out the in-situ hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehyde to prepare unsaturated alcohol and its by-products. The reaction products were filtered through organic microporous membranes and analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively by nuclear magnetic resonance and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The specific reaction properties are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Weigh 25mg 3Au@MoC x Catalyst is loaded in 100mL autoclave, adds 0.5mmol α, β-unsaturated aldehyde, adds 15mL 1,4-dioxane aqueous solution (V H2O :V 1,4-Dioxane =1:3), and then the reaction system was replaced with carbon monoxide gas, accumulatively five times. Then charge 3MPa carbon monoxide. After that, the reaction device was placed in the heating mantle, and the heating was started at 800 rpm, and the reaction was carried out for 5 h to carry out the in-situ hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehyde to prepare unsaturated alcohol and its by-products. The reaction products were filtered through organic microporous membranes and analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively by nuclear magnetic resonance and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The specific reaction properties are listed in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com