A method for the controllable preparation of cobalt/cobalt oxide nanofilms using an ionic liquid water interface
A technology of ionic liquids and nano-membranes, applied in the field of nano-materials, can solve the problems of no large-scale application of nano-membranes, the inability of independent existence of thin films, poor energy conservation and environmental protection, and achieve excellent Co redox and catalytic hydrogenation performance, Avoid the use of complex organic stabilizers, the effect of mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
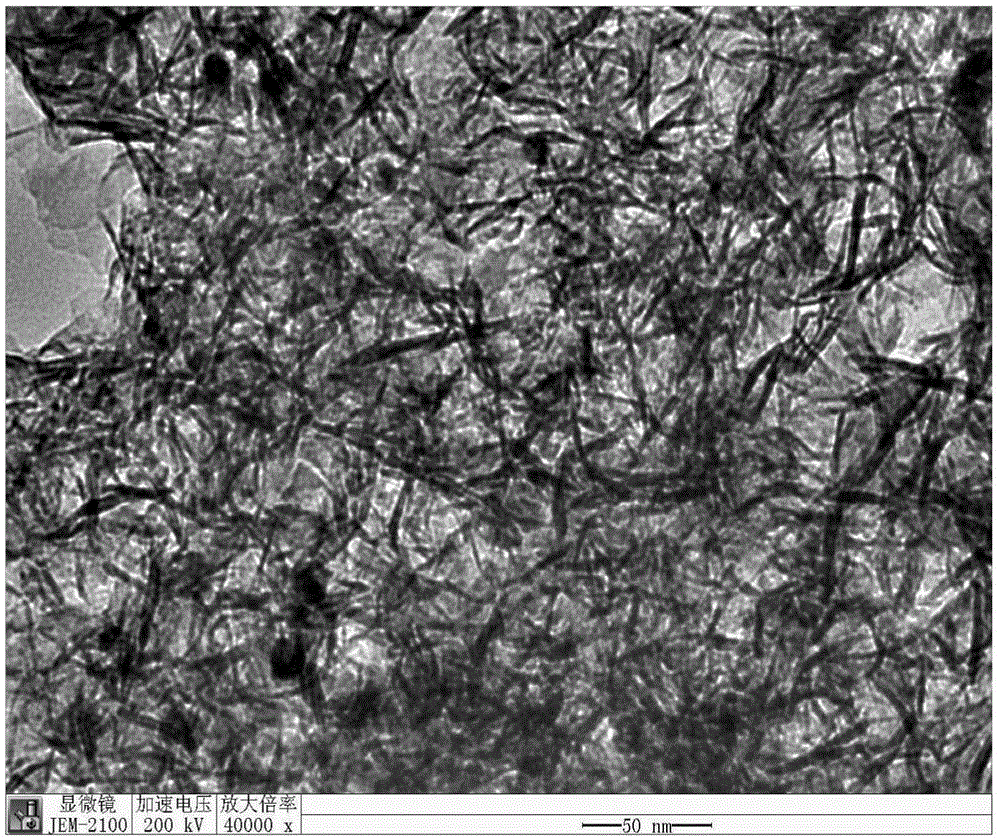
[0026] Embodiment 1: a kind of method that utilizes ionic liquid water interface to controllably prepare cobalt / cobalt oxide nano film, concrete steps are: put 6.00g ionic liquid (1 methyl-3 octylimidazolium salt hexafluorophosphoric acid [C 8 min]PF 6 , dosage can be adjusted) and KBH 4 (0.15mol / L, 20mL) aqueous solution was mixed in a three-necked flask and ultrasonically dispersed to form an ultra-fine dispersed microemulsion structure; then, under the conditions of Ar gas saturation, reflux and liquid seal, magnetic stirring and heating at 60 ° C as A solution; make cobalt acetate into a (30mmol / L, 20mL) aqueous solution as solution B; add solution B to solution A dropwise at a rate of 2 drops per second through a constant pressure funnel. Then, under the condition of magnetic stirring, the reaction was performed at a constant temperature of 60°C for 1 hour until a black colloidal solution was formed. The reaction flask was cooled to room temperature and allowed to stand...
Embodiment 2
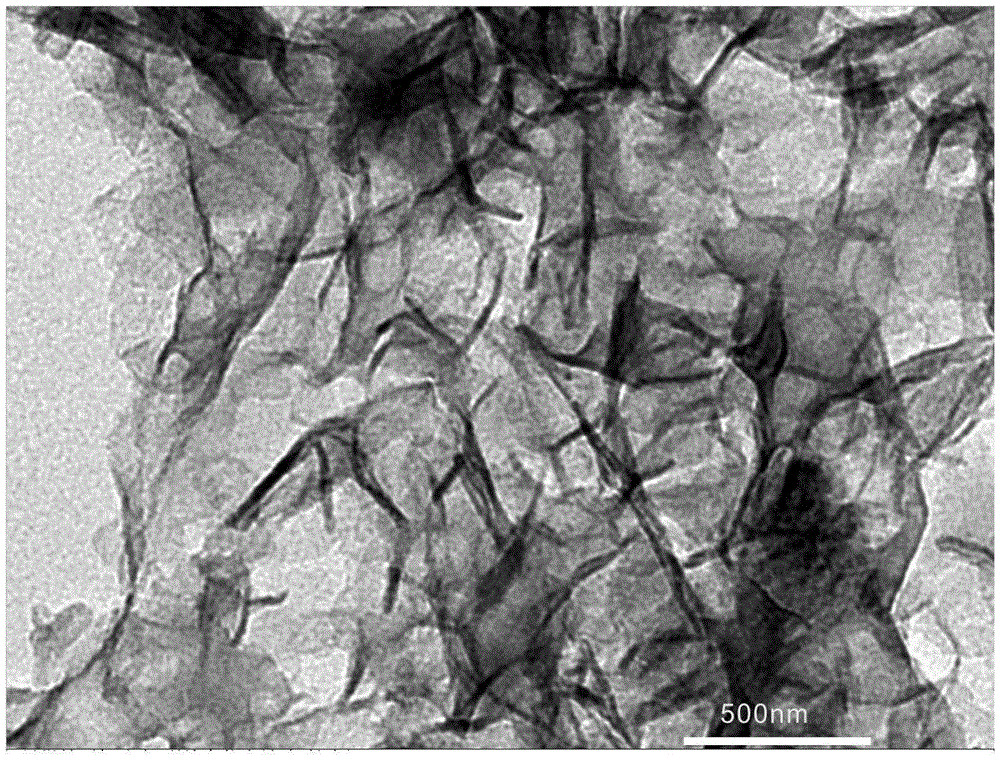
[0027] Example 2: The ionic liquid in Example 1 is replaced by 1,3-dioctyl imidazolium hexafluorophosphate [OOIM]PF 6 , others are the same as in Example 1, the result is as figure 2 . figure 2 Shown in [OOIM]PF 6 Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of Co nanofilms synthesized on ionic liquid water interfaces with a scale of 500nm; TEM images show that Co nanofilms synthesized on different ionic liquid water interfaces can achieve structural adjustment, and cobalt / cobalt oxide forms a clean The nano film has a thickness of 1-2nm and curls into a tubular structure at the edge of the film. By changing the different substituents on the imidazole ring, changing the template properties on the interface and the adsorption of ionic liquids on the metal surface, the controllable preparation of Co metal nanofilms is achieved. Infrared spectroscopy was performed on pure ionic liquids, supernatants, liquid cobalt / cobalt oxide colloids, and centrifuged dried solids, showing...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Embodiment 3: Adjust the reaction temperature in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 within the range of 60-100° C., and the others are the same as Scheme 1. Temperature has a great influence on the control of nanostructures. If the reaction temperature is too low, the reaction will not be complete; if the temperature is too high, the reaction speed will be too fast, the metal nucleation speed will be too fast, and the Co film structure will not form stably. The reaction temperature is controlled at 60-100°C, and the Co film structure can be adjusted by changing the reaction temperature. For example, the reaction temperature is 70°C for one hour at a constant temperature, and KBH is added 4 After that, the Co nucleation speed is accelerated, and the film formation time is shortened, but the area and integrity of the film will be reduced, and the nano-film can still be formed at a reaction temperature of 100 °C;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com