Construction of pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacterium and application of pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacterium in improvement of methanol assimilation rate and fixation of carbon dioxide
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and Pichia pastoris, applied in the field of strain metabolism transformation, can solve problems such as low methanol utilization efficiency, and achieve the effects of improving methanol assimilation efficiency, simple operation at the molecular level, and increasing biomass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] The FDH gene in the dissimilation pathway was knocked out in Pichia pastoris by CRISPR-Cas9 gene knockout technology, and the recombinant strain GS115-ΔFDH was obtained.
Embodiment 2
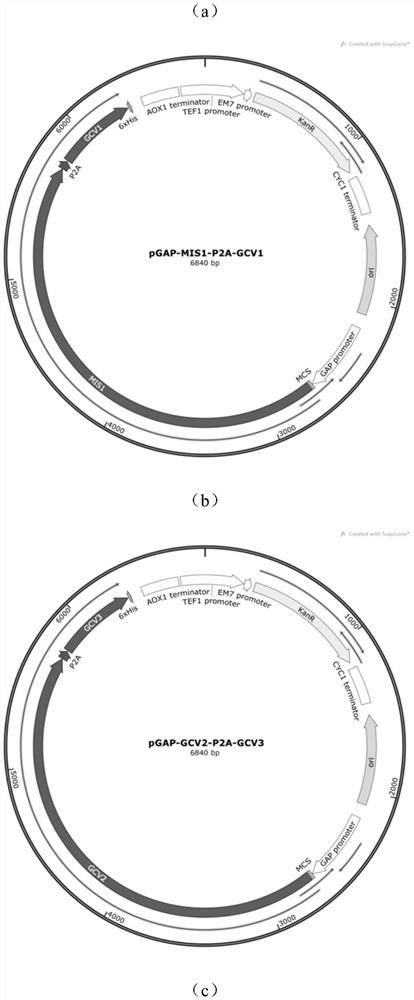
[0071] 1. Construction of pGAPZA-MIS1-P2A-GCV1 recombinant plasmid
[0072] Using the Pichia pastoris GS115 genome with MIS1 and GVC1 genes as a template, the nucleotide coding sequences of the corresponding genes were replicated by conventional PCR amplification.
[0073] The MIS1 upstream primers used have homology arms and the sequences are:
[0074] MIS1-F: TATTTCGAAACGAGGAATTGAAACGATGCTTTCAAGAATTGGATCTAGAAAATAAAG
[0075] The MIS1 downstream primer has a P2A sequence as a homology arm, and the sequence is:
[0076] MIS1-R:
[0077] ACGTCTCCTGCTTGCTTTAACAGAGAGAAGTTCGTGGCAAAATAA.
[0078] The GCV1 upstream primer used has the P2A sequence as the homology arm, and the sequence is:
[0079] GCV1-F: TAAAGCAAGCAGGAGACGTGGAAGAAAACCCCGGTCCTGAAACGA
[0080] The GCV1 downstream primer has homology arms and the sequence is:
[0081] GCV1-R:
[0082] AGATGAGTTTTTGTTCTAGTCACTCCGGCTTATAAAATTTGGGGGGC.
[0083] The reaction conditions were: 95 °C for 2 min, 95 °C for 20 s, 55 °C ...
Embodiment 3
[0182] Example 3 Phenotypic verification of recombinant strains
[0183] 1. Knockout strain fermentation verification
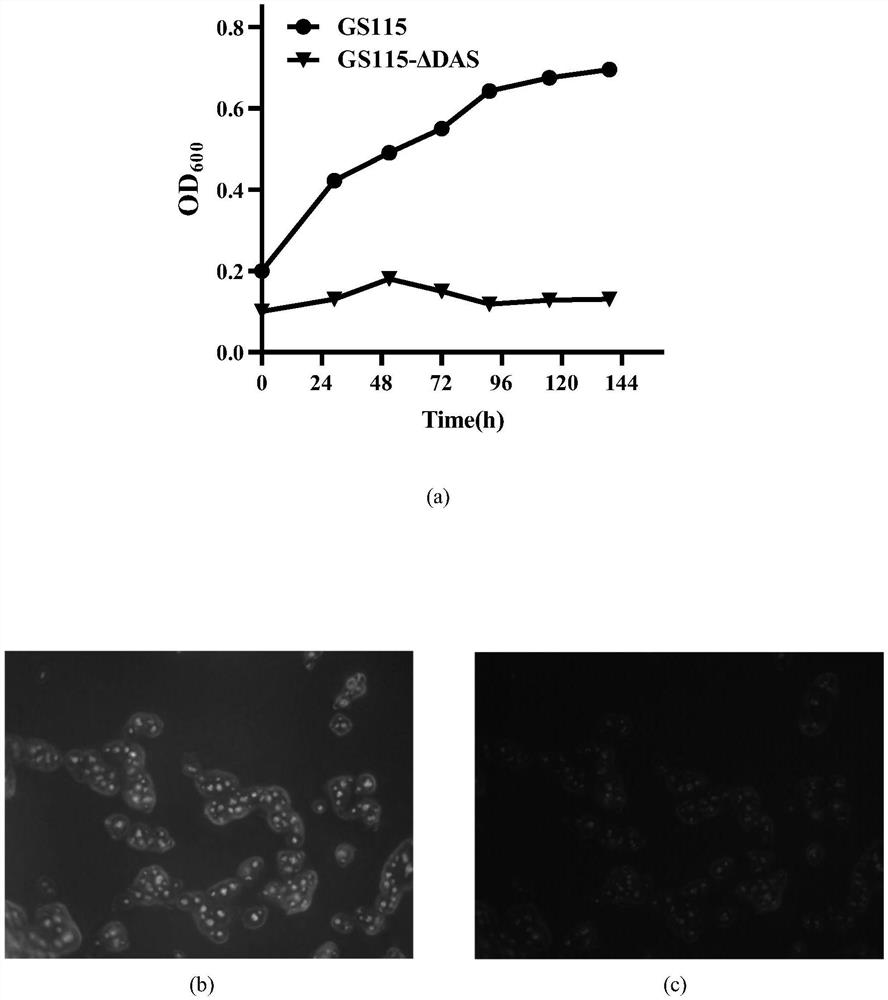
[0184] To verify the effect of knockout of the DAS gene on the assimilation of Pichia pastoris, the Pichia pastoris GS115 and GS115-ΔDAS strains were inoculated into 5 mL of YPD liquid medium, and shaken at 30 °C and 200 rpm to OD600≈5. The cultured bacterial liquids were all adjusted to the initial OD. 600 = 0.2 centrifugation and resuspension, inoculate in 100 mL of fresh M9 liquid medium and add 1% methanol by volume, shake culture at 30°C and 200 rpm, and take samples every 24 hours to measure the OD. 600 . From the fermentation verification structure, the strain after knocking out the DAS gene cannot grow in the medium with methanol as the only carbon source ( figure 2 (a)).
[0185] 2. Characterization of fermentation of recombinant strains by compartmentalization
[0186] To verify the localization effect of the signal peptide PTS1, the construct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com