Charging method and charging device of lithium metal battery
A lithium metal battery and charging method technology, applied in battery circuit devices, secondary battery charging/discharging, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as short life, potential safety hazards, and reduced battery life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
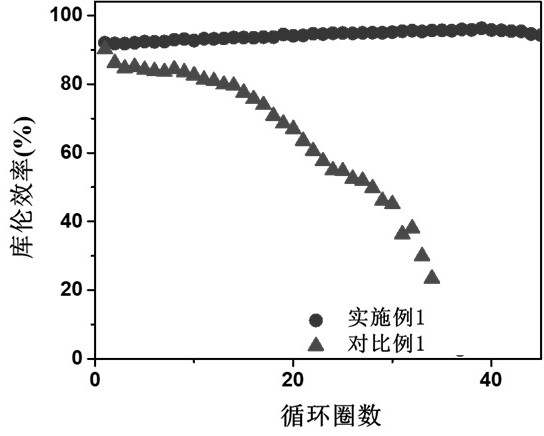
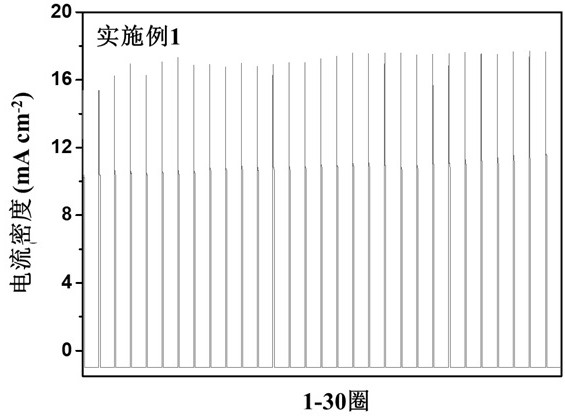
[0086] Assemble the same battery as in Comparative Example 1: Assemble the negative metal lithium and the positive copper sheet into a lithium copper battery, and the electrolyte is 1M LiTFSI / DOL-DME / 2% LiNO 3 .
[0087] The actual working voltage of the lithium-copper battery is calculated and detected by the charging device, which is 0V, and the rated power is 1mAh·cm -2 .
[0088] Example 1 is the whole process of constant voltage charging, and the deposition process adopts constant voltage, and the conditions are as follows: the deposition voltage is 0.25V, and the deposition power is 1mAh·cm -2 , the average deposition time is less than 5min; the stripping current is 1mA·cm -2 . The deposition power and the deposition time are the charging power and the charging time.
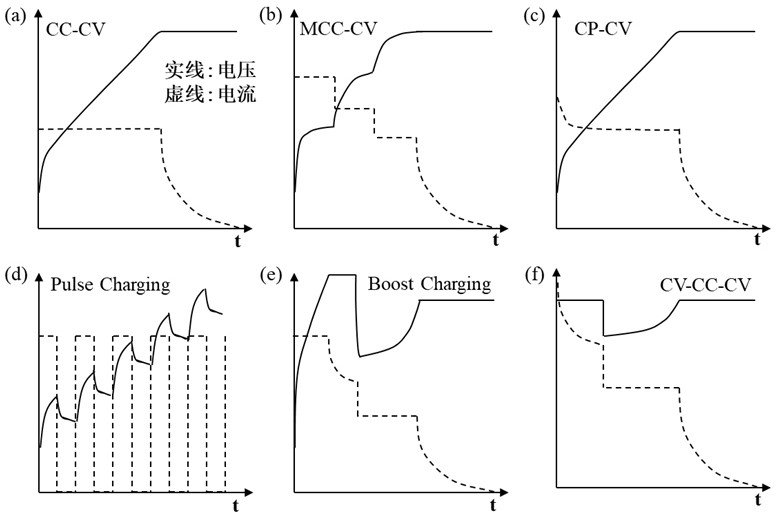
[0089] Constant voltage deposition is constant voltage charging, corresponding to CV 1 -CC-CV 2 CV in method 1 , CV 1 The value is the actual working voltage of the battery + 0.25V, that is, CV 1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Assemble the same battery as in Comparative Example 2: 45 μm thick thin metal lithium sheet is used as the negative electrode and the positive lithium titanate electrode is assembled into a lithium metal battery (lithium-lithium titanate battery), and the electrolyte is 1M LiTFSI / DOL-DME / 2 % LiNO 3 .
[0097] The actual working voltage of the lithium-lithium titanate battery is calculated and detected by the charging device, which is 1.55V (vs Li + / Li)), the rated power is the rated power described in Comparative Example 2.
[0098] using CV 1 -CC-CV 2 Protocol charging, cycle test, the conditions are as follows: constant voltage charging, charging voltage CV 1 The value is the actual working voltage of the battery +0.35V, which is 1.9 V (vs Li + / Li).
[0099] Example 2 is the whole process of constant voltage charging. The charging cut-off condition is that the charging current density is less than the minimum value, that is, less than 0.03C, and then the singl...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Assemble the same battery as in Comparative Example 3: a 45 μm thin metal lithium sheet is used as the negative electrode and the positive sulfur electrode sheet to assemble a lithium metal-based battery, and the electrolyte is 1M LiTFSI / DOL-DME / 2% LiNO 3 .
[0108] The actual working voltage of the lithium-sulfur battery is calculated and detected by the charging device, which is 2.1V (vs Li + / Li)), the rated power is the rated power described in Comparative Example 3.
[0109] Charging with CV 1 -CC-CV 2 method, the cycle test is carried out under the following conditions: constant voltage charging, charging voltage CV 1 The value is the actual working voltage of the battery +0.45V, which is 2.55 V (vs Li + / Li).
[0110] Example 3 is the whole process of constant voltage charging. The charging cut-off condition is that the charging current density is less than the minimum value, that is, less than 0.03C, and then the single-turn charging stops and discharges; t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com