Coxsackie virus A10 type strain and vaccine and application thereof
A coxsackie virus, A10 technology, applied in the direction of antiviral immunoglobulin, application, antiviral agent, etc., can solve the problem of low separation rate, achieve good immunogenicity, good passive immunity, strong cross-neutralization ability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Example 1 Isolation and culture of CV-A10 virus strain
[0092] 1. Processing of clinical samples
[0093] The clinical samples were processed according to the guidelines for the prevention and control of hand, foot and mouth disease (2009 edition).
[0094] 2. Virus isolation
[0095] The processed samples were inoculated into healthy, non-polluting African green monkey kidney passage cells (Vero) at a density of 80-90% in a certain proportion at 35°C, 5% CO. 2 Adsorbed in the incubator for more than half an hour, replenished to the culture volume, 35°C, 5% CO 2 The cells were cultured in an incubator, and a cell control without sample was set at the same time. Use an inverted microscope to observe the cells every day, such as enterovirus cytopathic effect (CPE): cells become round, the refraction is enhanced and detached from the tube wall, etc., the changes are recorded, and the changes in the cells in the inoculated wells and the control wells are continuously ob...
Embodiment 2
[0098] Example 2 Identification and detection of virus
[0099] The fourth-generation virus liquid of Coxsackie virus A10 strain V05790834 harvested in Example 1 was subjected to molecular identification, genome sequencing, titer detection and immunogenicity detection.
[0100] 1. Molecular identification and genome sequencing
[0101] The virus was identified by RT-PCR, and the general primers and VP1-specific primers used for enterovirus nucleic acid detection are shown in Table 1.
[0102] Table 1 Universal primers and VP1-specific primers for enterovirus nucleic acid detection
[0103]
[0104] (1) Virus nucleic acid extraction
[0105] Take the fourth-generation virus solution, add reagents and virus samples according to the instructions, then place it in a nucleic acid extractor, extract nucleic acids according to preset procedures, and store the extracted nucleic acids in a -70°C refrigerator.
[0106] (2) PCR detection of HEV-5UTR universal primers
[0107] Nest...
Embodiment 3
[0137] Example 3 Stability detection of CV-A10 strain
[0138] 1. Genetic stability
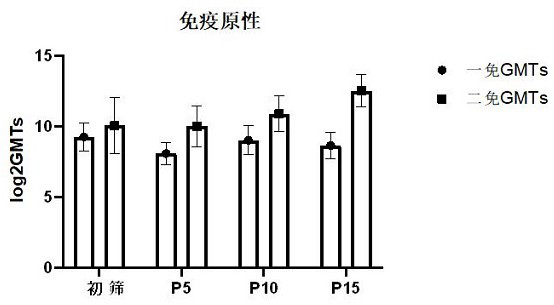
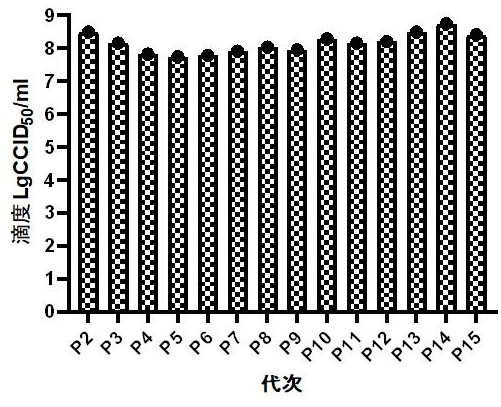
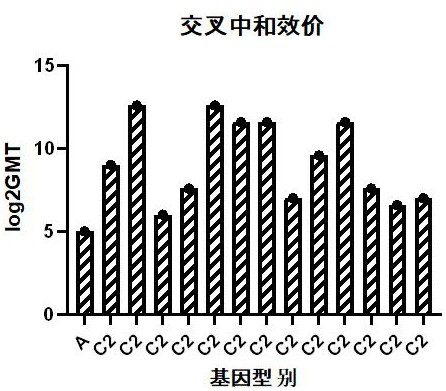
[0139] After plaque purification of Coxsackievirus A10 strain V05790834 was performed three times, serial passage was performed at the same MOI. The specific method is as follows: inoculate healthy and pollution-free Vero cells of passage ≤147 in a cell culture flask, and then grow to a density of about 90%. +++, harvest the virus solution and store it at -60°C or below. For each generation of harvest, the generation increases by one generation. The harvested virus solution was continuously passaged to P15 using the same method, and the virus harvest solution of each generation was replaced for P1 sequence amplification and sequencing.
[0140] P1 sequence amplification primers are shown below, and the target fragment size is about 3Kb:
[0141] CVA10-P1-F1 (5'-3'): TACCATATAGCCTATTGGATTGGCCATCCGG;
[0142] CVA10-P1-R (5'-3'): CTCGTGAGCTACTTTCCCATACTAAATTTG.
[0143] The amplification r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com