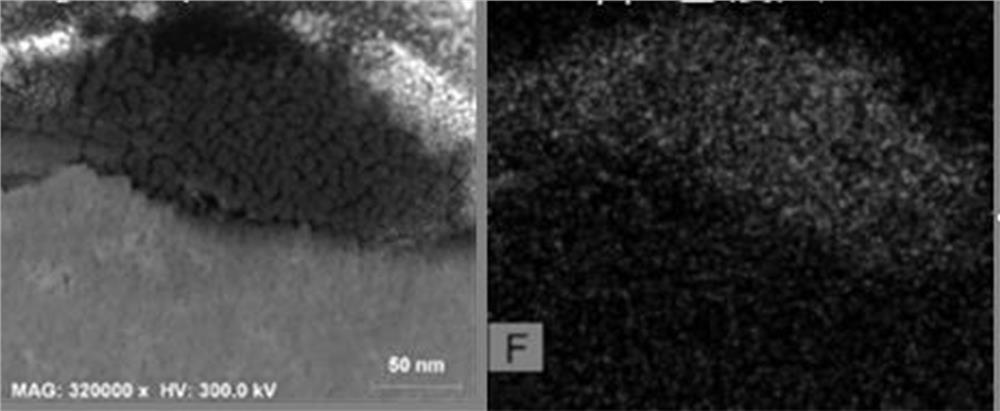
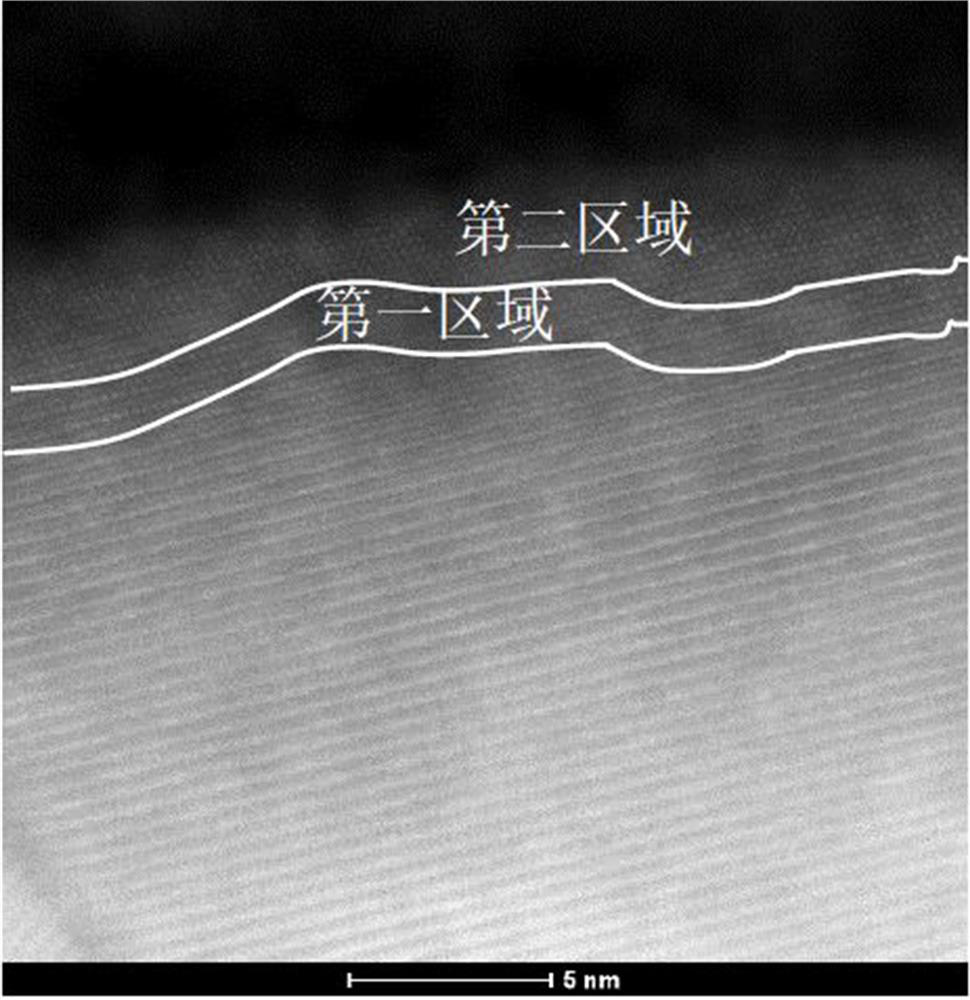
Positive electrode material, and electrochemical device and electronic device comprising same
A cathode material and electrochemical technology, which is applied in the field of electrochemical devices and electronic devices, can solve the problems of reducing energy density, increasing the specific surface area of primary grain size of material particles, and deteriorating the dynamic performance of materials.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] 1. Preparation of cathode materials
[0100] (1) Mix nickel sulfate, cobalt sulfate and manganese sulfate into deionized water to prepare a mixed salt solution, add sodium hydroxide to deionized water to prepare an alkaline solution, select ammonia water as a complexing agent, and then mix the salt solution and alkaline solution. Add the complexing agent into the reaction kettle, and add aluminum sulfate and titanium sulfate solution for reaction. The reaction temperature was controlled to be 25° C. and the pH was 11. When the particle size Dv50 reached a predetermined value of 4.5 μm, the reaction slurry was filtered, washed and dried to obtain the precursor. In the precursor co-precipitation reaction, aluminum sulfate solution and titanium sulfate solution are added to uniformly disperse the doping elements in the precursor matrix. In this example, the Ni / Co / Mn / Al / The molar ratio of Ti is 0.5:0.02:0.465:0.01:0.005.
[0101] (2) The lithium source Li 2 CO 3 It is ...
Embodiment 2
[0114] The difference compared with Example 1 is only in the following aspects of the preparation steps of the positive electrode material:
[0115] In step (1), the molar ratio of Ni / Co / Mn / Al / Ti in the doped hydroxide precursor component is 0.5:0.1:0.385:0.01:0.005;
[0116] In step (2), the primary sintering temperature is 945°C;
[0117] The cathode material matrix in step (3) is LiNi 0.5 Co 0.1 Mn 0.385 Al 0.01 Ti 0.005 O 2 , primary sintering material and coating additive nano-Co(OH) 2 and Al 2 O 3 The mass ratio of Co element is 100:29.1:2.1, the mole percentage W1 of Co element in the first cladding layer is 40.0%, and the mole percentage W2 of Co element in the matrix is 10%.
Embodiment 3
[0119] The difference compared with Example 1 is only in the following aspects of the preparation steps of the positive electrode material:
[0120] In step (1), the molar ratio of Ni / Co / Mn / Al / Ti in the doped hydroxide precursor component is 0.6:0.1:0.285:0.01:0.005;
[0121] In step (2), the primary sintering temperature is 935°C;
[0122] The cathode material matrix in step (3) is LiNi 0.6 Co 0.1 Mn 0.285 Al 0.01 Ti 0.005 O 2 , primary sintering material and coating additive nano-Co(OH) 2 and Al 2 O 3 The mass ratio of Co element is 100:29.0:2.1; the mole percentage W1 of Co element in the first cladding layer is 40.0%, and the mole percentage W2 of Co element in the matrix is 10.0%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com