Method for in-situ preparation of titanium dioxide/cellulose nano-composite microspheres
A technology of cellulose microspheres and titanium dioxide, applied in chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, etc., can solve difficult titanium dioxide/cellulose composite microspheres, reduce active sites , Reduce photocatalytic activity and other issues, achieve the effect of easy to master the preparation process, excellent photocatalytic performance, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
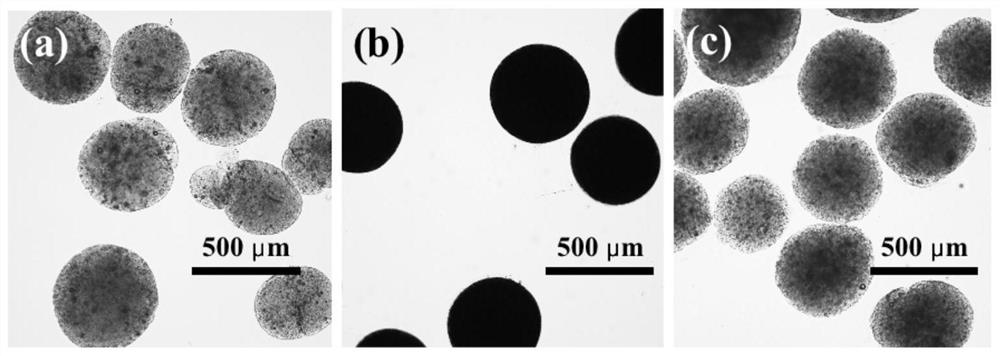
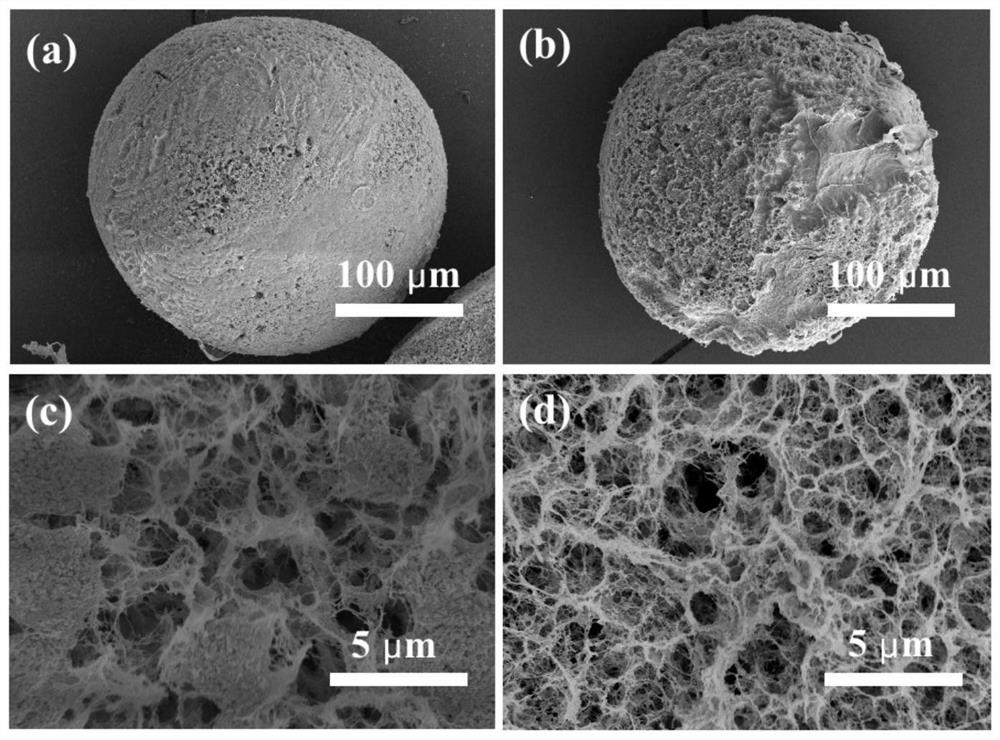
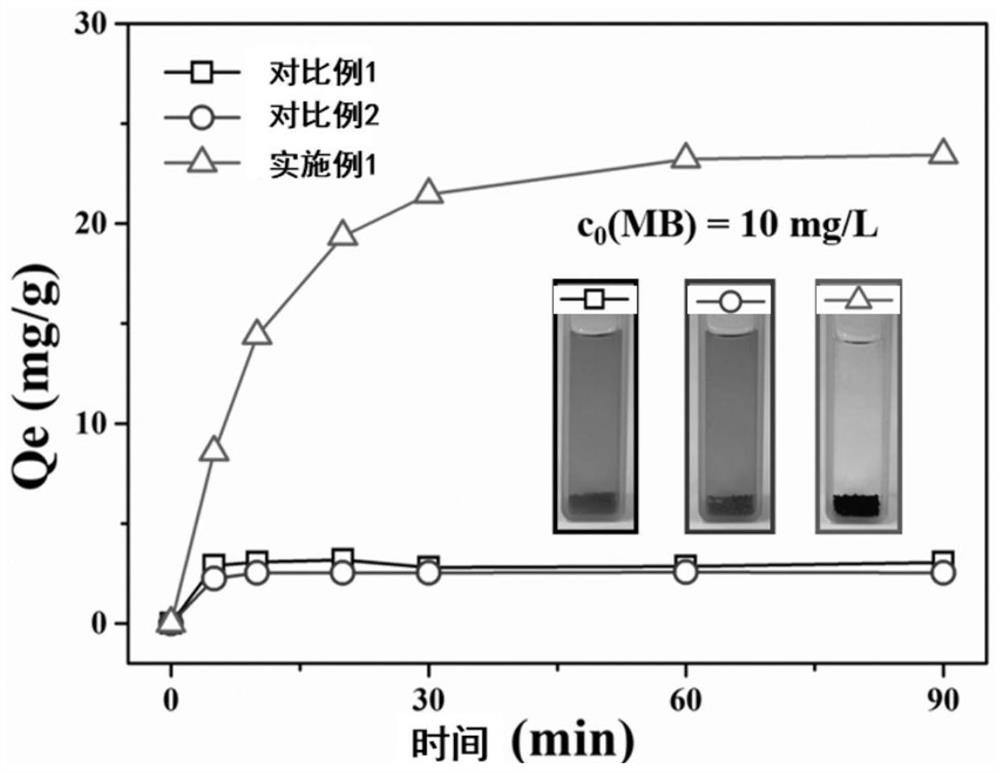
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] A method for in-situ preparation of titanium dioxide / cellulose nanocomposite microspheres, the raw materials and reagents used are as follows:
[0037] Raw materials: virgin cellulose (cotton linters, degree of polymerization 500), n-butyl titanate Reagents: lithium hydroxide, urea, triethanolamine, Span 80, liquid paraffin, deionized water The preparation method adopts the following steps:
[0038] (1) Preparation of n-butyl titanate pre-hydrolysis solution: at room temperature, n-butyl titanate and triethanolamine were mixed in a molar ratio of 1:2, and deionized water was added dropwise to the mixture to obtain the final concentration of n-butyl titanate. Be 1.25mol / L, reaction obtains pre-hydrolyzate;
[0039](2) Preparation of gel prefabricated solution: Lithium hydroxide and urea are dissolved in deionized water, and then frozen. The dried 2.57g cellulose was added to the frozen 100g mixed solvent, and 5.0 mL of the n-butyl titanate prehydrolyzate obtained in ste...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A method for modifying titanium dioxide / cellulose nanocomposite microspheres prepared in situ, the raw materials and reagents used are as follows:
[0042] Raw material: Microspheres prepared in Example 1
[0043] Reagents: Rhodamine B, hydrogen peroxide, deionized water
[0044] The preparation method adopts the following steps:
[0045] (1) Preparation of Rhodamine B solution: Weigh a certain amount of Rhodamine B and dissolve it in deionized water, and set the volume for use;
[0046] (2) Rhodamine B degradation intermediate modified microspheres: The microspheres in Example 1 were added to the Rhodamine B solution, and a certain amount of hydrogen peroxide was added to degrade Rhodamine B under light conditions. When the solution was colorless and transparent, the modified microspheres were obtained by sedimentation separation.
Embodiment 3~20
[0047] Embodiments 3 to 20 are shown in Table 1:
[0048] Table 1. Preparation conditions of Examples 3-20
[0049]
[0050] Table 2 Example 3-20 Size, Titanium Dioxide Load, Adsorption, Degradation Performance Comparison Table
[0051]
[0052]
[0053] *Degradation time is 70 minutes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com