Feed addictive
A feed additive and probiotic technology, applied in application, animal feed, animal feed, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, labor and time, high price, etc., and achieve cost reduction, simple manufacturing process and high feed conversion rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Konjac flour is selected as the polycarbohydrate, Bacillus subtilis is selected as the probiotic, and peptone and beef extract are selected as the nitrogen source. It is made by using the β-mannanase produced by Bacillus subtilis itself to decompose konjac flour to produce mannose and mannooligosaccharides by fermentation. The final product contains mannose, manno-oligosaccharides, β-mannanase and Bacillus subtilis. The konjac flour used in this embodiment is konjac flour containing more than 80% β-glucomannan, wherein the content of starch accounts for 2.4%.
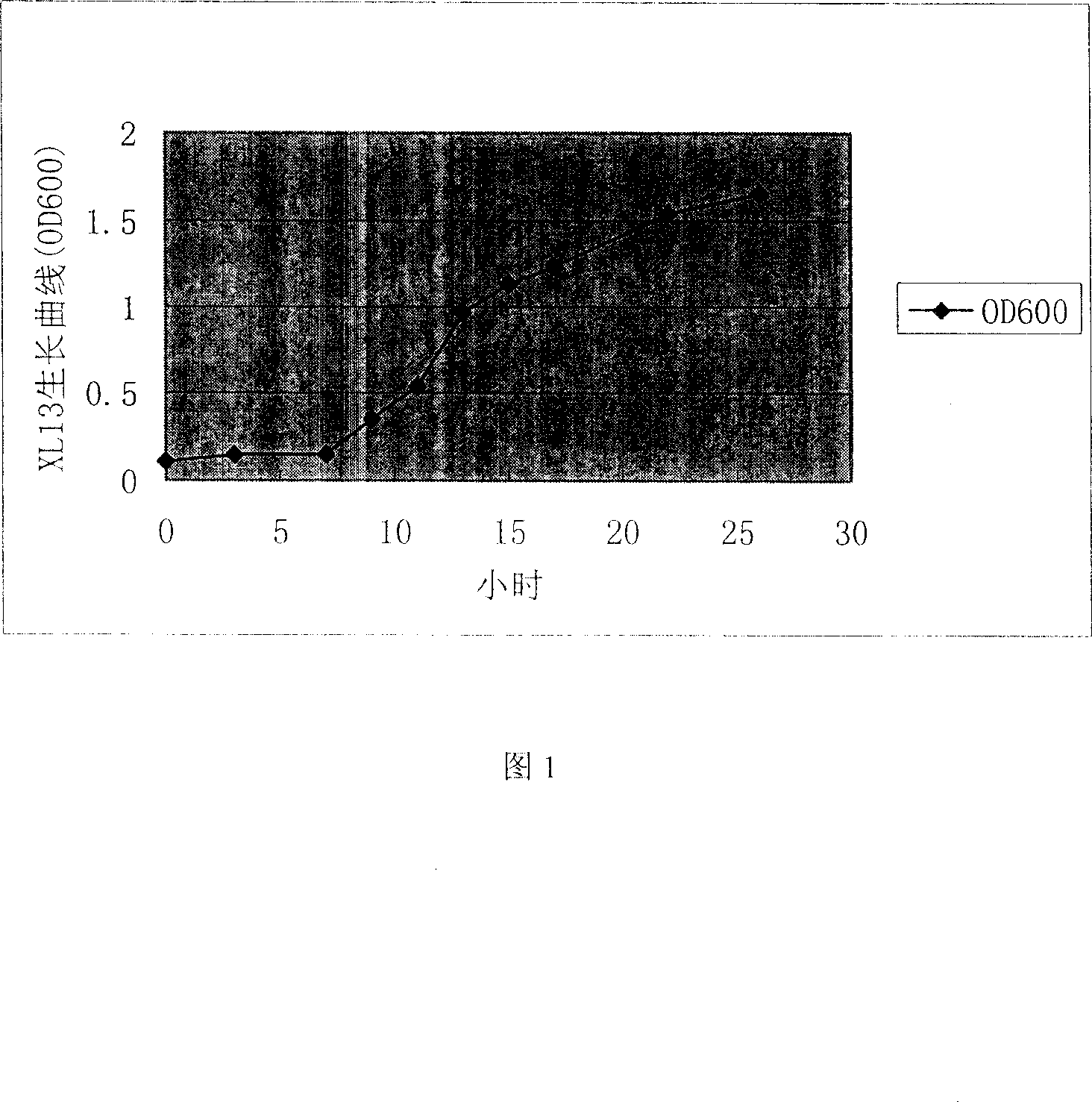
[0047] Preparation method: 5% Bacillus subtilis XL13 strain is inoculated into culture medium containing 0.1% ground taro powder (content: 1 g / L). Medium selection: beef extract 3g / L, peptone 10g / L, sodium chloride 5g / L. The pH value is 7.0-7.2; culture on a shaker at 37°C for 24 hours. The growth was measured with a UV spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 600 mm, and the growth curve of Bacillus subtilis XL13...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Probiotics, polycarbohydrates, and nitrogen sources are selected as in Example 1, and the preparation method is as follows: 5% Bacillus subtilis XL13 is inoculated in a medium containing 2.0% ground taro powder (content: 20g / L). The composition of the medium was as described in Example 1. Samples were taken at 0 hour, 8 hours, 27 hours, 62 hours, and 72 hours, and the reducing sugar content in the fermentation broth was determined by the 3,5-2 nitrosalicylic acid colorimetric method (Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 26, 323). Enzyme activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to release 1 μmol of reducing sugar equivalent to D-mannose per minute as 1 enzyme activity unit. The results are shown in Table 1. The highest enzyme activity reaches 162IU / ml.
[0050] Table 1:
[0051] strain
Embodiment 3
[0053] Probiotics, polycarbohydrates, and carbon sources are selected as in Example 1, and the preparation method is as follows: 5% Bacillus licheniformis XL42 is inoculated in a medium containing 2.0% taro powder. The medium components are as described in Example 1. Samples were taken at 0 hour, 8 hours, 27 hours, 62 hours, and 72 hours, and the reducing sugar content in the fermentation broth was determined by the 3,5-2 nitrosalicylic acid colorimetric method (Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 26, 323). Enzyme activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to release 1 μmol of reducing sugar equivalent to D-mannose per minute as 1 enzyme activity unit. The results are shown in Table 2. The highest enzyme activity reaches 38IU / ml.
[0054] Table 2:
[0055] strain
[0056] 5% lichen buds
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com